 TensorFlow.org で表示 TensorFlow.org で表示
|
 Google Colabで実行 Google Colabで実行
|
 GitHub でソースを表示 GitHub でソースを表示 |
 ノートブックをダウンロード ノートブックをダウンロード |
 TF Hub モデルを参照 TF Hub モデルを参照 |
この Colab では、文章の類似性タスクにユニバーサルセンテンスエンコーダー Lite を使用する方法を説明します。このモジュールは、ユニバーサルセンテンスエンコーダーによく似ていますが、入力文章に SentencePiece 処理を実行する必要があります。
ユニバーサルセンテンスエンコーダーでは、これまで各単語の埋め込みをルックアップしてきたのと同じくらい簡単に文章レベルの埋め込みを取得することができます。取得された文章埋め込みは、文章レベルでの意味の類似性を計算するためだけではなく、少ない教師ありトレーニングデータを使うことで、ダウンストリームの分類タスクのパフォーマンスを改善するために使用することができます。
はじめに
セットアップ
# Install seaborn for pretty visualizationspip3 install --quiet seaborn# Install SentencePiece package# SentencePiece package is needed for Universal Sentence Encoder Lite. We'll# use it for all the text processing and sentence feature ID lookup.pip3 install --quiet sentencepiece
from absl import logging
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import sentencepiece as spm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
import seaborn as sns
2024-01-11 18:29:08.165053: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9261] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-01-11 18:29:08.165097: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:607] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-01-11 18:29:08.166638: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1515] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/tensorflow/python/compat/v2_compat.py:108: disable_resource_variables (from tensorflow.python.ops.variable_scope) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: non-resource variables are not supported in the long term
TF-Hub からモジュールを読み込む
module = hub.Module("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder-lite/2")
input_placeholder = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None, None])
encodings = module(
inputs=dict(
values=input_placeholder.values,
indices=input_placeholder.indices,
dense_shape=input_placeholder.dense_shape))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
TF-Hub モジュールから SentencePiece モデルを読み込む
SentencePiece モデルは、モジュールのアセットに格納されています。プロセッサを初期化するには、このモデルが読み込まれている必要があります。
with tf.Session() as sess:
spm_path = sess.run(module(signature="spm_path"))
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(spm_path, mode="rb") as f:
sp.LoadFromSerializedProto(f.read())
print("SentencePiece model loaded at {}.".format(spm_path))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore SentencePiece model loaded at b'/tmpfs/tmp/tfhub_modules/539544f0a997d91c327c23285ea00c37588d92cc/assets/universal_encoder_8k_spm.model'.
def process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, sentences):
# An utility method that processes sentences with the sentence piece processor
# 'sp' and returns the results in tf.SparseTensor-similar format:
# (values, indices, dense_shape)
ids = [sp.EncodeAsIds(x) for x in sentences]
max_len = max(len(x) for x in ids)
dense_shape=(len(ids), max_len)
values=[item for sublist in ids for item in sublist]
indices=[[row,col] for row in range(len(ids)) for col in range(len(ids[row]))]
return (values, indices, dense_shape)
いくつかの例を使ってモジュールをテストする
# Compute a representation for each message, showing various lengths supported.
word = "Elephant"
sentence = "I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding."
paragraph = (
"Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. "
"There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer "
"the more 'diluted' the embedding will be.")
messages = [word, sentence, paragraph]
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, messages)
# Reduce logging output.
logging.set_verbosity(logging.ERROR)
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run([tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.tables_initializer()])
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
for i, message_embedding in enumerate(np.array(message_embeddings).tolist()):
print("Message: {}".format(messages[i]))
print("Embedding size: {}".format(len(message_embedding)))
message_embedding_snippet = ", ".join(
(str(x) for x in message_embedding[:3]))
print("Embedding: [{}, ...]\n".format(message_embedding_snippet))
Message: Elephant Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.05338747799396515, 0.053194381296634674, -0.052356019616127014, ...] Message: I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.03533294051885605, -0.04714978113770485, 0.012305602431297302, ...] Message: Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer the more 'diluted' the embedding will be. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [-0.004081614315509796, -0.08954868465662003, 0.037371955811977386, ...]
セマンティックテキストの類似性(STS)タスクの例
ユニバーサルセンテンスエンコーダーによって生成される埋め込みは、おおよそ正規化されています。2 つの文章の意味的類似性は、エンコーディングの内積として簡単に計算することができます。
def plot_similarity(labels, features, rotation):
corr = np.inner(features, features)
sns.set(font_scale=1.2)
g = sns.heatmap(
corr,
xticklabels=labels,
yticklabels=labels,
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
cmap="YlOrRd")
g.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=rotation)
g.set_title("Semantic Textual Similarity")
def run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages):
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp,messages)
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
plot_similarity(messages, message_embeddings, 90)
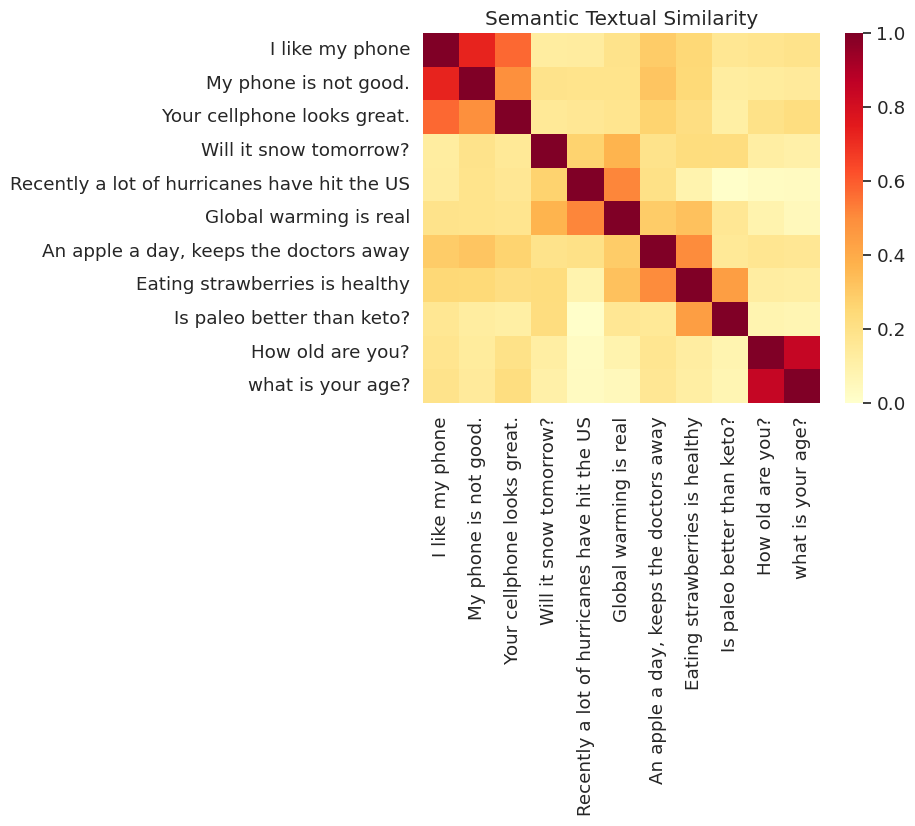
類似性の視覚化
ここでは、ヒートマップに類似性を表示します。最終的なグラフは 9x9 の行列で、各エントリ [i, j] は、文章 i と j のエンコーディングの内積に基づいて色付けされます。
messages = [
# Smartphones
"I like my phone",
"My phone is not good.",
"Your cellphone looks great.",
# Weather
"Will it snow tomorrow?",
"Recently a lot of hurricanes have hit the US",
"Global warming is real",
# Food and health
"An apple a day, keeps the doctors away",
"Eating strawberries is healthy",
"Is paleo better than keto?",
# Asking about age
"How old are you?",
"what is your age?",
]
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages)
評価: STS(セマンティックテキストの類似性)ベンチマーク
STS ベンチマークは、文章埋め込みを使って計算された類似性スコアが人の判定に適合する程度の本質的評価です。ベンチマークでは、システムは多様な文章ペアに対して類似性スコアを返す必要があります。その後で、ピアソン相関を使用して、人の判定に対して機械の類似性スコアの質が評価されます。
データのダウンロード
import pandas
import scipy
import math
def load_sts_dataset(filename):
# Loads a subset of the STS dataset into a DataFrame. In particular both
# sentences and their human rated similarity score.
sent_pairs = []
with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
for line in f:
ts = line.strip().split("\t")
# (sent_1, sent_2, similarity_score)
sent_pairs.append((ts[5], ts[6], float(ts[4])))
return pandas.DataFrame(sent_pairs, columns=["sent_1", "sent_2", "sim"])
def download_and_load_sts_data():
sts_dataset = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname="Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
origin="http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
extract=True)
sts_dev = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-dev.csv"))
sts_test = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-test.csv"))
return sts_dev, sts_test
sts_dev, sts_test = download_and_load_sts_data()
Downloading data from http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz 409630/409630 [==============================] - 1s 2us/step
評価グラフの構築
sts_input1 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
sts_input2 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
# For evaluation we use exactly normalized rather than
# approximately normalized.
sts_encode1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input1.values,
indices=sts_input1.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input1.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sts_encode2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input2.values,
indices=sts_input2.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input2.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sim_scores = -tf.acos(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(sts_encode1, sts_encode2), axis=1))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
文章埋め込みの評価
Choose dataset for benchmark
dataset = sts_dev
values1, indices1, dense_shape1 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_1'].tolist())
values2, indices2, dense_shape2 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_2'].tolist())
similarity_scores = dataset['sim'].tolist()
def run_sts_benchmark(session):
"""Returns the similarity scores"""
scores = session.run(
sim_scores,
feed_dict={
sts_input1.values: values1,
sts_input1.indices: indices1,
sts_input1.dense_shape: dense_shape1,
sts_input2.values: values2,
sts_input2.indices: indices2,
sts_input2.dense_shape: dense_shape2,
})
return scores
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
scores = run_sts_benchmark(session)
pearson_correlation = scipy.stats.pearsonr(scores, similarity_scores)
print('Pearson correlation coefficient = {0}\np-value = {1}'.format(
pearson_correlation[0], pearson_correlation[1]))
Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.7856484786672012 p-value = 1.0658233773e-314
