 View on TensorFlow.org View on TensorFlow.org
|
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
 View on GitHub View on GitHub
|
 Download notebook Download notebook
|
Welcome to the Automated hyper-parameter tuning tutorial. In this colab, you will learn how to improve your models using automated hyper-parameter tuning with TensorFlow Decision Forests.
More precicely we will:
- Train a model without hyper-parameter tuning. This model will be used to measure the quality improvement of hyper-parameter tuning.
- Train a model with hyper-parameter tuning using TF-DF's tuner. The hyper-parameters to optimize will be defined manually.
- Train another model with hyper-parameter tuning using TF-DF's tuner. But this time, the hyper-parameters to optimize will be set automatically. This is the recommanded first approach to try when using hyper-parameter tuning.
- Finally, we will train a model with hyper-parameter tuning using Keras's tuner.
Introduction
A learning algorithm trains a machine learning model on a training dataset. The parameters of a learning algorithm–called "hyper-parameters"–control how the model is trained and impact its quality. Therefore, finding the best hyper-parameters is an important stage of modeling.
Some hyper-parameters are simple to configure. For example, increasing the
number of trees (num_trees) in a random forest increases the quality of the
model until a plateau. Therefore, setting the largest value compatible with the
serving constraints (more trees means a larger model) is a valid rule of thumb.
However, other hyper-parameters have a more complex interaction with the model
and cannot be chosen with such a simple rule. For example, increasing the
maximum tree depth (max_depth) of a gradient boosted tree model can both
increase or decrease the quality of the model. Furthermore, hyper-parameters can
interact between each others, and the optimal value of a hyper-parameter cannot
be found in isolation.
There are three main approaches to select the hyper-parameter values:
The default approach: Learning algorithms come with default values. While not ideal in all cases, those values produce reasonable results in most situations. This approach is recommended as the first approach to use in any modeling. This page lists the default values of TF Decision Forests.
The template hyper-parameter approach: In addition to the default values, TF Decision Forests also exposes the hyper-parameter templates. Those are benchmark-tuned hyper-parameter values with excellent performance but high training cost (e.g.
hyperparameter_template="benchmark_rank1").The manual tuning approach: You can manually test different hyper-parameter values and select the one that performs best. This guide give some advice.
The automated tuning approach: A tuning algorithm can be used to find automatically the best hyper-parameter values. This approach gives often the best results and does not require expertise. The main downside of this approach is the time it takes for large datasets.
In this colab, we shows the default and automated tuning approaches with the TensorFlow Decision Forests library.
Hyper-parameter tuning algorithms
Automated tuning algorithms work by generating and evaluating a large number of hyper-parameter values. Each of those iterations is called a "trial". The evaluation of a trial is expensive as it requires to train a new model each time. At the end of the tuning, the hyper-parameter with the best evaluation is used.
Tuning algorithm are configured as follow:
The search space
The search space is the list of hyper-parameters to optimize and the values they can take. For example, the maximum depth of a tree could be optimized for values in between 1 and 32. Exploring more hyper-parameters and more possible values often leads to better models but also takes more time. The hyper-parameters hyper-parameters are listed in the documentation.
When the possible value of one hyper-parameter depends on the value of another hyper-parameter, the search space is said to be conditional.
The number of trials
The number of trials defines how many models will be trained and evaluated. Larger number of trials generally leads to better models, but takes more time.
The optimizer
The optimizer selects the next hyper-parameter to evaluate the past trial evaluations. The simplest and often reasonable optimizer is the one that selects the hyper-parameter at random.
The objective / trial score
The objective is the metric optimized by the tuner. Often, this metric is a measure of quality (e.g. accuracy, log loss) of the model evaluated on a validation dataset.
Train-valid-test
The validation dataset should be different from the training datasets: If the training and validation datasets are the same, the selected hyper-parameters will be irrelevant. The validation dataset should also be different from the testing dataset (also called holdout dataset): Because hyper-parameter tuning is a form of training, if the testing and validation datasets are the same, you are effectively training on the test dataset. In this case, you might overfit on your test dataset without a way to measure it.
Cross-validation
In the case of a small dataset, for example a dataset with less than 100k examples, hyper-parameter tuning can be coupled with cross-validation: Instead of being evaluated from a single training-test round, the objective/trial score is evaluated as the average of the metric over multiple cross-validation rounds.
Similarly as to the train-valid-and-test datasets, the cross-validation used to evaluate the objective/score during hyper-parameter tuning should be different from the cross-validation used to evaluate the quality of the model.
Out-of-bag evaluation
Some models, like Random Forests, can be evaluated on the training datasets using the "out-of-bag evaluation" method. While not as accurate as cross-validation, the "out-of-bag evaluation" is much faster than cross-validation and does not require a separate validation datasets.
In tensorflow decision forests
In TF-DF, the model "self" evaluation is always a fair way to evaluate a model. For example, an out-of-bag evaluation is used for Random Forest models while a validation dataset is used for Gradient Boosted models.
Hyper-parameter tuning with TF Decision Forests
TF-DF supports automatic hyper-parameter tuning with minimal configuration. In the next example, we will train and compare two models: One trained with default hyper-parameters, and one trained with hyper-parameter tuning.
Setup
# Install TensorFlow Dececision Forestspip install tensorflow_decision_forests -U -qq
Install Wurlitzer. Wurlitzer is required to show the detailed training logs in colabs (with verbose=2).
pip install wurlitzer -U -qqImport the necessary libraries.
import tensorflow_decision_forests as tfdf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
2026-01-12 14:18:15.421375: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:467] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR E0000 00:00:1768227495.444213 162095 cuda_dnn.cc:8579] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered E0000 00:00:1768227495.451830 162095 cuda_blas.cc:1407] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered W0000 00:00:1768227495.470274 162095 computation_placer.cc:177] computation placer already registered. Please check linkage and avoid linking the same target more than once. W0000 00:00:1768227495.470293 162095 computation_placer.cc:177] computation placer already registered. Please check linkage and avoid linking the same target more than once. W0000 00:00:1768227495.470296 162095 computation_placer.cc:177] computation placer already registered. Please check linkage and avoid linking the same target more than once. W0000 00:00:1768227495.470298 162095 computation_placer.cc:177] computation placer already registered. Please check linkage and avoid linking the same target more than once.
The hidden code cell limits the output height in colab.
Define "set_cell_height".
from IPython.core.magic import register_line_magic
from IPython.display import Javascript
from IPython.display import display
# Some of the model training logs can cover the full
# screen if not compressed to a smaller viewport.
# This magic allows setting a max height for a cell.
@register_line_magic
def set_cell_height(size):
display(
Javascript("google.colab.output.setIframeHeight(0, true, {maxHeight: " +
str(size) + "})"))
Training a model without Automated hyper-parameter tuning
We will train a model on the Adult dataset available on the UCI. Let's download the dataset.
# Download a copy of the adult dataset.wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/yggdrasil-decision-forests/main/yggdrasil_decision_forests/test_data/dataset/adult_train.csv -O /tmp/adult_train.csvwget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/yggdrasil-decision-forests/main/yggdrasil_decision_forests/test_data/dataset/adult_test.csv -O /tmp/adult_test.csv
Split the dataset into a training and a testing dataset.
# Load the dataset in memory
train_df = pd.read_csv("/tmp/adult_train.csv")
test_df = pd.read_csv("/tmp/adult_test.csv")
# , and convert it into a TensorFlow dataset.
train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_df, label="income")
test_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(test_df, label="income")
I0000 00:00:1768227501.012516 162095 gpu_device.cc:2019] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 13638 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:05.0, compute capability: 7.5 I0000 00:00:1768227501.014917 162095 gpu_device.cc:2019] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:1 with 13756 MB memory: -> device: 1, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:06.0, compute capability: 7.5 I0000 00:00:1768227501.017290 162095 gpu_device.cc:2019] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:2 with 13756 MB memory: -> device: 2, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:07.0, compute capability: 7.5 I0000 00:00:1768227501.019386 162095 gpu_device.cc:2019] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:3 with 13756 MB memory: -> device: 3, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:08.0, compute capability: 7.5
First, we train and evaluate the quality of a Gradient Boosted Trees model trained with the default hyper-parameters.
%%time
# Train a model with default hyper-parameters
model = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel()
model.fit(train_ds)
Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmpklam3fjb as temporary training directory
Reading training dataset...
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
W0000 00:00:1768227501.435142 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227501.435184 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227501.435187 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB".
Training dataset read in 0:00:03.933074. Found 22792 examples.
Training model...
I0000 00:00:1768227505.394855 162095 kernel.cc:782] Start Yggdrasil model training
I0000 00:00:1768227505.394890 162095 kernel.cc:783] Collect training examples
I0000 00:00:1768227505.394899 162095 kernel.cc:795] Dataspec guide:
column_guides {
column_name_pattern: "^__LABEL$"
type: CATEGORICAL
categorial {
min_vocab_frequency: 0
max_vocab_count: -1
}
}
default_column_guide {
categorial {
max_vocab_count: 2000
}
discretized_numerical {
maximum_num_bins: 255
}
}
ignore_columns_without_guides: false
detect_numerical_as_discretized_numerical: false
I0000 00:00:1768227505.395296 162095 kernel.cc:401] Number of batches: 23
I0000 00:00:1768227505.395315 162095 kernel.cc:402] Number of examples: 22792
I0000 00:00:1768227505.402644 162095 data_spec_inference.cc:354] 1 item(s) have been pruned (i.e. they are considered out of dictionary) for the column native_country (40 item(s) left) because min_value_count=5 and max_number_of_unique_values=2000
I0000 00:00:1768227505.402683 162095 data_spec_inference.cc:354] 1 item(s) have been pruned (i.e. they are considered out of dictionary) for the column occupation (13 item(s) left) because min_value_count=5 and max_number_of_unique_values=2000
I0000 00:00:1768227505.402701 162095 data_spec_inference.cc:354] 1 item(s) have been pruned (i.e. they are considered out of dictionary) for the column workclass (7 item(s) left) because min_value_count=5 and max_number_of_unique_values=2000
I0000 00:00:1768227505.408546 162095 kernel.cc:802] Training dataset:
Number of records: 22792
Number of columns: 15
Number of columns by type:
CATEGORICAL: 9 (60%)
NUMERICAL: 6 (40%)
Columns:
CATEGORICAL: 9 (60%)
0: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:3 no-ood-item
4: "education" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:17 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"HS-grad" 7340 (32.2043%)
8: "marital_status" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:8 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Married-civ-spouse" 10431 (45.7661%)
9: "native_country" CATEGORICAL num-nas:407 (1.78571%) has-dict vocab-size:41 num-oods:1 (0.00446728%) most-frequent:"United-States" 20436 (91.2933%)
10: "occupation" CATEGORICAL num-nas:1260 (5.52826%) has-dict vocab-size:14 num-oods:4 (0.018577%) most-frequent:"Prof-specialty" 2870 (13.329%)
11: "race" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:6 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"White" 19467 (85.4115%)
12: "relationship" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:7 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Husband" 9191 (40.3256%)
13: "sex" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Male" 15165 (66.5365%)
14: "workclass" CATEGORICAL num-nas:1257 (5.51509%) has-dict vocab-size:8 num-oods:3 (0.0139308%) most-frequent:"Private" 15879 (73.7358%)
NUMERICAL: 6 (40%)
1: "age" NUMERICAL mean:38.6153 min:17 max:90 sd:13.661
2: "capital_gain" NUMERICAL mean:1081.9 min:0 max:99999 sd:7509.48
3: "capital_loss" NUMERICAL mean:87.2806 min:0 max:4356 sd:403.01
5: "education_num" NUMERICAL mean:10.0927 min:1 max:16 sd:2.56427
6: "fnlwgt" NUMERICAL mean:189879 min:12285 max:1.4847e+06 sd:106423
7: "hours_per_week" NUMERICAL mean:40.3955 min:1 max:99 sd:12.249
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute whose type is manually defined by the user, i.e., the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
I0000 00:00:1768227505.408588 162095 kernel.cc:818] Configure learner
W0000 00:00:1768227505.408802 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227505.408815 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227505.408818 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB".
I0000 00:00:1768227505.408855 162095 kernel.cc:831] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "^age$"
features: "^capital_gain$"
features: "^capital_loss$"
features: "^education$"
features: "^education_num$"
features: "^fnlwgt$"
features: "^hours_per_week$"
features: "^marital_status$"
features: "^native_country$"
features: "^occupation$"
features: "^race$"
features: "^relationship$"
features: "^sex$"
features: "^workclass$"
label: "^__LABEL$"
task: CLASSIFICATION
random_seed: 123456
metadata {
framework: "TF Keras"
}
pure_serving_model: false
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 6
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
keep_non_leaf_label_distribution: true
num_candidate_attributes: -1
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
uplift {
min_examples_in_treatment: 5
split_score: KULLBACK_LEIBLER
}
numerical_vector_sequence {
max_num_test_examples: 1000
num_random_selected_anchors: 100
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
loss: DEFAULT
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
validation_interval_in_trees: 1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
xe_ndcg {
ndcg_truncation: 5
}
stochastic_gradient_boosting {
ratio: 1
}
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
early_stopping_initial_iteration: 10
}
I0000 00:00:1768227505.409177 162095 kernel.cc:834] Deployment config:
cache_path: "/tmpfs/tmp/tmpklam3fjb/working_cache"
num_threads: 32
try_resume_training: true
I0000 00:00:1768227505.409385 162322 kernel.cc:895] Train model
I0000 00:00:1768227505.409525 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:577] Default loss set to BINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
I0000 00:00:1768227505.409547 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1190] Training gradient boosted tree on 22792 example(s) and 14 feature(s).
I0000 00:00:1768227505.415524 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1230] 20533 examples used for training and 2259 examples used for validation
I0000 00:00:1768227505.422347 162322 gpu.cc:93] Cannot initialize GPU: Not compiled with GPU support
I0000 00:00:1768227505.437829 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1632] Train tree 1/300 train-loss:1.015975 train-accuracy:0.761895 valid-loss:1.071430 valid-accuracy:0.736609 [total:0.02s iter:0.02s]
I0000 00:00:1768227505.451975 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1632] Train tree 2/300 train-loss:0.955303 train-accuracy:0.761895 valid-loss:1.007908 valid-accuracy:0.736609 [total:0.03s iter:0.01s]
I0000 00:00:1768227505.465446 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1634] Train tree 3/300 train-loss:0.907290 train-accuracy:0.761895 valid-loss:0.957415 valid-accuracy:0.736609 [total:0.04s iter:0.01s]
Model trained in 0:00:01.977522
Compiling model...
I0000 00:00:1768227507.300760 162322 early_stopping.cc:54] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.579561
I0000 00:00:1768227507.300808 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1669] Create final snapshot of the model at iteration 165
I0000 00:00:1768227507.309359 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:279] Truncates the model to 136 tree(s) i.e. 136 iteration(s).
I0000 00:00:1768227507.309643 162322 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:341] Final model num-trees:136 valid-loss:0.579561 valid-accuracy:0.870297
I0000 00:00:1768227507.312500 162322 kernel.cc:926] Export model in log directory: /tmpfs/tmp/tmpklam3fjb with prefix bb454b5f0b464cf4
I0000 00:00:1768227507.318548 162322 kernel.cc:944] Save model in resources
I0000 00:00:1768227507.321876 162095 abstract_model.cc:921] Model self evaluation:
Task: CLASSIFICATION
Label: __LABEL
Loss (BINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD): 0.579561
Accuracy: 0.870297 CI95[W][0 1]
ErrorRate: : 0.129703
Confusion Table:
truth\prediction
1 2
1 1573 91
2 202 393
Total: 2259
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
I0000 00:00:1768227507.365258 162095 quick_scorer_extended.cc:927] The binary was compiled without AVX2 support, but your CPU supports it. Enable it for faster model inference.
I0000 00:00:1768227507.366429 162095 abstract_model.cc:1439] Engine "GradientBoostedTreesQuickScorerExtended" built
Model compiled.
CPU times: user 9 s, sys: 1.25 s, total: 10.3 s
Wall time: 6.75 s
<tf_keras.src.callbacks.History at 0x7f6635c6cbe0>
# Evaluate the model
model.compile(["accuracy"])
test_accuracy = model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)["accuracy"]
print(f"Test accuracy without hyper-parameter tuning: {test_accuracy:.4f}")
Test accuracy without hyper-parameter tuning: 0.8744
The default hyper-parameters of the model are available with the learner_params function. The definition of those parameters is available in the documentation.
print("Default hyper-parameters of the model:\n", model.learner_params)
Default hyper-parameters of the model:
{'adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration': False, 'allow_na_conditions': False, 'apply_link_function': True, 'categorical_algorithm': 'CART', 'categorical_set_split_greedy_sampling': 0.1, 'categorical_set_split_max_num_items': -1, 'categorical_set_split_min_item_frequency': 1, 'compute_permutation_variable_importance': False, 'cross_entropy_ndcg_truncation': 5, 'dart_dropout': None, 'early_stopping': 'LOSS_INCREASE', 'early_stopping_initial_iteration': 10, 'early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead': 30, 'focal_loss_alpha': 0.5, 'focal_loss_gamma': 2.0, 'forest_extraction': 'MART', 'goss_alpha': 0.2, 'goss_beta': 0.1, 'growing_strategy': 'LOCAL', 'honest': False, 'honest_fixed_separation': False, 'honest_ratio_leaf_examples': 0.5, 'in_split_min_examples_check': True, 'keep_non_leaf_label_distribution': True, 'l1_regularization': 0.0, 'l2_categorical_regularization': 1.0, 'l2_regularization': 0.0, 'lambda_loss': 1.0, 'loss': 'DEFAULT', 'max_depth': 6, 'max_num_nodes': None, 'maximum_model_size_in_memory_in_bytes': -1.0, 'maximum_training_duration_seconds': -1.0, 'mhld_oblique_max_num_attributes': None, 'mhld_oblique_sample_attributes': None, 'min_examples': 5, 'missing_value_policy': 'GLOBAL_IMPUTATION', 'ndcg_truncation': 5, 'num_candidate_attributes': -1, 'num_candidate_attributes_ratio': -1.0, 'num_trees': 300, 'numerical_vector_sequence_num_examples': 1000, 'numerical_vector_sequence_num_random_anchors': 100, 'pure_serving_model': False, 'random_seed': 123456, 'sampling_method': 'RANDOM', 'selective_gradient_boosting_ratio': 0.01, 'shrinkage': 0.1, 'sorting_strategy': 'PRESORT', 'sparse_oblique_max_num_features': None, 'sparse_oblique_max_num_projections': None, 'sparse_oblique_normalization': None, 'sparse_oblique_num_projections_exponent': None, 'sparse_oblique_projection_density_factor': None, 'sparse_oblique_weights': None, 'sparse_oblique_weights_integer_maximum': None, 'sparse_oblique_weights_integer_minimum': None, 'sparse_oblique_weights_power_of_two_max_exponent': None, 'sparse_oblique_weights_power_of_two_min_exponent': None, 'split_axis': 'AXIS_ALIGNED', 'subsample': 1.0, 'uplift_min_examples_in_treatment': 5, 'uplift_split_score': 'KULLBACK_LEIBLER', 'use_hessian_gain': False, 'validation_interval_in_trees': 1, 'validation_ratio': 0.1}
Training a model with automated hyper-parameter tuning and manual definition of the hyper-parameters
Hyper-parameter tuning is enabled by specifying the tuner constructor argument of the model. The tuner object contains all the configuration of the tuner (search space, optimizer, trial and objective).
# Configure the tuner.
# Create a Random Search tuner with 50 trials.
tuner = tfdf.tuner.RandomSearch(num_trials=50)
# Define the search space.
#
# Adding more parameters generaly improve the quality of the model, but make
# the tuning last longer.
tuner.choice("min_examples", [2, 5, 7, 10])
tuner.choice("categorical_algorithm", ["CART", "RANDOM"])
# Some hyper-parameters are only valid for specific values of other
# hyper-parameters. For example, the "max_depth" parameter is mostly useful when
# "growing_strategy=LOCAL" while "max_num_nodes" is better suited when
# "growing_strategy=BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL".
local_search_space = tuner.choice("growing_strategy", ["LOCAL"])
local_search_space.choice("max_depth", [3, 4, 5, 6, 8])
# merge=True indicates that the parameter (here "growing_strategy") is already
# defined, and that new values are added to it.
global_search_space = tuner.choice("growing_strategy", ["BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL"], merge=True)
global_search_space.choice("max_num_nodes", [16, 32, 64, 128, 256])
tuner.choice("use_hessian_gain", [True, False])
tuner.choice("shrinkage", [0.02, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15])
tuner.choice("num_candidate_attributes_ratio", [0.2, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0])
# Uncomment some (or all) of the following hyper-parameters to increase the
# quality of the search. The number of trial should be increased accordingly.
# tuner.choice("split_axis", ["AXIS_ALIGNED"])
# oblique_space = tuner.choice("split_axis", ["SPARSE_OBLIQUE"], merge=True)
# oblique_space.choice("sparse_oblique_normalization",
# ["NONE", "STANDARD_DEVIATION", "MIN_MAX"])
# oblique_space.choice("sparse_oblique_weights", ["BINARY", "CONTINUOUS"])
# oblique_space.choice("sparse_oblique_num_projections_exponent", [1.0, 1.5])
<tensorflow_decision_forests.component.tuner.tuner.SearchSpace at 0x7f6601d3f9d0>
%%time
%set_cell_height 300
# Tune the model. Notice the `tuner=tuner`.
tuned_model = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(tuner=tuner)
tuned_model.fit(train_ds, verbose=2)
# The `num_threads` model constructor argument (not specified in the example
# above) controls how many trials are run in parallel (one per thread). If
# `num_threads` is not specified (like in the example above), one thread is
# allocated for each available CPU core.
#
# If the training is interrupted (for example, by pressing on the "stop" button
# on the top-left of the colab cell), the best model so-far will be returned.
# In the training logs, you can see lines such as `[10/50] Score: -0.45 / -0.40
# HParams: ...`. This indicates that 10 of the 50 trials have been completed.
# And that the last trial returned a score of "-0.45" and that the best trial so
# far has a score of "-0.40". In this example, the model is optimized by
# logloss. Since scores are maximized and log loss should be minimized, the
# score is effectively minus the log loss.
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmptyvba0mb as temporary training directory
Reading training dataset...
Training tensor examples:
Features: {'age': <tf.Tensor 'data:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'workclass': <tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'fnlwgt': <tf.Tensor 'data_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'education': <tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'education_num': <tf.Tensor 'data_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'marital_status': <tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'occupation': <tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'relationship': <tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'race': <tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'sex': <tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'capital_gain': <tf.Tensor 'data_10:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'capital_loss': <tf.Tensor 'data_11:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'hours_per_week': <tf.Tensor 'data_12:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'native_country': <tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>}
Label: Tensor("data_14:0", shape=(None,), dtype=int64)
Weights: None
Normalized tensor features:
{'age': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'workclass': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'fnlwgt': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'education': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'education_num': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'marital_status': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'occupation': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'relationship': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'race': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'sex': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'capital_gain': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'capital_loss': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'hours_per_week': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'native_country': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>)}
W0000 00:00:1768227508.592477 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227508.592510 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227508.592514 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB".
Training dataset read in 0:00:00.376009. Found 22792 examples.
Training model...
Standard output detected as not visible to the user e.g. running in a notebook. Creating a training log redirection. If training gets stuck, try calling tfdf.keras.set_training_logs_redirection(False).
Model trained in 0:02:55.695377
Compiling model...
Model compiled.
CPU times: user 2min 56s, sys: 126 ms, total: 2min 56s
Wall time: 2min 56s
<tf_keras.src.callbacks.History at 0x7f6626c5b520>
# Evaluate the model
tuned_model.compile(["accuracy"])
tuned_test_accuracy = tuned_model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)["accuracy"]
print(f"Test accuracy with the TF-DF hyper-parameter tuner: {tuned_test_accuracy:.4f}")
Test accuracy with the TF-DF hyper-parameter tuner: 0.8722
The hyper-parameters and objective scores of the trials are available in the model inspector. The score value is always maximized. In this example, the score is the negative log loss on the validation dataset (selected automatically).
# Display the tuning logs.
tuning_logs = tuned_model.make_inspector().tuning_logs()
tuning_logs.head()
The single rows with best=True is the one used in the final model.
# Best hyper-parameters.
tuning_logs[tuning_logs.best].iloc[0]
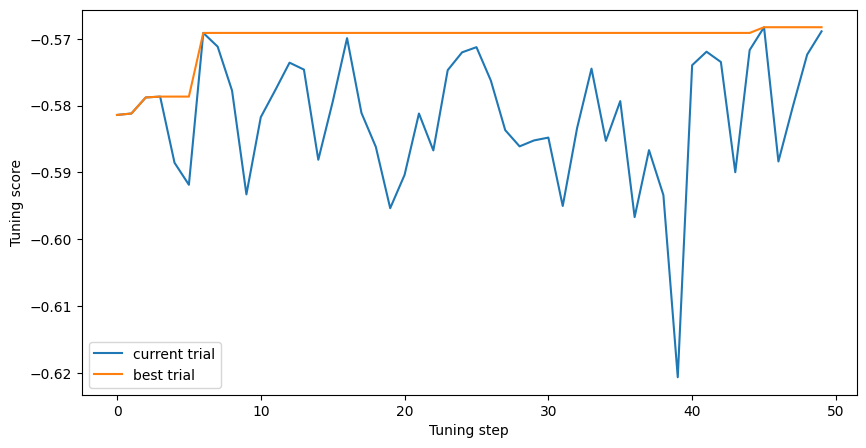
score -0.568272 evaluation_time 154.636092 best True min_examples 5 categorical_algorithm CART growing_strategy BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL max_num_nodes 256.0 use_hessian_gain true shrinkage 0.1 num_candidate_attributes_ratio 0.9 max_depth NaN Name: 45, dtype: object
Next, we plot the evaluation of the best score during the tuning.
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(tuning_logs["score"], label="current trial")
plt.plot(tuning_logs["score"].cummax(), label="best trial")
plt.xlabel("Tuning step")
plt.ylabel("Tuning score")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Training a model with automated hyper-parameter tuning and automatic definition of the hyper-parameters (recommended approach)
As before, hyper-parameter tuning is enabled by specifying the tuner constructor argument of the model. Set use_predefined_hps=True to automatically configure the search space for the hyper-parameters.
%%time
%set_cell_height 300
# Create a Random Search tuner with 50 trials and automatic hp configuration.
tuner = tfdf.tuner.RandomSearch(num_trials=50, use_predefined_hps=True)
# Define and train the model.
tuned_model = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(tuner=tuner)
tuned_model.fit(train_ds, verbose=2)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmpdh8cv1hr as temporary training directory
Reading training dataset...
Training tensor examples:
Features: {'age': <tf.Tensor 'data:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'workclass': <tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'fnlwgt': <tf.Tensor 'data_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'education': <tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'education_num': <tf.Tensor 'data_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'marital_status': <tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'occupation': <tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'relationship': <tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'race': <tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'sex': <tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'capital_gain': <tf.Tensor 'data_10:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'capital_loss': <tf.Tensor 'data_11:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'hours_per_week': <tf.Tensor 'data_12:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'native_country': <tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>}
Label: Tensor("data_14:0", shape=(None,), dtype=int64)
Weights: None
Normalized tensor features:
{'age': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'workclass': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'fnlwgt': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'education': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'education_num': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'marital_status': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'occupation': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'relationship': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'race': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'sex': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'capital_gain': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'capital_loss': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'hours_per_week': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'native_country': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>)}
W0000 00:00:1768227685.246198 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227685.246233 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768227685.246237 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB".
Training dataset read in 0:00:00.363152. Found 22792 examples.
Training model...
Model trained in 0:40:05.749702
Compiling model...
Model compiled.
CPU times: user 40min 8s, sys: 1.57 s, total: 40min 10s
Wall time: 40min 6s
<tf_keras.src.callbacks.History at 0x7f6626b30370>
# Evaluate the model
tuned_model.compile(["accuracy"])
tuned_test_accuracy = tuned_model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)["accuracy"]
print(f"Test accuracy with the TF-DF hyper-parameter tuner: {tuned_test_accuracy:.4f}")
Test accuracy with the TF-DF hyper-parameter tuner: 0.8741
Same as before, display the tuning logs.
# Display the tuning logs.
tuning_logs = tuned_model.make_inspector().tuning_logs()
tuning_logs.head()
Same as before, shows the best hyper-parameters.
# Best hyper-parameters.
tuning_logs[tuning_logs.best].iloc[0]
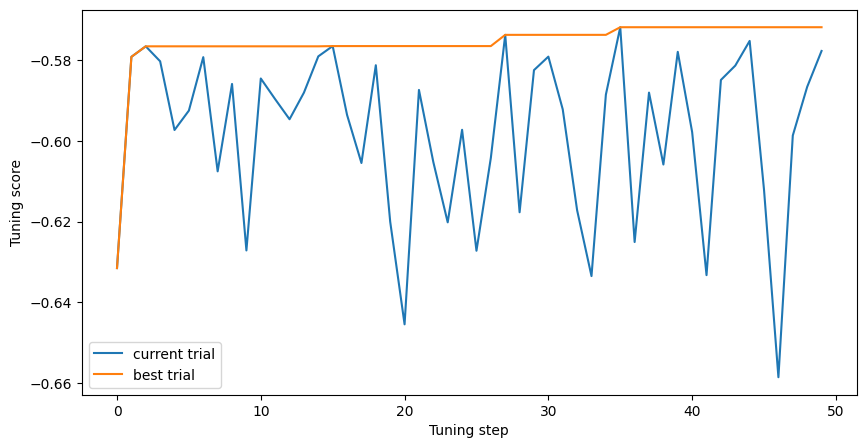
score -0.571786 evaluation_time 1790.338509 best True split_axis SPARSE_OBLIQUE sparse_oblique_projection_density_factor 2.0 sparse_oblique_normalization NONE sparse_oblique_weights BINARY categorical_algorithm RANDOM growing_strategy BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL max_num_nodes 64.0 sampling_method RANDOM subsample 0.9 shrinkage 0.1 min_examples 7 use_hessian_gain false num_candidate_attributes_ratio 1.0 max_depth NaN Name: 35, dtype: object
Finally, plots the evolution of the quality of the model during tuning:
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(tuning_logs["score"], label="current trial")
plt.plot(tuning_logs["score"].cummax(), label="best trial")
plt.xlabel("Tuning step")
plt.ylabel("Tuning score")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Training a model with Keras Tuner (Alternative approach)
TensorFlow Decision Forests is based on the Keras framework, and it is compatible with the Keras tuner.
Currently, the TF-DF Tuner and the Keras Tuner are complementary.
TF-DF Tuner
- Automatic configuration of the objective.
- Automatic extraction of validation dataset (if needed).
- Support model self evaluation (e.g. out-of-bag evaluation).
- Distributed hyper-parameter tuning.
- Shared dataset access in between the trials: The tensorflow dataset is read only once, speeding-up tuning significantly on small datasets.
Keras Tuner
- Support tuning of the pre-processing parameters.
- Support hyper-band optimizer.
- Support custom objectives.
Let's tune a TF-DF model using the Keras tuner.
# Install the Keras tuner
!pip install keras-tuner -U -qq
import keras_tuner as kt
%%time
def build_model(hp):
"""Creates a model."""
model = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(
min_examples=hp.Choice("min_examples", [2, 5, 7, 10]),
categorical_algorithm=hp.Choice("categorical_algorithm", ["CART", "RANDOM"]),
max_depth=hp.Choice("max_depth", [4, 5, 6, 7]),
# The keras tuner convert automaticall boolean parameters to integers.
use_hessian_gain=bool(hp.Choice("use_hessian_gain", [True, False])),
shrinkage=hp.Choice("shrinkage", [0.02, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15]),
num_candidate_attributes_ratio=hp.Choice("num_candidate_attributes_ratio", [0.2, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0]),
)
# Optimize the model accuracy as computed on the validation dataset.
model.compile(metrics=["accuracy"])
return model
keras_tuner = kt.RandomSearch(
build_model,
objective="val_accuracy",
max_trials=50,
overwrite=True,
directory="/tmp/keras_tuning")
# Important: The tuning should not be done on the test dataset.
# Extract a validation dataset from the training dataset. The new training
# dataset is called the "sub-training-dataset".
def split_dataset(dataset, test_ratio=0.30):
"""Splits a panda dataframe in two."""
test_indices = np.random.rand(len(dataset)) < test_ratio
return dataset[~test_indices], dataset[test_indices]
sub_train_df, sub_valid_df = split_dataset(train_df)
sub_train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(sub_train_df, label="income")
sub_valid_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(sub_valid_df, label="income")
# Tune the model
keras_tuner.search(sub_train_ds, validation_data=sub_valid_ds)
Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus. WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus. Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmpe031zm8r as temporary training directory Search: Running Trial #1 Value |Best Value So Far |Hyperparameter 10 |10 |min_examples RANDOM |RANDOM |categorical_algorithm 5 |5 |max_depth 1 |1 |use_hessian_gain 0.1 |0.1 |shrinkage 1 |1 |num_candidate_attributes_ratio W0000 00:00:1768230093.697230 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS". W0000 00:00:1768230093.697266 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS". W0000 00:00:1768230093.697271 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB". Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus. WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus. Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmpexsf9llp as temporary training directory W0000 00:00:1768230094.194538 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS". W0000 00:00:1768230094.194602 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS". W0000 00:00:1768230094.194612 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB". --------------------------------------------------------------------------- FatalTypeError Traceback (most recent call last) File <timed exec>:40 File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/base_tuner.py:234, in BaseTuner.search(self, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 231 continue 233 self.on_trial_begin(trial) --> 234 self._try_run_and_update_trial(trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 235 self.on_trial_end(trial) 236 self.on_search_end() File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/base_tuner.py:279, in BaseTuner._try_run_and_update_trial(self, trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 277 except Exception as e: 278 if isinstance(e, errors.FatalError): --> 279 raise e 280 if config_module.DEBUG: 281 # Printing the stacktrace and the error. 282 traceback.print_exc() File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/base_tuner.py:274, in BaseTuner._try_run_and_update_trial(self, trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 272 def _try_run_and_update_trial(self, trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs): 273 try: --> 274 self._run_and_update_trial(trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 275 trial.status = trial_module.TrialStatus.COMPLETED 276 return File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/base_tuner.py:239, in BaseTuner._run_and_update_trial(self, trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 238 def _run_and_update_trial(self, trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs): --> 239 results = self.run_trial(trial, *fit_args, **fit_kwargs) 240 if self.oracle.get_trial(trial.trial_id).metrics.exists( 241 self.oracle.objective.name 242 ): 243 # The oracle is updated by calling `self.oracle.update_trial()` in 244 # `Tuner.run_trial()`. For backward compatibility, we support this 245 # use case. No further action needed in this case. 246 warnings.warn( 247 "The use case of calling " 248 "`self.oracle.update_trial(trial_id, metrics)` " (...) 254 stacklevel=2, 255 ) File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/tuner.py:314, in Tuner.run_trial(self, trial, *args, **kwargs) 312 callbacks.append(model_checkpoint) 313 copied_kwargs["callbacks"] = callbacks --> 314 obj_value = self._build_and_fit_model(trial, *args, **copied_kwargs) 316 histories.append(obj_value) 317 return histories File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/tuner.py:232, in Tuner._build_and_fit_model(self, trial, *args, **kwargs) 214 """For AutoKeras to override. 215 216 DO NOT REMOVE this function. AutoKeras overrides the function to tune (...) 229 The fit history. 230 """ 231 hp = trial.hyperparameters --> 232 model = self._try_build(hp) 233 results = self.hypermodel.fit(hp, model, *args, **kwargs) 235 # Save the build config for model loading later. File /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras_tuner/src/engine/tuner.py:167, in Tuner._try_build(self, hp) 165 # Stop if `build()` does not return a valid model. 166 if not isinstance(model, keras.models.Model): --> 167 raise errors.FatalTypeError( 168 "Expected the model-building function, or HyperModel.build() " 169 "to return a valid Keras Model instance. " 170 f"Received: {model} of type {type(model)}." 171 ) 172 # Check model size. 173 size = maybe_compute_model_size(model) FatalTypeError: Expected the model-building function, or HyperModel.build() to return a valid Keras Model instance. Received: <tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel object at 0x7f6601db96a0> of type <class 'tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel'>.
The best hyper-parameter are available with get_best_hyperparameters:
# Tune the model
best_hyper_parameters = keras_tuner.get_best_hyperparameters()[0].values
print("Best hyper-parameters:", keras_tuner.get_best_hyperparameters()[0].values)
Best hyper-parameters: {'min_examples': 10, 'categorical_algorithm': 'RANDOM', 'max_depth': 5, 'use_hessian_gain': 1, 'shrinkage': 0.1, 'num_candidate_attributes_ratio': 1.0}
The model should be re-trained with the best hyper-parameters:
%set_cell_height 300
# Train the model
# The keras tuner convert automaticall boolean parameters to integers.
best_hyper_parameters["use_hessian_gain"] = bool(best_hyper_parameters["use_hessian_gain"])
best_model = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(**best_hyper_parameters)
best_model.fit(train_ds, verbose=2)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
Warning: The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
WARNING:absl:The `num_threads` constructor argument is not set and the number of CPU is os.cpu_count()=32 > 32. Setting num_threads to 32. Set num_threads manually to use more than 32 cpus.
Use /tmpfs/tmp/tmpu5aufxfh as temporary training directory
Reading training dataset...
Training tensor examples:
Features: {'age': <tf.Tensor 'data:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'workclass': <tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'fnlwgt': <tf.Tensor 'data_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'education': <tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'education_num': <tf.Tensor 'data_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'marital_status': <tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'occupation': <tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'relationship': <tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'race': <tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'sex': <tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>, 'capital_gain': <tf.Tensor 'data_10:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'capital_loss': <tf.Tensor 'data_11:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'hours_per_week': <tf.Tensor 'data_12:0' shape=(None,) dtype=int64>, 'native_country': <tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>}
Label: Tensor("data_14:0", shape=(None,), dtype=int64)
Weights: None
Normalized tensor features:
{'age': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'workclass': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'fnlwgt': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_1:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'education': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'education_num': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_2:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'marital_status': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'occupation': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_6:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'relationship': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_7:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'race': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_8:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'sex': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_9:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>), 'capital_gain': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_3:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'capital_loss': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_4:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'hours_per_week': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.NUMERICAL: 1>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'Cast_5:0' shape=(None,) dtype=float32>), 'native_country': SemanticTensor(semantic=<Semantic.CATEGORICAL: 2>, tensor=<tf.Tensor 'data_13:0' shape=(None,) dtype=string>)}
W0000 00:00:1768230094.686542 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1873] "goss_alpha" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768230094.686591 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1883] "goss_beta" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "GOSS".
W0000 00:00:1768230094.686599 162095 gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1897] "selective_gradient_boosting_ratio" set but "sampling_method" not equal to "SELGB".
Training dataset read in 0:00:00.371304. Found 22792 examples.
Training model...
Model trained in 0:00:03.327534
Compiling model...
Model compiled.
<tf_keras.src.callbacks.History at 0x7f6460405e50>
We can then evaluate the tuned model:
# Evaluate the model
best_model.compile(["accuracy"])
tuned_test_accuracy = best_model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True, verbose=0)["accuracy"]
print(f"Test accuracy with the Keras Tuner: {tuned_test_accuracy:.4f}")
Test accuracy with the Keras Tuner: 0.8742
