 TensorFlow.org এ দেখুন TensorFlow.org এ দেখুন |  Google Colab-এ চালান Google Colab-এ চালান |  GitHub-এ উৎস দেখুন GitHub-এ উৎস দেখুন |  নোটবুক ডাউনলোড করুন নোটবুক ডাউনলোড করুন |
ওভারভিউ
TfL premade মোট ফাংশন মডেল দ্রুত এবং সহজ উপায়ে TfL গড়ে তুলতে হয় tf.keras.model জটিল অ্যাগ্রিগেশন ফাংশন শেখার জন্যে দৃষ্টান্ত। এই নির্দেশিকাটি একটি TFL প্রিমেড এগ্রিগেট ফাংশন মডেল তৈরি করতে এবং এটিকে প্রশিক্ষণ/পরীক্ষা করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় পদক্ষেপগুলির রূপরেখা দেয়।
সেটআপ
টিএফ ল্যাটিস প্যাকেজ ইনস্টল করা হচ্ছে:
pip install -q tensorflow-lattice pydot
প্রয়োজনীয় প্যাকেজ আমদানি করা হচ্ছে:
import tensorflow as tf
import collections
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
পাজলস ডেটাসেট ডাউনলোড করা হচ্ছে:
train_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/train.csv')
train_dataframe.head()
test_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/test.csv')
test_dataframe.head()
বৈশিষ্ট্য এবং লেবেল নিষ্কাশন এবং রূপান্তর
# Features:
# - star_rating rating out of 5 stars (1-5)
# - word_count number of words in the review
# - is_amazon 1 = reviewed on amazon; 0 = reviewed on artifact website
# - includes_photo if the review includes a photo of the puzzle
# - num_helpful number of people that found this review helpful
# - num_reviews total number of reviews for this puzzle (we construct)
#
# This ordering of feature names will be the exact same order that we construct
# our model to expect.
feature_names = [
'star_rating', 'word_count', 'is_amazon', 'includes_photo', 'num_helpful',
'num_reviews'
]
def extract_features(dataframe, label_name):
# First we extract flattened features.
flattened_features = {
feature_name: dataframe[feature_name].values.astype(float)
for feature_name in feature_names[:-1]
}
# Construct mapping from puzzle name to feature.
star_rating = collections.defaultdict(list)
word_count = collections.defaultdict(list)
is_amazon = collections.defaultdict(list)
includes_photo = collections.defaultdict(list)
num_helpful = collections.defaultdict(list)
labels = {}
# Extract each review.
for i in range(len(dataframe)):
row = dataframe.iloc[i]
puzzle_name = row['puzzle_name']
star_rating[puzzle_name].append(float(row['star_rating']))
word_count[puzzle_name].append(float(row['word_count']))
is_amazon[puzzle_name].append(float(row['is_amazon']))
includes_photo[puzzle_name].append(float(row['includes_photo']))
num_helpful[puzzle_name].append(float(row['num_helpful']))
labels[puzzle_name] = float(row[label_name])
# Organize data into list of list of features.
names = list(star_rating.keys())
star_rating = [star_rating[name] for name in names]
word_count = [word_count[name] for name in names]
is_amazon = [is_amazon[name] for name in names]
includes_photo = [includes_photo[name] for name in names]
num_helpful = [num_helpful[name] for name in names]
num_reviews = [[len(ratings)] * len(ratings) for ratings in star_rating]
labels = [labels[name] for name in names]
# Flatten num_reviews
flattened_features['num_reviews'] = [len(reviews) for reviews in num_reviews]
# Convert data into ragged tensors.
star_rating = tf.ragged.constant(star_rating)
word_count = tf.ragged.constant(word_count)
is_amazon = tf.ragged.constant(is_amazon)
includes_photo = tf.ragged.constant(includes_photo)
num_helpful = tf.ragged.constant(num_helpful)
num_reviews = tf.ragged.constant(num_reviews)
labels = tf.constant(labels)
# Now we can return our extracted data.
return (star_rating, word_count, is_amazon, includes_photo, num_helpful,
num_reviews), labels, flattened_features
train_xs, train_ys, flattened_features = extract_features(train_dataframe, 'Sales12-18MonthsAgo')
test_xs, test_ys, _ = extract_features(test_dataframe, 'SalesLastSixMonths')
# Let's define our label minimum and maximum.
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
এই নির্দেশিকায় প্রশিক্ষণের জন্য ব্যবহৃত ডিফল্ট মান সেট করা:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
MIDDLE_DIM = 3
MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE = 2
MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS = 16
OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS = 8
বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগার
বৈশিষ্ট্য ক্রমাঙ্কন এবং প্রতি-বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগারেশনের ব্যবহার নির্ধারণ করা হয় tfl.configs.FeatureConfig । বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগারেশনের monotonicity সীমাবদ্ধতা, প্রতি-বৈশিষ্ট্য নিয়মিতকরণ (দেখুন অন্তর্ভুক্ত tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig ), এবং জাফরি মডেলের জন্য জাফরি মাপ।
মনে রাখবেন যে আমরা আমাদের মডেল চিনতে চাই এমন যে কোনও বৈশিষ্ট্যের জন্য আমাদের অবশ্যই বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগার সম্পূর্ণরূপে নির্দিষ্ট করতে হবে। অন্যথায় মডেলটির জানার কোন উপায় থাকবে না যে এই ধরনের একটি বৈশিষ্ট্য বিদ্যমান। একত্রীকরণ মডেলের জন্য, এই বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে বিবেচনা করা হবে এবং সঠিকভাবে র্যাগড হিসাবে পরিচালনা করা হবে।
কোয়ান্টাইল গণনা করুন
যদিও জন্য ডিফল্ট সেটিং pwl_calibration_input_keypoints মধ্যে tfl.configs.FeatureConfig 'quantiles', premade মডেলের জন্য আমরা ম্যানুয়ালি ইনপুট keypoints সংজ্ঞায়িত করতে হবে। এটি করার জন্য, আমরা প্রথমে কোয়ান্টাইল গণনার জন্য আমাদের নিজস্ব সহায়ক ফাংশন সংজ্ঞায়িত করি।
def compute_quantiles(features,
num_keypoints=10,
clip_min=None,
clip_max=None,
missing_value=None):
# Clip min and max if desired.
if clip_min is not None:
features = np.maximum(features, clip_min)
features = np.append(features, clip_min)
if clip_max is not None:
features = np.minimum(features, clip_max)
features = np.append(features, clip_max)
# Make features unique.
unique_features = np.unique(features)
# Remove missing values if specified.
if missing_value is not None:
unique_features = np.delete(unique_features,
np.where(unique_features == missing_value))
# Compute and return quantiles over unique non-missing feature values.
return np.quantile(
unique_features,
np.linspace(0., 1., num=num_keypoints),
interpolation='nearest').astype(float)
আমাদের বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগার সংজ্ঞায়িত করা
এখন যেহেতু আমরা আমাদের কোয়ান্টাইলগুলি গণনা করতে পারি, আমরা প্রতিটি বৈশিষ্ট্যের জন্য একটি বৈশিষ্ট্য কনফিগার সংজ্ঞায়িত করি যা আমরা আমাদের মডেলটিকে ইনপুট হিসাবে নিতে চাই।
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='star_rating',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['star_rating'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='word_count',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['word_count'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='is_amazon',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='includes_photo',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_helpful',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_helpful'], num_keypoints=5),
# Larger num_helpful indicating more trust in star_rating.
reflects_trust_in=[
tfl.configs.TrustConfig(
feature_name="star_rating", trust_type="trapezoid"),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_reviews',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_reviews'], num_keypoints=5),
)
]
সামগ্রিক ফাংশন মডেল
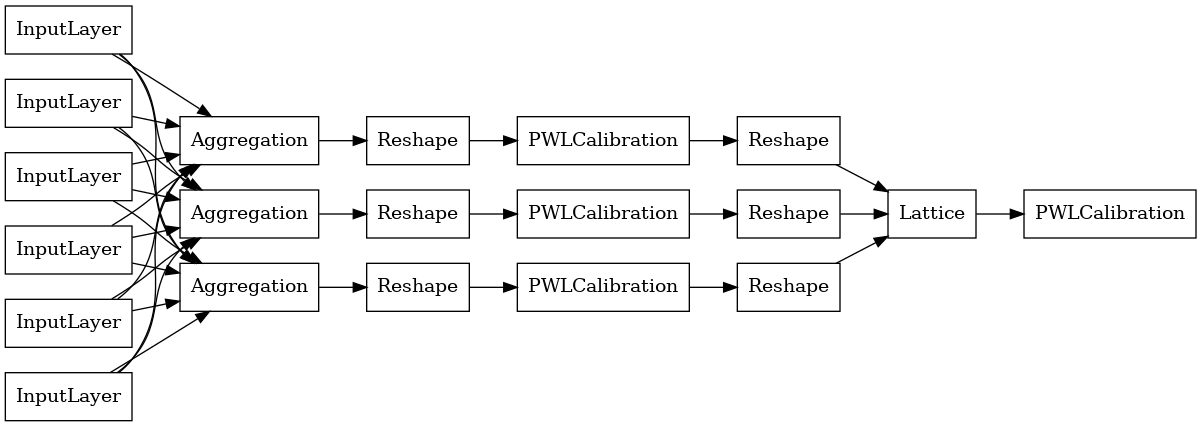
একটি TfL premade প্রতিরূপ গঠন করে, প্রথম থেকে একটি মডেল কনফিগারেশন গঠন করা tfl.configs । একটি সমষ্টিগত ফাংশন মডেল ব্যবহার করে নির্মিত হয় tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig । এটি টুকরো টুকরো-রৈখিক এবং শ্রেণীবদ্ধ ক্রমাঙ্কন প্রযোজ্য, তারপরে র্যাগড ইনপুটের প্রতিটি মাত্রায় একটি জালি মডেল অনুসরণ করে। তারপরে এটি প্রতিটি মাত্রার জন্য আউটপুটের উপর একটি সমষ্টি স্তর প্রয়োগ করে। এটি তারপর একটি ঐচ্ছিক আউটপুট পিসওয়াইজ-লিনিয়ার ক্রমাঙ্কন দ্বারা অনুসরণ করা হয়।
# Model config defines the model structure for the aggregate function model.
aggregate_function_model_config = tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
middle_dimension=MIDDLE_DIM,
middle_lattice_size=MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE,
middle_calibration=True,
middle_calibration_num_keypoints=MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS,
middle_monotonicity='increasing',
output_min=min_label,
output_max=max_label,
output_calibration=True,
output_calibration_num_keypoints=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS,
output_initialization=np.linspace(
min_label, max_label, num=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS))
# An AggregateFunction premade model constructed from the given model config.
aggregate_function_model = tfl.premade.AggregateFunction(
aggregate_function_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregate_function_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
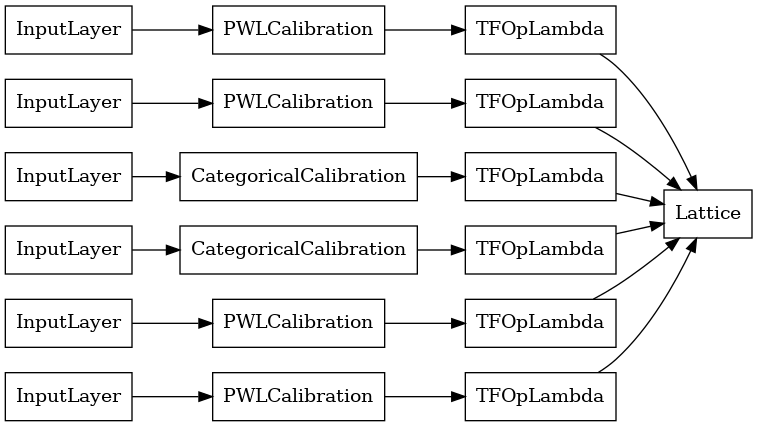
প্রতিটি অ্যাগ্রিগেশন লেয়ারের আউটপুট হল রাগ করা ইনপুটগুলির উপর একটি ক্যালিব্রেটেড জালির গড় আউটপুট। এখানে প্রথম একত্রিতকরণ স্তরের ভিতরে ব্যবহৃত মডেলটি রয়েছে:
aggregation_layers = [
layer for layer in aggregate_function_model.layers
if isinstance(layer, tfl.layers.Aggregation)
]
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregation_layers[0].model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
এখন, অন্য কোন মত tf.keras.Model , আমরা এবং কম্পাইল আমাদের তথ্য মডেল মাপসই করা হবে।
aggregate_function_model.compile(
loss='mae',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
aggregate_function_model.fit(
train_xs, train_ys, epochs=NUM_EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, verbose=False)
<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fee7d3033c8>
আমাদের মডেল প্রশিক্ষণের পর, আমরা আমাদের পরীক্ষার সেটে এটি মূল্যায়ন করতে পারি।
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(aggregate_function_model.evaluate(test_xs, test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 7/7 [==============================] - 2s 3ms/step - loss: 53.4633 53.4632682800293
