パブリック最終クラスDynamicStitch
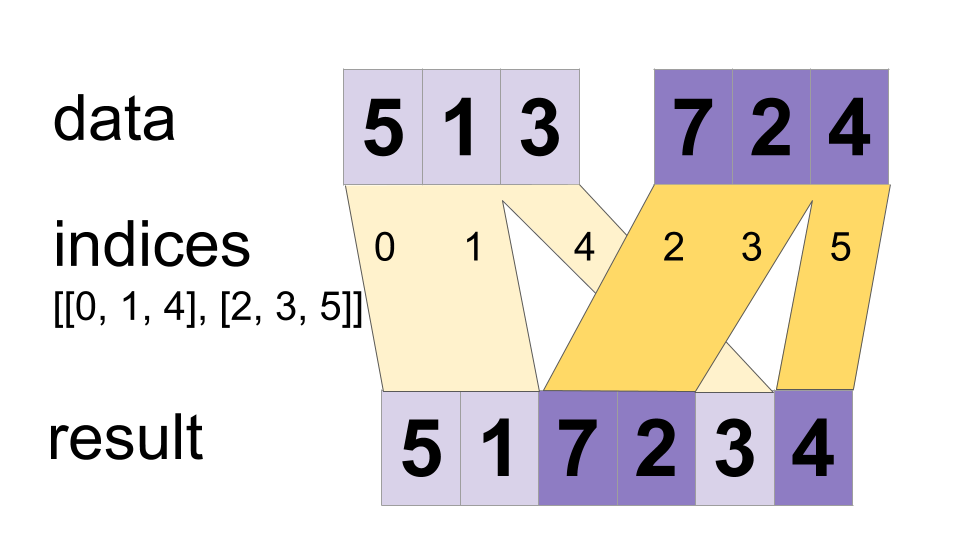
「data」テンソルの値を単一のテンソルにインターリーブします。
merged[indices[m][i, ..., j], ...] = data[m][i, ..., j, ...]
# Scalar indices:
merged[indices[m], ...] = data[m][...]
# Vector indices:
merged[indices[m][i], ...] = data[m][i, ...]
merged.shape = [max(インデックス) + 1] + 定数
値は順番にマージされるため、インデックスが `(m,i) < (n,j)` の `indices[m][i]` と `indices[n][j]` の両方に出現する場合、スライス `dataマージ結果には [n][j]` が表示されます。この保証が必要ない場合は、一部のデバイスでは ParallelDynamicStitch のパフォーマンスが向上する可能性があります。
例:
indices[0] = 6
indices[1] = [4, 1]
indices[2] = [[5, 2], [0, 3]]
data[0] = [61, 62]
data[1] = [[41, 42], [11, 12]]
data[2] = [[[51, 52], [21, 22]], [[1, 2], [31, 32]]]
merged = [[1, 2], [11, 12], [21, 22], [31, 32], [41, 42],
[51, 52], [61, 62]]
# Apply function (increments x_i) on elements for which a certain condition
# apply (x_i != -1 in this example).
x=tf.constant([0.1, -1., 5.2, 4.3, -1., 7.4])
condition_mask=tf.not_equal(x,tf.constant(-1.))
partitioned_data = tf.dynamic_partition(
x, tf.cast(condition_mask, tf.int32) , 2)
partitioned_data[1] = partitioned_data[1] + 1.0
condition_indices = tf.dynamic_partition(
tf.range(tf.shape(x)[0]), tf.cast(condition_mask, tf.int32) , 2)
x = tf.dynamic_stitch(condition_indices, partitioned_data)
# Here x=[1.1, -1., 6.2, 5.3, -1, 8.4], the -1. values remain
# unchanged.
パブリックメソッド
| 出力<T> | asOutput () テンソルのシンボリック ハンドルを返します。 |
| 静的 <T>ダイナミックステッチ<T> | |
| 出力<T> | 統合されました() |
継承されたメソッド
パブリックメソッド
public Output <T> asOutput ()
テンソルのシンボリック ハンドルを返します。
TensorFlow オペレーションへの入力は、別の TensorFlow オペレーションの出力です。このメソッドは、入力の計算を表すシンボリック ハンドルを取得するために使用されます。
public static DynamicStitch <T> create (スコープスコープ、Iterable< Operand <Integer>> インデックス、Iterable< Operand <T>> データ)
新しい DynamicStitch オペレーションをラップするクラスを作成するためのファクトリ メソッド。
パラメーター
| 範囲 | 現在のスコープ |
|---|
戻り値
- DynamicStitch の新しいインスタンス

