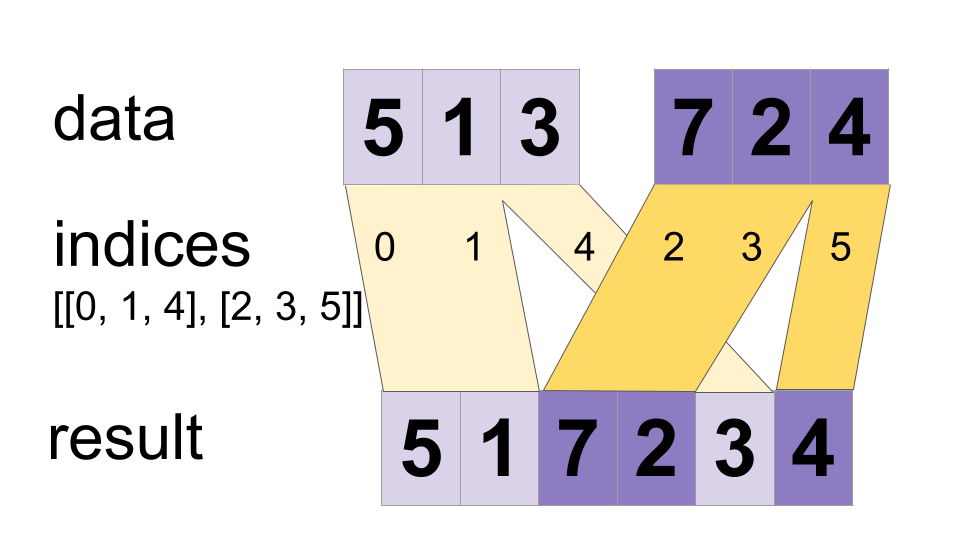
Interleave the values from the `data` tensors into a single tensor.
Builds a merged tensor such that
merged[indices[m][i, ..., j], ...] = data[m][i, ..., j, ...]
# Scalar indices:
merged[indices[m], ...] = data[m][...]
# Vector indices:
merged[indices[m][i], ...] = data[m][i, ...]
merged.shape = [max(indices) + 1] + constant
Values are merged in order, so if an index appears in both `indices[m][i]` and `indices[n][j]` for `(m,i) < (n,j)` the slice `data[n][j]` will appear in the merged result. If you do not need this guarantee, ParallelDynamicStitch might perform better on some devices.
For example:
indices[0] = 6
indices[1] = [4, 1]
indices[2] = [[5, 2], [0, 3]]
data[0] = [61, 62]
data[1] = [[41, 42], [11, 12]]
data[2] = [[[51, 52], [21, 22]], [[1, 2], [31, 32]]]
merged = [[1, 2], [11, 12], [21, 22], [31, 32], [41, 42],
[51, 52], [61, 62]]
# Apply function (increments x_i) on elements for which a certain condition
# apply (x_i != -1 in this example).
x=tf.constant([0.1, -1., 5.2, 4.3, -1., 7.4])
condition_mask=tf.not_equal(x,tf.constant(-1.))
partitioned_data = tf.dynamic_partition(
x, tf.cast(condition_mask, tf.int32) , 2)
partitioned_data[1] = partitioned_data[1] + 1.0
condition_indices = tf.dynamic_partition(
tf.range(tf.shape(x)[0]), tf.cast(condition_mask, tf.int32) , 2)
x = tf.dynamic_stitch(condition_indices, partitioned_data)
# Here x=[1.1, -1., 6.2, 5.3, -1, 8.4], the -1. values remain
# unchanged.
Public Methods
| Output<T> |
asOutput()
Returns the symbolic handle of a tensor.
|
| static <T> DynamicStitch<T> | |
| Output<T> |
merged()
|
Inherited Methods
Public Methods
public Output<T> asOutput ()
Returns the symbolic handle of a tensor.
Inputs to TensorFlow operations are outputs of another TensorFlow operation. This method is used to obtain a symbolic handle that represents the computation of the input.
public static DynamicStitch<T> create (Scope scope, Iterable<Operand<Integer>> indices, Iterable<Operand<T>> data)
Factory method to create a class wrapping a new DynamicStitch operation.
Parameters
| scope | current scope |
|---|
Returns
- a new instance of DynamicStitch
