 عرض على TensorFlow.org عرض على TensorFlow.org |  تشغيل في Google Colab تشغيل في Google Colab |  عرض على جيثب عرض على جيثب |  تحميل دفتر تحميل دفتر |  انظر نموذج TF Hub انظر نموذج TF Hub |
يوضح Colab استخدام وحدة TF Hub على أساس شبكة الخصومة التوليدية (GAN). تعين الوحدة النمطية من متجهات الأبعاد N ، والتي تسمى الفضاء الكامن ، إلى صور RGB.
يتم توفير مثالين:
- رسم من الفضاء الكامنة إلى صور، و
- إعطاء صورة الهدف، وذلك باستخدام التدرج النسب لإيجاد ناقلات الكامنة التي تولد صورة مماثلة لصورة الهدف.
المتطلبات الأساسية الاختيارية
- الإلمام بالمفاهيم Tensorflow مستوى منخفض .
- توليدي شبكة الخصومة على ويكيبيديا.
- ورقة على GANS التقدمي: التقدمي زراعة GANS لتحسين الجودة والاستقرار، والتباين .
المزيد من النماذج
هنا يمكنك أن تجد كل النماذج استضافت حاليا على tfhub.dev التي يمكن أن تولد الصور.
يثبت
# Install imageio for creating animations.pip -q install imageiopip -q install scikit-imagepip install git+https://github.com/tensorflow/docs
الواردات وتعريفات الوظائف
from absl import logging
import imageio
import PIL.Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(0)
import tensorflow_hub as hub
from tensorflow_docs.vis import embed
import time
try:
from google.colab import files
except ImportError:
pass
from IPython import display
from skimage import transform
# We could retrieve this value from module.get_input_shapes() if we didn't know
# beforehand which module we will be using.
latent_dim = 512
# Interpolates between two vectors that are non-zero and don't both lie on a
# line going through origin. First normalizes v2 to have the same norm as v1.
# Then interpolates between the two vectors on the hypersphere.
def interpolate_hypersphere(v1, v2, num_steps):
v1_norm = tf.norm(v1)
v2_norm = tf.norm(v2)
v2_normalized = v2 * (v1_norm / v2_norm)
vectors = []
for step in range(num_steps):
interpolated = v1 + (v2_normalized - v1) * step / (num_steps - 1)
interpolated_norm = tf.norm(interpolated)
interpolated_normalized = interpolated * (v1_norm / interpolated_norm)
vectors.append(interpolated_normalized)
return tf.stack(vectors)
# Simple way to display an image.
def display_image(image):
image = tf.constant(image)
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, tf.uint8)
return PIL.Image.fromarray(image.numpy())
# Given a set of images, show an animation.
def animate(images):
images = np.array(images)
converted_images = np.clip(images * 255, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
imageio.mimsave('./animation.gif', converted_images)
return embed.embed_file('./animation.gif')
logging.set_verbosity(logging.ERROR)
الاستيفاء الفضاء الكامن
نواقل عشوائية
الاستيفاء الفراغي الكامن بين متجهين مهيئين عشوائياً. سوف نستخدم وحدة TF محور progan-128 التي تحتوي على التقدمي GAN المدربين قبل.
progan = hub.load("https://tfhub.dev/google/progan-128/1").signatures['default']
def interpolate_between_vectors():
v1 = tf.random.normal([latent_dim])
v2 = tf.random.normal([latent_dim])
# Creates a tensor with 25 steps of interpolation between v1 and v2.
vectors = interpolate_hypersphere(v1, v2, 50)
# Uses module to generate images from the latent space.
interpolated_images = progan(vectors)['default']
return interpolated_images
interpolated_images = interpolate_between_vectors()
animate(interpolated_images)

العثور على أقرب متجه في الفضاء الكامن
إصلاح صورة الهدف. كمثال ، استخدم صورة تم إنشاؤها من الوحدة أو قم بتحميل الصورة الخاصة بك.
image_from_module_space = True # @param { isTemplate:true, type:"boolean" }
def get_module_space_image():
vector = tf.random.normal([1, latent_dim])
images = progan(vector)['default'][0]
return images
def upload_image():
uploaded = files.upload()
image = imageio.imread(uploaded[list(uploaded.keys())[0]])
return transform.resize(image, [128, 128])
if image_from_module_space:
target_image = get_module_space_image()
else:
target_image = upload_image()
display_image(target_image)

بعد تحديد دالة الخسارة بين الصورة الهدف والصورة التي تم إنشاؤها بواسطة متغير مساحة كامنة ، يمكننا استخدام نزول التدرج للعثور على قيم متغيرة تقلل من الخسارة.
tf.random.set_seed(42)
initial_vector = tf.random.normal([1, latent_dim])
display_image(progan(initial_vector)['default'][0])

def find_closest_latent_vector(initial_vector, num_optimization_steps,
steps_per_image):
images = []
losses = []
vector = tf.Variable(initial_vector)
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.01)
loss_fn = tf.losses.MeanAbsoluteError(reduction="sum")
for step in range(num_optimization_steps):
if (step % 100)==0:
print()
print('.', end='')
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
image = progan(vector.read_value())['default'][0]
if (step % steps_per_image) == 0:
images.append(image.numpy())
target_image_difference = loss_fn(image, target_image[:,:,:3])
# The latent vectors were sampled from a normal distribution. We can get
# more realistic images if we regularize the length of the latent vector to
# the average length of vector from this distribution.
regularizer = tf.abs(tf.norm(vector) - np.sqrt(latent_dim))
loss = target_image_difference + regularizer
losses.append(loss.numpy())
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [vector])
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, [vector]))
return images, losses
num_optimization_steps=200
steps_per_image=5
images, loss = find_closest_latent_vector(initial_vector, num_optimization_steps, steps_per_image)
.................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................
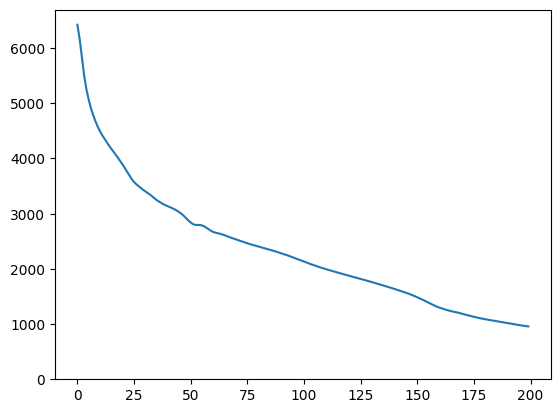
plt.plot(loss)
plt.ylim([0,max(plt.ylim())])
(0.0, 6696.301751708985)
animate(np.stack(images))

قارن النتيجة بالهدف:
display_image(np.concatenate([images[-1], target_image], axis=1))

اللعب مع المثال أعلاه
إذا كانت الصورة من مساحة الوحدة النمطية ، فسيكون الانحدار سريعًا ويتقارب إلى عينة معقولة. جرب تنازلي إلى صورة ليست من الفضاء حدة. لن يتقارب الهبوط إلا إذا كانت الصورة قريبة بشكل معقول من مساحة صور التدريب.
كيف تجعله ينزل بشكل أسرع وإلى صورة أكثر واقعية؟ يمكن للمرء أن يحاول:
- باستخدام خسارة مختلفة في اختلاف الصورة ، على سبيل المثال تربيعي ،
- باستخدام منظم مختلف على المتجه الكامن ،
- التهيئة من متجه عشوائي في دورات متعددة ،
- إلخ.
