 Voir sur TensorFlow.org Voir sur TensorFlow.org |  Exécuter dans Google Colab Exécuter dans Google Colab |  Voir la source sur GitHub Voir la source sur GitHub |  Télécharger le cahier Télécharger le cahier |
Aperçu
Vous pouvez utiliser les couches TFL Keras pour construire des modèles Keras avec une monotonie et d'autres contraintes de forme. Cet exemple crée et entraîne un modèle de réseau calibré pour l'ensemble de données cardiaques UCI à l'aide de couches TFL.
Dans un modèle de réseau calibré, chaque fonction est transformée par un tfl.layers.PWLCalibration ou un tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration couche et les résultats sont fusionnés de façon non linéaire en utilisant un tfl.layers.Lattice .
Installer
Installation du package TF Lattice :
pip install -q tensorflow-lattice pydot
Importation des packages requis :
import tensorflow as tf
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
from tensorflow import feature_column as fc
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
Téléchargement du jeu de données UCI Statlog (Heart) :
# UCI Statlog (Heart) dataset.
csv_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'heart.csv', 'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv')
training_data_df = pd.read_csv(csv_file).sample(
frac=1.0, random_state=41).reset_index(drop=True)
training_data_df.head()
Définition des valeurs par défaut utilisées pour la formation dans ce guide :
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 100
Modèle Keras séquentiel
Cet exemple crée un modèle Keras séquentiel et utilise uniquement des couches TFL.
Couches réticulaires attendent input[i] être dans [0, lattice_sizes[i] - 1.0] , donc nous avons besoin de définir le réseau des tailles avant des couches d'étalonnage afin que nous puissions correctement spécifier la plage de sortie des couches d'étalonnage.
# Lattice layer expects input[i] to be within [0, lattice_sizes[i] - 1.0], so
lattice_sizes = [3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
Nous utilisons une tfl.layers.ParallelCombination couche aux couches d'étalonnage ensemble du groupe qui doivent être exécutés en parallèle afin de pouvoir créer un modèle séquentiel.
combined_calibrators = tfl.layers.ParallelCombination()
Nous créons une couche de calibrage pour chaque entité et l'ajoutons à la couche de combinaison parallèle. Pour connaître les caractéristiques numériques que nous utilisons tfl.layers.PWLCalibration , et pour les fonctions catégoriques que nous utilisons tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration .
# ############### age ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Every PWLCalibration layer must have keypoints of piecewise linear
# function specified. Easiest way to specify them is to uniformly cover
# entire input range by using numpy.linspace().
input_keypoints=np.linspace(
training_data_df['age'].min(), training_data_df['age'].max(), num=5),
# You need to ensure that input keypoints have same dtype as layer input.
# You can do it by setting dtype here or by providing keypoints in such
# format which will be converted to desired tf.dtype by default.
dtype=tf.float32,
# Output range must correspond to expected lattice input range.
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[0] - 1.0,
)
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### sex ###############
# For boolean features simply specify CategoricalCalibration layer with 2
# buckets.
calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=2,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[1] - 1.0,
# Initializes all outputs to (output_min + output_max) / 2.0.
kernel_initializer='constant')
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### cp ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Here instead of specifying dtype of layer we convert keypoints into
# np.float32.
input_keypoints=np.linspace(1, 4, num=4, dtype=np.float32),
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[2] - 1.0,
monotonicity='increasing',
# You can specify TFL regularizers as a tuple ('regularizer name', l1, l2).
kernel_regularizer=('hessian', 0.0, 1e-4))
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### trestbps ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Alternatively, you might want to use quantiles as keypoints instead of
# uniform keypoints
input_keypoints=np.quantile(training_data_df['trestbps'],
np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num=5)),
dtype=tf.float32,
# Together with quantile keypoints you might want to initialize piecewise
# linear function to have 'equal_slopes' in order for output of layer
# after initialization to preserve original distribution.
kernel_initializer='equal_slopes',
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[3] - 1.0,
# You might consider clamping extreme inputs of the calibrator to output
# bounds.
clamp_min=True,
clamp_max=True,
monotonicity='increasing')
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### chol ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Explicit input keypoint initialization.
input_keypoints=[126.0, 210.0, 247.0, 286.0, 564.0],
dtype=tf.float32,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[4] - 1.0,
# Monotonicity of calibrator can be decreasing. Note that corresponding
# lattice dimension must have INCREASING monotonicity regardless of
# monotonicity direction of calibrator.
monotonicity='decreasing',
# Convexity together with decreasing monotonicity result in diminishing
# return constraint.
convexity='convex',
# You can specify list of regularizers. You are not limited to TFL
# regularizrs. Feel free to use any :)
kernel_regularizer=[('laplacian', 0.0, 1e-4),
tf.keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001)])
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### fbs ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=2,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[5] - 1.0,
# For categorical calibration layer monotonicity is specified for pairs
# of indices of categories. Output for first category in pair will be
# smaller than output for second category.
#
# Don't forget to set monotonicity of corresponding dimension of Lattice
# layer to '1'.
monotonicities=[(0, 1)],
# This initializer is identical to default one('uniform'), but has fixed
# seed in order to simplify experimentation.
kernel_initializer=tf.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(
minval=0.0, maxval=lattice_sizes[5] - 1.0, seed=1))
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
# ############### restecg ###############
calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=3,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[6] - 1.0,
# Categorical monotonicity can be partial order.
monotonicities=[(0, 1), (0, 2)],
# Categorical calibration layer supports standard Keras regularizers.
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001),
kernel_initializer='constant')
combined_calibrators.append(calibrator)
Nous créons ensuite une couche de treillis pour fusionner de manière non linéaire les sorties des calibrateurs.
Notez que nous devons spécifier que la monotonie du réseau doit être croissante pour les dimensions requises. La composition avec la direction de la monotonie dans l'étalonnage se traduira par la direction correcte de bout en bout de la monotonie. Cela inclut la monotonie partielle de la couche CategoricalCalibration.
lattice = tfl.layers.Lattice(
lattice_sizes=lattice_sizes,
monotonicities=[
'increasing', 'none', 'increasing', 'increasing', 'increasing',
'increasing', 'increasing'
],
output_min=0.0,
output_max=1.0)
Nous pouvons ensuite créer un modèle séquentiel en utilisant les calibrateurs et les couches de réseau combinés.
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(combined_calibrators)
model.add(lattice)
La formation fonctionne de la même manière que tout autre modèle de Keras.
features = training_data_df[[
'age', 'sex', 'cp', 'trestbps', 'chol', 'fbs', 'restecg'
]].values.astype(np.float32)
target = training_data_df[['target']].values.astype(np.float32)
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.mean_squared_error,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE))
model.fit(
features,
target,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.2,
shuffle=False,
verbose=0)
model.evaluate(features, target)
10/10 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1551 0.15506614744663239
Modèle Keras fonctionnel
Cet exemple utilise une API fonctionnelle pour la construction du modèle Keras.
Comme il est mentionné dans la section précédente, les couches treillis attendent input[i] être dans [0, lattice_sizes[i] - 1.0] , donc nous avons besoin de définir les dimensions treillis avant des couches d'étalonnage afin que nous puissions correctement spécifier la plage de sortie du couches d'étalonnage.
# We are going to have 2-d embedding as one of lattice inputs.
lattice_sizes = [3, 2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2]
Pour chaque entité, nous devons créer une couche d'entrée suivie d'une couche de calibrage. Pour connaître les caractéristiques numériques que nous utilisons tfl.layers.PWLCalibration et caractéristiques qualitatives que nous utilisons tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration .
model_inputs = []
lattice_inputs = []
# ############### age ###############
age_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='age')
model_inputs.append(age_input)
age_calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Every PWLCalibration layer must have keypoints of piecewise linear
# function specified. Easiest way to specify them is to uniformly cover
# entire input range by using numpy.linspace().
input_keypoints=np.linspace(
training_data_df['age'].min(), training_data_df['age'].max(), num=5),
# You need to ensure that input keypoints have same dtype as layer input.
# You can do it by setting dtype here or by providing keypoints in such
# format which will be converted to desired tf.dtype by default.
dtype=tf.float32,
# Output range must correspond to expected lattice input range.
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[0] - 1.0,
monotonicity='increasing',
name='age_calib',
)(
age_input)
lattice_inputs.append(age_calibrator)
# ############### sex ###############
# For boolean features simply specify CategoricalCalibration layer with 2
# buckets.
sex_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='sex')
model_inputs.append(sex_input)
sex_calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=2,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[1] - 1.0,
# Initializes all outputs to (output_min + output_max) / 2.0.
kernel_initializer='constant',
name='sex_calib',
)(
sex_input)
lattice_inputs.append(sex_calibrator)
# ############### cp ###############
cp_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='cp')
model_inputs.append(cp_input)
cp_calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Here instead of specifying dtype of layer we convert keypoints into
# np.float32.
input_keypoints=np.linspace(1, 4, num=4, dtype=np.float32),
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[2] - 1.0,
monotonicity='increasing',
# You can specify TFL regularizers as tuple ('regularizer name', l1, l2).
kernel_regularizer=('hessian', 0.0, 1e-4),
name='cp_calib',
)(
cp_input)
lattice_inputs.append(cp_calibrator)
# ############### trestbps ###############
trestbps_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='trestbps')
model_inputs.append(trestbps_input)
trestbps_calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Alternatively, you might want to use quantiles as keypoints instead of
# uniform keypoints
input_keypoints=np.quantile(training_data_df['trestbps'],
np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num=5)),
dtype=tf.float32,
# Together with quantile keypoints you might want to initialize piecewise
# linear function to have 'equal_slopes' in order for output of layer
# after initialization to preserve original distribution.
kernel_initializer='equal_slopes',
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[3] - 1.0,
# You might consider clamping extreme inputs of the calibrator to output
# bounds.
clamp_min=True,
clamp_max=True,
monotonicity='increasing',
name='trestbps_calib',
)(
trestbps_input)
lattice_inputs.append(trestbps_calibrator)
# ############### chol ###############
chol_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='chol')
model_inputs.append(chol_input)
chol_calibrator = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
# Explicit input keypoint initialization.
input_keypoints=[126.0, 210.0, 247.0, 286.0, 564.0],
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[4] - 1.0,
# Monotonicity of calibrator can be decreasing. Note that corresponding
# lattice dimension must have INCREASING monotonicity regardless of
# monotonicity direction of calibrator.
monotonicity='decreasing',
# Convexity together with decreasing monotonicity result in diminishing
# return constraint.
convexity='convex',
# You can specify list of regularizers. You are not limited to TFL
# regularizrs. Feel free to use any :)
kernel_regularizer=[('laplacian', 0.0, 1e-4),
tf.keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001)],
name='chol_calib',
)(
chol_input)
lattice_inputs.append(chol_calibrator)
# ############### fbs ###############
fbs_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='fbs')
model_inputs.append(fbs_input)
fbs_calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=2,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[5] - 1.0,
# For categorical calibration layer monotonicity is specified for pairs
# of indices of categories. Output for first category in pair will be
# smaller than output for second category.
#
# Don't forget to set monotonicity of corresponding dimension of Lattice
# layer to '1'.
monotonicities=[(0, 1)],
# This initializer is identical to default one ('uniform'), but has fixed
# seed in order to simplify experimentation.
kernel_initializer=tf.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(
minval=0.0, maxval=lattice_sizes[5] - 1.0, seed=1),
name='fbs_calib',
)(
fbs_input)
lattice_inputs.append(fbs_calibrator)
# ############### restecg ###############
restecg_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[1], name='restecg')
model_inputs.append(restecg_input)
restecg_calibrator = tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration(
num_buckets=3,
output_min=0.0,
output_max=lattice_sizes[6] - 1.0,
# Categorical monotonicity can be partial order.
monotonicities=[(0, 1), (0, 2)],
# Categorical calibration layer supports standard Keras regularizers.
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001),
kernel_initializer='constant',
name='restecg_calib',
)(
restecg_input)
lattice_inputs.append(restecg_calibrator)
Nous créons ensuite une couche de treillis pour fusionner de manière non linéaire les sorties des calibrateurs.
Notez que nous devons spécifier que la monotonie du réseau doit être croissante pour les dimensions requises. La composition avec la direction de la monotonie dans l'étalonnage se traduira par la direction correcte de bout en bout de la monotonie. Cela comprend la monotonicité partielle de tfl.layers.CategoricalCalibration couche.
lattice = tfl.layers.Lattice(
lattice_sizes=lattice_sizes,
monotonicities=[
'increasing', 'none', 'increasing', 'increasing', 'increasing',
'increasing', 'increasing'
],
output_min=0.0,
output_max=1.0,
name='lattice',
)(
lattice_inputs)
Pour ajouter plus de flexibilité au modèle, nous ajoutons une couche de calibrage de sortie.
model_output = tfl.layers.PWLCalibration(
input_keypoints=np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 5),
name='output_calib',
)(
lattice)
Nous pouvons maintenant créer un modèle en utilisant les entrées et les sorties.
model = tf.keras.models.Model(
inputs=model_inputs,
outputs=model_output)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, rankdir='LR')
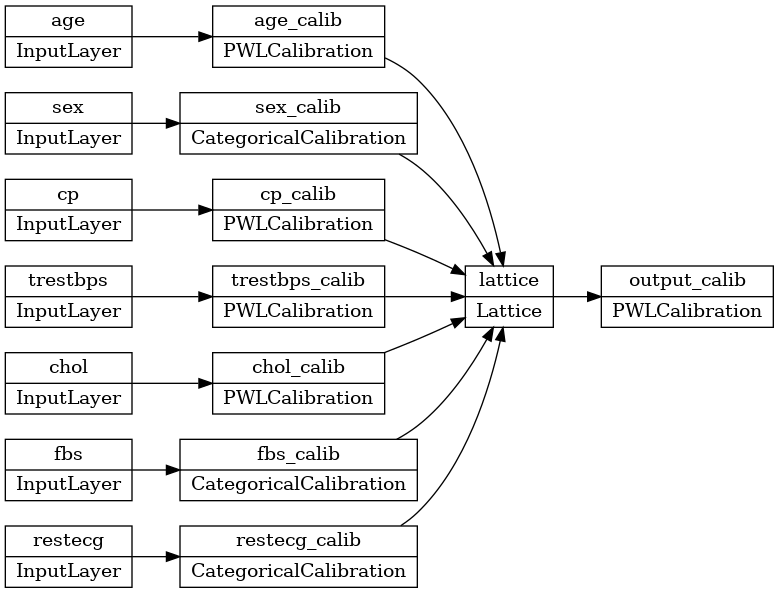
La formation fonctionne de la même manière que tout autre modèle de Keras. Notez que, avec notre configuration, les caractéristiques d'entrée sont transmises en tant que tenseurs distincts.
feature_names = ['age', 'sex', 'cp', 'trestbps', 'chol', 'fbs', 'restecg']
features = np.split(
training_data_df[feature_names].values.astype(np.float32),
indices_or_sections=len(feature_names),
axis=1)
target = training_data_df[['target']].values.astype(np.float32)
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.mean_squared_error,
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(LEARNING_RATE))
model.fit(
features,
target,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.2,
shuffle=False,
verbose=0)
model.evaluate(features, target)
10/10 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1590 0.15900751948356628
