TensorFlow.org'da görüntüleyin TensorFlow.org'da görüntüleyin |  Google Colab'da çalıştırın Google Colab'da çalıştırın |  Kaynağı GitHub'da görüntüleyin Kaynağı GitHub'da görüntüleyin | 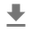 Not defterini indir Not defterini indir |
genel bakış
Bu not defteri, Eklentiler paketinden Koşullu Graident Optimize Edici'nin nasıl kullanılacağını gösterecektir.
KoşulluGradient
Bir sinir ağının parametrelerinin sınırlandırılmasının, altta yatan düzenlileştirme etkilerinden dolayı eğitimde faydalı olduğu gösterilmiştir. Çoğu zaman, parametreler yumuşak bir ceza (kısıtlama memnuniyetini asla garanti etmez) veya bir projeksiyon işlemi (hesaplama açısından pahalı olan) yoluyla sınırlandırılır. Koşullu gradyan (CG) optimize edici ise, pahalı bir projeksiyon adımına ihtiyaç duymadan kısıtlamaları kesinlikle uygular. Kısıtlama kümesi içinde hedefin doğrusal bir yaklaşımını en aza indirerek çalışır. Bu not defterinde, MNIST veri setinde CG optimizer aracılığıyla Frobenius norm kısıtlamasının uygulamasını gösteriyorsunuz. CG artık bir tensorflow API olarak mevcuttur. İyileştirici fazla detay mevcuttur https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.06453.pdf
Kurmak
pip install -q -U tensorflow-addons
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_addons as tfa
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# Hyperparameters
batch_size=64
epochs=10
Modeli Oluştur
model_1 = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, input_shape=(784,), activation='relu', name='dense_1'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu', name='dense_2'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax', name='predictions'),
])
Verileri Hazırlayın
# Load MNIST dataset as NumPy arrays
dataset = {}
num_validation = 10000
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# Preprocess the data
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 784).astype('float32') / 255
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 784).astype('float32') / 255
Özel Geri Çağırma İşlevi Tanımlayın
def frobenius_norm(m):
"""This function is to calculate the frobenius norm of the matrix of all
layer's weight.
Args:
m: is a list of weights param for each layers.
"""
total_reduce_sum = 0
for i in range(len(m)):
total_reduce_sum = total_reduce_sum + tf.math.reduce_sum(m[i]**2)
norm = total_reduce_sum**0.5
return norm
CG_frobenius_norm_of_weight = []
CG_get_weight_norm = tf.keras.callbacks.LambdaCallback(
on_epoch_end=lambda batch, logs: CG_frobenius_norm_of_weight.append(
frobenius_norm(model_1.trainable_weights).numpy()))
Eğitin ve Değerlendirin: CG'yi Optimize Edici Olarak Kullanma
Tipik keras optimizerlerini yeni tfa optimizer ile değiştirin
# Compile the model
model_1.compile(
optimizer=tfa.optimizers.ConditionalGradient(
learning_rate=0.99949, lambda_=203), # Utilize TFA optimizer
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
history_cg = model_1.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=[CG_get_weight_norm])
Epoch 1/10 938/938 [==============================] - 4s 3ms/step - loss: 0.6034 - accuracy: 0.8162 - val_loss: 0.2282 - val_accuracy: 0.9313 Epoch 2/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1968 - accuracy: 0.9411 - val_loss: 0.1865 - val_accuracy: 0.9411 Epoch 3/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1502 - accuracy: 0.9552 - val_loss: 0.1356 - val_accuracy: 0.9590 Epoch 4/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1349 - accuracy: 0.9598 - val_loss: 0.1084 - val_accuracy: 0.9679 Epoch 5/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1261 - accuracy: 0.9609 - val_loss: 0.1162 - val_accuracy: 0.9648 Epoch 6/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1119 - accuracy: 0.9662 - val_loss: 0.1277 - val_accuracy: 0.9567 Epoch 7/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1096 - accuracy: 0.9671 - val_loss: 0.1009 - val_accuracy: 0.9685 Epoch 8/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1045 - accuracy: 0.9687 - val_loss: 0.1015 - val_accuracy: 0.9698 Epoch 9/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1011 - accuracy: 0.9688 - val_loss: 0.1180 - val_accuracy: 0.9627 Epoch 10/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1029 - accuracy: 0.9689 - val_loss: 0.1590 - val_accuracy: 0.9516
Eğitin ve Değerlendirin: SGD'yi Optimize Edici Olarak Kullanma
model_2 = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, input_shape=(784,), activation='relu', name='dense_1'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu', name='dense_2'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax', name='predictions'),
])
SGD_frobenius_norm_of_weight = []
SGD_get_weight_norm = tf.keras.callbacks.LambdaCallback(
on_epoch_end=lambda batch, logs: SGD_frobenius_norm_of_weight.append(
frobenius_norm(model_2.trainable_weights).numpy()))
# Compile the model
model_2.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(0.01), # Utilize SGD optimizer
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
history_sgd = model_2.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=[SGD_get_weight_norm])
Epoch 1/10 938/938 [==============================] - 3s 3ms/step - loss: 1.4885 - accuracy: 0.5945 - val_loss: 0.4230 - val_accuracy: 0.8838 Epoch 2/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4087 - accuracy: 0.8875 - val_loss: 0.3222 - val_accuracy: 0.9073 Epoch 3/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3267 - accuracy: 0.9075 - val_loss: 0.2867 - val_accuracy: 0.9178 Epoch 4/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2903 - accuracy: 0.9186 - val_loss: 0.2605 - val_accuracy: 0.9259 Epoch 5/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2691 - accuracy: 0.9233 - val_loss: 0.2468 - val_accuracy: 0.9292 Epoch 6/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2466 - accuracy: 0.9291 - val_loss: 0.2265 - val_accuracy: 0.9352 Epoch 7/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2210 - accuracy: 0.9370 - val_loss: 0.2106 - val_accuracy: 0.9404 Epoch 8/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2137 - accuracy: 0.9387 - val_loss: 0.2029 - val_accuracy: 0.9424 Epoch 9/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1996 - accuracy: 0.9429 - val_loss: 0.1937 - val_accuracy: 0.9441 Epoch 10/10 938/938 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1925 - accuracy: 0.9450 - val_loss: 0.1831 - val_accuracy: 0.9469
Frobenius Ağırlık Normu: CG ve SGD
CG optimizer'ın mevcut uygulaması, Frobenius Norm'u hedef fonksiyonda düzenleyici olarak dikkate alarak Frobenius Norm'a dayanmaktadır. Bu nedenle, CG'nin düzenlileştirilmiş etkisini, Frobenius Norm düzenleyicisini dayatmayan SGD optimizer ile karşılaştırırsınız.
plt.plot(
CG_frobenius_norm_of_weight,
color='r',
label='CG_frobenius_norm_of_weights')
plt.plot(
SGD_frobenius_norm_of_weight,
color='b',
label='SGD_frobenius_norm_of_weights')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Frobenius norm of weights')
plt.legend(loc=1)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fada7ab12e8>
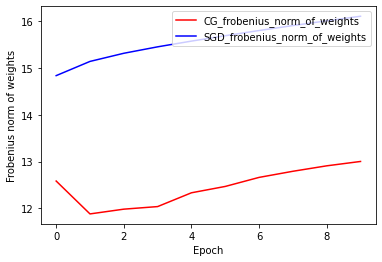
Eğitim ve Doğrulama Doğruluğu: CG ve SGD
plt.plot(history_cg.history['accuracy'], color='r', label='CG_train')
plt.plot(history_cg.history['val_accuracy'], color='g', label='CG_test')
plt.plot(history_sgd.history['accuracy'], color='pink', label='SGD_train')
plt.plot(history_sgd.history['val_accuracy'], color='b', label='SGD_test')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc=4)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fada7983e80>