 הצג באתר TensorFlow.org הצג באתר TensorFlow.org |  הפעל בגוגל קולאב הפעל בגוגל קולאב |  צפה במקור ב-GitHub צפה במקור ב-GitHub |  הורד מחברת הורד מחברת |
סקירה כללית
מודלי Premade דרכים קלות ומהירות לבנות TFL tf.keras.model מקרים למקרים של שימוש טיפוסיים. מדריך זה מתאר את השלבים הדרושים לבניית דגם TFL Premade ולהכשיר/לבדוק אותו.
להכין
התקנת חבילת TF Lattice:
pip install tensorflow-lattice pydot
ייבוא חבילות נדרשות:
import tensorflow as tf
import copy
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
הגדרת ערכי ברירת המחדל המשמשים לאימון במדריך זה:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
PREFITTING_NUM_EPOCHS = 10
הורדת מערך הנתונים של UCI Statlog (לב):
heart_csv_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'heart.csv',
'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv')
heart_df = pd.read_csv(heart_csv_file)
thal_vocab_list = ['normal', 'fixed', 'reversible']
heart_df['thal'] = heart_df['thal'].map(
{v: i for i, v in enumerate(thal_vocab_list)})
heart_df = heart_df.astype(float)
heart_train_size = int(len(heart_df) * 0.8)
heart_train_dict = dict(heart_df[:heart_train_size])
heart_test_dict = dict(heart_df[heart_train_size:])
# This ordering of input features should match the feature configs. If no
# feature config relies explicitly on the data (i.e. all are 'quantiles'),
# then you can construct the feature_names list by simply iterating over each
# feature config and extracting it's name.
feature_names = [
'age', 'sex', 'cp', 'chol', 'fbs', 'trestbps', 'thalach', 'restecg',
'exang', 'oldpeak', 'slope', 'ca', 'thal'
]
# Since we have some features that manually construct their input keypoints,
# we need an index mapping of the feature names.
feature_name_indices = {name: index for index, name in enumerate(feature_names)}
label_name = 'target'
heart_train_xs = [
heart_train_dict[feature_name] for feature_name in feature_names
]
heart_test_xs = [heart_test_dict[feature_name] for feature_name in feature_names]
heart_train_ys = heart_train_dict[label_name]
heart_test_ys = heart_test_dict[label_name]
Downloading data from http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv 16384/13273 [=====================================] - 0s 0us/step 24576/13273 [=======================================================] - 0s 0us/step
תצורות תכונה
כיול Feature ותצורות לכל תכונה נקבעים באמצעות tfl.configs.FeatureConfig . תצורות Feature כוללות מגבלות מונוטוניות, לכול תכונת הסדרה (ראה tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig ), וגדל סריג עבור דגמי סריג.
שים לב שעלינו לציין באופן מלא את תצורת התכונה עבור כל תכונה שאנו רוצים שהמודל שלנו יזהה. אחרת לא תהיה למודל שום דרך לדעת שקיימת תכונה כזו.
הגדרת תצורות התכונות שלנו
כעת, כשנוכל לחשב את הקוונטילים שלנו, אנו מגדירים תצורת תכונה עבור כל תכונה שאנו רוצים שהמודל שלנו ייקח כקלט.
# Features:
# - age
# - sex
# - cp chest pain type (4 values)
# - trestbps resting blood pressure
# - chol serum cholestoral in mg/dl
# - fbs fasting blood sugar > 120 mg/dl
# - restecg resting electrocardiographic results (values 0,1,2)
# - thalach maximum heart rate achieved
# - exang exercise induced angina
# - oldpeak ST depression induced by exercise relative to rest
# - slope the slope of the peak exercise ST segment
# - ca number of major vessels (0-3) colored by flourosopy
# - thal normal; fixed defect; reversable defect
#
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
heart_feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='age',
lattice_size=3,
monotonicity='increasing',
# We must set the keypoints manually.
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='quantiles',
pwl_calibration_clip_max=100,
# Per feature regularization.
regularizer_configs=[
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_wrinkle', l2=0.1),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='sex',
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='cp',
monotonicity='increasing',
# Keypoints that are uniformly spaced.
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=4,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=np.linspace(
np.min(heart_train_xs[feature_name_indices['cp']]),
np.max(heart_train_xs[feature_name_indices['cp']]),
num=4),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='chol',
monotonicity='increasing',
# Explicit input keypoints initialization.
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=[126.0, 210.0, 247.0, 286.0, 564.0],
# Calibration can be forced to span the full output range by clamping.
pwl_calibration_clamp_min=True,
pwl_calibration_clamp_max=True,
# Per feature regularization.
regularizer_configs=[
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_hessian', l2=1e-4),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='fbs',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1)
monotonicity=[(0, 1)],
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='trestbps',
monotonicity='decreasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='quantiles',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='thalach',
monotonicity='decreasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='quantiles',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='restecg',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1), output(0) <= output(2)
monotonicity=[(0, 1), (0, 2)],
num_buckets=3,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='exang',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1)
monotonicity=[(0, 1)],
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='oldpeak',
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='quantiles',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='slope',
# Partial monotonicity: output(0) <= output(1), output(1) <= output(2)
monotonicity=[(0, 1), (1, 2)],
num_buckets=3,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='ca',
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=4,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints='quantiles',
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='thal',
# Partial monotonicity:
# output(normal) <= output(fixed)
# output(normal) <= output(reversible)
monotonicity=[('normal', 'fixed'), ('normal', 'reversible')],
num_buckets=3,
# We must specify the vocabulary list in order to later set the
# monotonicities since we used names and not indices.
vocabulary_list=thal_vocab_list,
),
]
הגדר מונוטוניות ונקודות מפתח
לאחר מכן עלינו לוודא להגדיר כראוי את המונוטוניות עבור תכונות שבהן השתמשנו באוצר מילים מותאם אישית (כגון 'תאל' למעלה).
tfl.premade_lib.set_categorical_monotonicities(heart_feature_configs)
לבסוף נוכל להשלים את הגדרות התכונה שלנו על ידי חישוב והגדרת נקודות המפתח.
feature_keypoints = tfl.premade_lib.compute_feature_keypoints(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs, features=heart_train_dict)
tfl.premade_lib.set_feature_keypoints(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs,
feature_keypoints=feature_keypoints,
add_missing_feature_configs=False)
מודל ליניארי מכויל
כדי לבנות מודל premade TFL, ראשון לבנות תצורת מודל מ tfl.configs . מודל ליניארי מכויל בנוי באמצעות tfl.configs.CalibratedLinearConfig . הוא מחיל כיול חלקי-ליניארי וקטגורי על תכונות הקלט, ואחריו שילוב ליניארי וכיול פלט אופציונלי חלקי-ליניארי. בעת שימוש בכיול פלט או כאשר מוגדרים גבולות פלט, השכבה הליניארית תחיל ממוצע משוקלל על תשומות מכוילות.
דוגמה זו יוצרת מודל ליניארי מכויל על 5 התכונות הראשונות.
# Model config defines the model structure for the premade model.
linear_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLinearConfig(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs[:5],
use_bias=True,
output_calibration=True,
output_calibration_num_keypoints=10,
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=np.linspace(-2.0, 2.0, num=10),
regularizer_configs=[
# Regularizer for the output calibrator.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='output_calib_hessian', l2=1e-4),
])
# A CalibratedLinear premade model constructed from the given model config.
linear_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLinear(linear_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(linear_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
2022-01-14 12:36:31.295751: E tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:271] failed call to cuInit: CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected
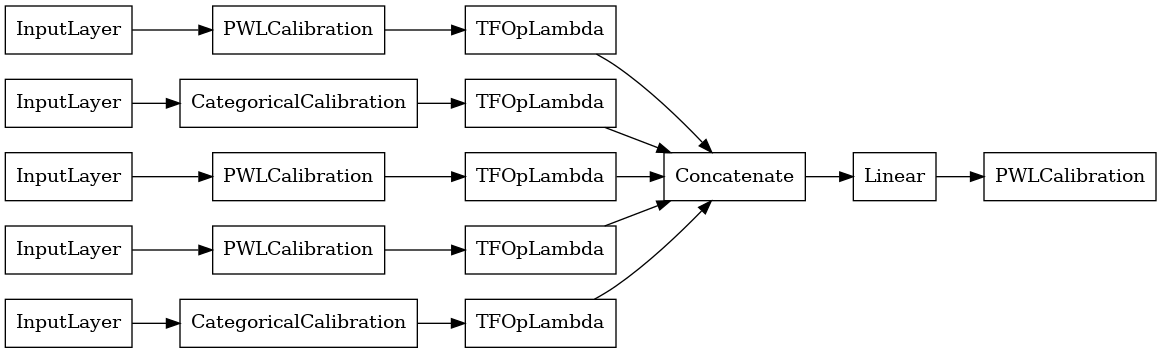
עכשיו, כמו כל האחרים tf.keras.Model , אנחנו לקמפל להתאים את המודל לנתונים שלנו.
linear_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
linear_model.fit(
heart_train_xs[:5],
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fe4385f0290>
לאחר אימון המודל שלנו, נוכל להעריך אותו במערך המבחנים שלנו.
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(linear_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs[:5], heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4728 - auc: 0.8252 [0.47278329730033875, 0.8251879215240479]
דגם סריג מכויל
מודל סריג מכויל נבנה באמצעות tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeConfig . מודל סריג מכויל מיישם כיול חלקי-ליניארי וקטגורי על תכונות הקלט, ואחריו מודל סריג וכיול פלט אופציונלי חלקי-ליניארי.
דוגמה זו יוצרת מודל סריג מכויל על 5 התכונות הראשונות.
# This is a calibrated lattice model: inputs are calibrated, then combined
# non-linearly using a lattice layer.
lattice_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeConfig(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs[:5],
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=[-2.0, 2.0],
regularizer_configs=[
# Torsion regularizer applied to the lattice to make it more linear.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='torsion', l2=1e-2),
# Globally defined calibration regularizer is applied to all features.
tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig(name='calib_hessian', l2=1e-2),
])
# A CalibratedLattice premade model constructed from the given model config.
lattice_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLattice(lattice_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(lattice_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
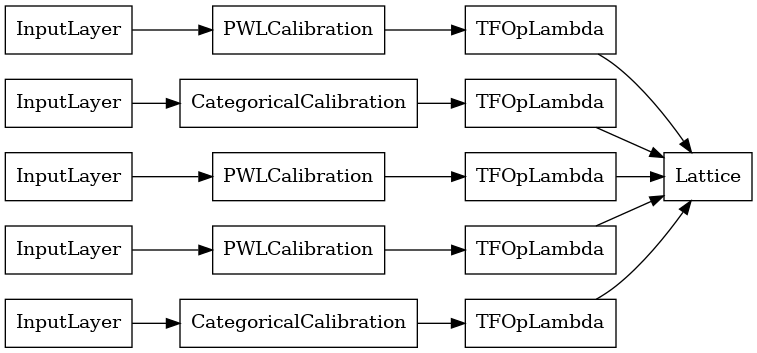
כמו בעבר, אנו מרכיבים, מתאימים ומעריכים את המודל שלנו.
lattice_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
lattice_model.fit(
heart_train_xs[:5],
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(lattice_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs[:5], heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 1s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4709 - auc_1: 0.8302 [0.4709009826183319, 0.8302004933357239]
דגם אנסמבל סריג מכויל
כאשר מספר התכונות גדול, אתה יכול להשתמש במודל אנסמבל, שיוצר מספר סריג קטן יותר עבור תת-קבוצות של התכונות וממוצע את הפלט שלהן במקום ליצור רק סריג ענק אחד. מודלי סריג אנסמבל בנוי באמצעות tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig . מודל אנסמבל סריג מכויל מחיל כיול חלקי-ליניארי וקטגורי על תכונת הקלט, ואחריו מכלול של דגמי סריג וכיול פלט אופציונלי חלקי-ליניארי.
אתחול אנסמבל סריג מפורש
אם אתה כבר יודע אילו קבוצות משנה של תכונות אתה רוצה להזין לתוך הסריג שלך, אז אתה יכול להגדיר במפורש את הסריג באמצעות שמות תכונות. דוגמה זו יוצרת דגם אנסמבל סריג מכויל עם 5 סריג ו-3 תכונות לכל סריג.
# This is a calibrated lattice ensemble model: inputs are calibrated, then
# combined non-linearly and averaged using multiple lattice layers.
explicit_ensemble_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs,
lattices=[['trestbps', 'chol', 'ca'], ['fbs', 'restecg', 'thal'],
['fbs', 'cp', 'oldpeak'], ['exang', 'slope', 'thalach'],
['restecg', 'age', 'sex']],
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3,
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=[-2.0, 2.0])
# A CalibratedLatticeEnsemble premade model constructed from the given
# model config.
explicit_ensemble_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLatticeEnsemble(
explicit_ensemble_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
explicit_ensemble_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
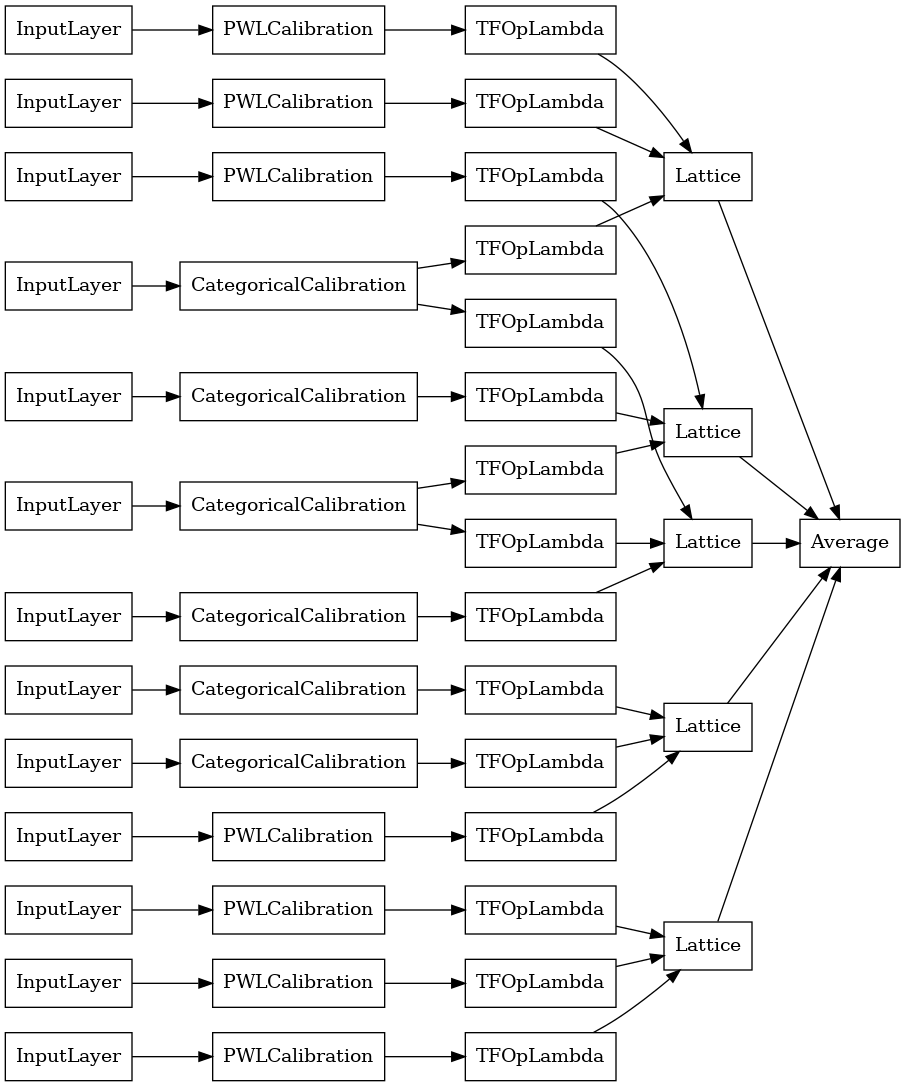
כמו בעבר, אנו מרכיבים, מתאימים ומעריכים את המודל שלנו.
explicit_ensemble_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
explicit_ensemble_model.fit(
heart_train_xs,
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(explicit_ensemble_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs, heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3768 - auc_2: 0.8954 [0.3768467903137207, 0.895363450050354]
אנסמבל סריג אקראי
אם אינך בטוח אילו קבוצות משנה של תכונות להזין לתוך הסריג שלך, אפשרות נוספת היא להשתמש בקבוצות משנה אקראיות של תכונות עבור כל סריג. דוגמה זו יוצרת דגם אנסמבל סריג מכויל עם 5 סריג ו-3 תכונות לכל סריג.
# This is a calibrated lattice ensemble model: inputs are calibrated, then
# combined non-linearly and averaged using multiple lattice layers.
random_ensemble_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs,
lattices='random',
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3,
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=[-2.0, 2.0],
random_seed=42)
# Now we must set the random lattice structure and construct the model.
tfl.premade_lib.set_random_lattice_ensemble(random_ensemble_model_config)
# A CalibratedLatticeEnsemble premade model constructed from the given
# model config.
random_ensemble_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLatticeEnsemble(
random_ensemble_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
random_ensemble_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
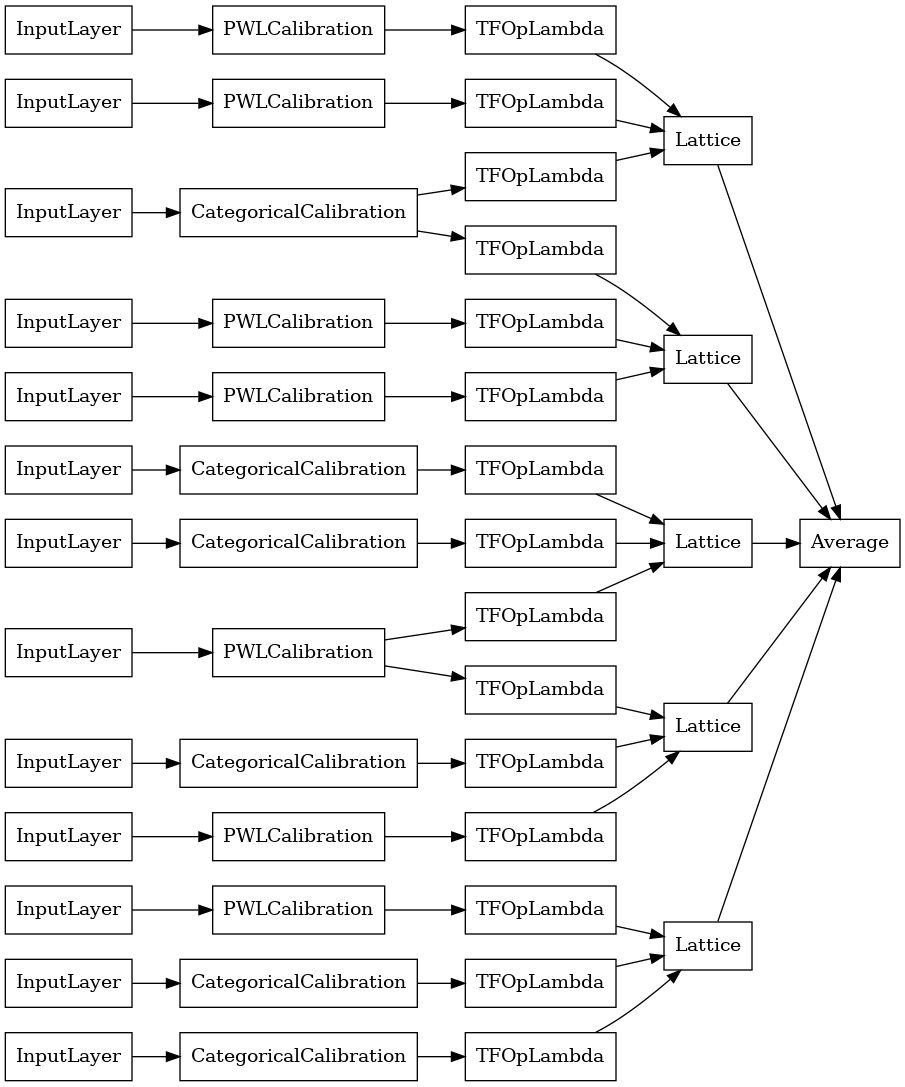
כמו בעבר, אנו מרכיבים, מתאימים ומעריכים את המודל שלנו.
random_ensemble_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
random_ensemble_model.fit(
heart_train_xs,
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(random_ensemble_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs, heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3739 - auc_3: 0.8997 [0.3739270567893982, 0.8997493982315063]
אנסמבל סריג אקראי של RTL Layer
בעת שימוש אקראי סריג אנסמבל, ניתן לציין כי המודל להשתמש יחיד tfl.layers.RTL השכבה. נציין כי tfl.layers.RTL תומך רק אילוצים מונוטוניות ואת חייבת להיות באותו גודל סריג עבור כל התכונות לא הסדרת שידורי תכונה. שים לב ששימוש tfl.layers.RTL שכבה מאפשר לך סולם כדי רכבים הרבה יותר גדולים מאשר שימוש נפרד tfl.layers.Lattice מקרים.
דוגמה זו יוצרת דגם אנסמבל סריג מכויל עם 5 סריג ו-3 תכונות לכל סריג.
# Make sure our feature configs have the same lattice size, no per-feature
# regularization, and only monotonicity constraints.
rtl_layer_feature_configs = copy.deepcopy(heart_feature_configs)
for feature_config in rtl_layer_feature_configs:
feature_config.lattice_size = 2
feature_config.unimodality = 'none'
feature_config.reflects_trust_in = None
feature_config.dominates = None
feature_config.regularizer_configs = None
# This is a calibrated lattice ensemble model: inputs are calibrated, then
# combined non-linearly and averaged using multiple lattice layers.
rtl_layer_ensemble_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=rtl_layer_feature_configs,
lattices='rtl_layer',
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3,
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=[-2.0, 2.0],
random_seed=42)
# A CalibratedLatticeEnsemble premade model constructed from the given
# model config. Note that we do not have to specify the lattices by calling
# a helper function (like before with random) because the RTL Layer will take
# care of that for us.
rtl_layer_ensemble_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLatticeEnsemble(
rtl_layer_ensemble_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
rtl_layer_ensemble_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
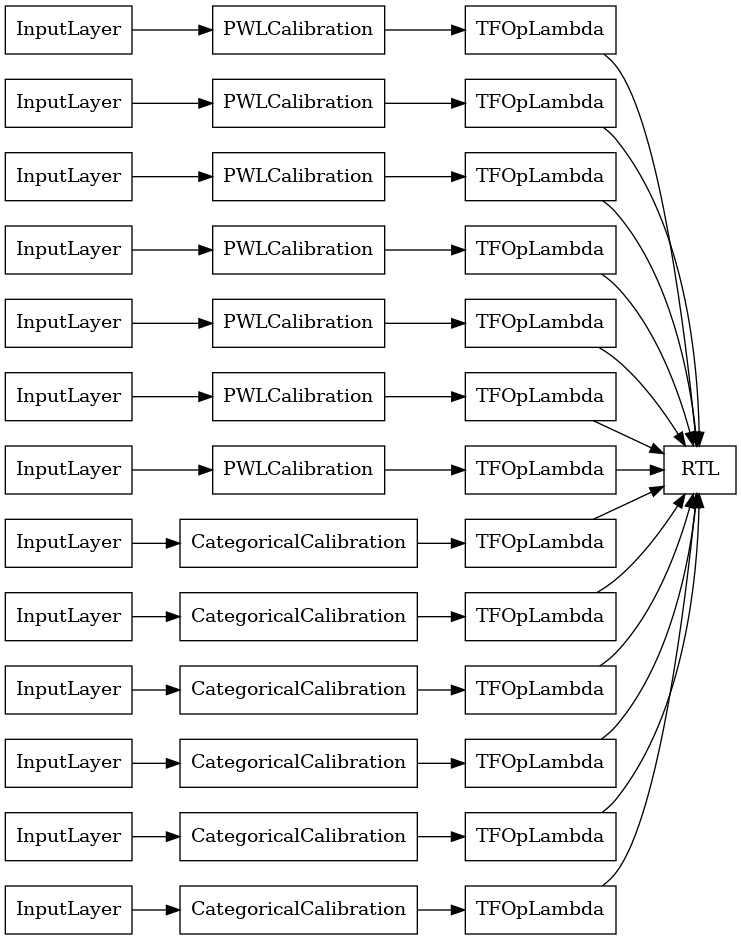
כמו בעבר, אנו מרכיבים, מתאימים ומעריכים את המודל שלנו.
rtl_layer_ensemble_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
rtl_layer_ensemble_model.fit(
heart_train_xs,
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(rtl_layer_ensemble_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs, heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3614 - auc_4: 0.9079 [0.36142951250076294, 0.9078947305679321]
אנסמבל סריג קריסטלים
Premade מספק גם אלגוריתם הסדר תכונה היוריסטית, שנקרא קריסטלים . כדי להשתמש באלגוריתם הקריסטלים, תחילה אנו מאמנים מודל התאמה מראש המאומד אינטראקציות בין תכונות בזוגיות. לאחר מכן אנו מסדרים את האנסמבל הסופי כך שתכונות עם יותר אינטראקציות לא ליניאריות נמצאות באותם סריג.
הספרייה Premade מציעה פונקציות מסייעות לבניית תצורת הדגם המוקדם וחילוץ מבנה הגבישים. שימו לב שדגם ההתאמה המוקדם אינו צריך להיות מאומן במלואו, כך שמספר עידנים אמור להספיק.
דוגמה זו יוצרת דגם אנסמבל סריג מכויל עם 5 סריג ו-3 תכונות לכל סריג.
# This is a calibrated lattice ensemble model: inputs are calibrated, then
# combines non-linearly and averaged using multiple lattice layers.
crystals_ensemble_model_config = tfl.configs.CalibratedLatticeEnsembleConfig(
feature_configs=heart_feature_configs,
lattices='crystals',
num_lattices=5,
lattice_rank=3,
# We initialize the output to [-2.0, 2.0] since we'll be using logits.
output_initialization=[-2.0, 2.0],
random_seed=42)
# Now that we have our model config, we can construct a prefitting model config.
prefitting_model_config = tfl.premade_lib.construct_prefitting_model_config(
crystals_ensemble_model_config)
# A CalibratedLatticeEnsemble premade model constructed from the given
# prefitting model config.
prefitting_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLatticeEnsemble(
prefitting_model_config)
# We can compile and train our prefitting model as we like.
prefitting_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
prefitting_model.fit(
heart_train_xs,
heart_train_ys,
epochs=PREFITTING_NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
# Now that we have our trained prefitting model, we can extract the crystals.
tfl.premade_lib.set_crystals_lattice_ensemble(crystals_ensemble_model_config,
prefitting_model_config,
prefitting_model)
# A CalibratedLatticeEnsemble premade model constructed from the given
# model config.
crystals_ensemble_model = tfl.premade.CalibratedLatticeEnsemble(
crystals_ensemble_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
crystals_ensemble_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
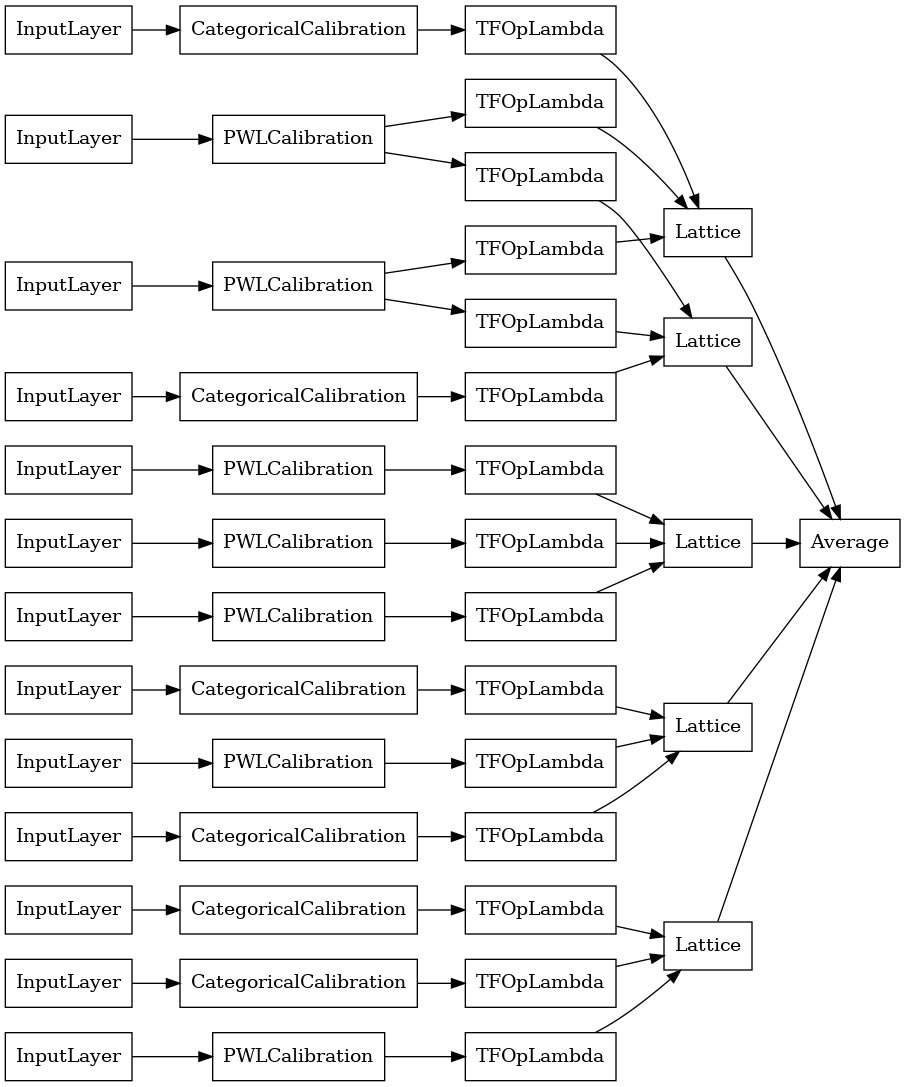
כמו בעבר, אנו מרכיבים, מתאימים ומעריכים את המודל שלנו.
crystals_ensemble_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.AUC(from_logits=True)],
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
crystals_ensemble_model.fit(
heart_train_xs,
heart_train_ys,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
verbose=False)
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(crystals_ensemble_model.evaluate(heart_test_xs, heart_test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 2/2 [==============================] - 1s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3404 - auc_5: 0.9179 [0.34039050340652466, 0.9179198145866394]
