 Zobacz na TensorFlow.org Zobacz na TensorFlow.org |  Uruchom w Google Colab Uruchom w Google Colab |  Wyświetl źródło na GitHub Wyświetl źródło na GitHub |  Pobierz notatnik Pobierz notatnik |
Przegląd
Ten poradnik skupia się na streaming danych z Elasticsearch klastra w tf.data.Dataset który jest następnie wykorzystywany w połączeniu z tf.keras na szkolenia i wnioskowania.
Elasticseach jest przede wszystkim rozproszoną wyszukiwarką, która obsługuje przechowywanie ustrukturyzowanych, nieustrukturyzowanych, geoprzestrzennych, numerycznych danych itp. Na potrzeby tego samouczka używany jest zestaw danych z ustrukturyzowanymi rekordami.
Pakiety instalacyjne
elasticsearch pakietów jest wykorzystywany do przygotowywania i przechowywania danych wewnątrz wskaźników elasticsearch tylko dla celów demonstracyjnych. W rzeczywistych klastrach produkcyjnych z wieloma węzłami klaster może otrzymywać dane z łączników, takich jak logstash itp.
Gdy dane są dostępne w klastrze elasticsearch tylko tensorflow-io jest wymagany do przesyłania danych do modeli.
Zainstaluj wymagane pakiety tensorflow-io i elasticsearch
pip install tensorflow-iopip install elasticsearch
Importuj paczki
import os
import time
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental import preprocessing
import tensorflow_io as tfio
Sprawdź poprawność importu tf i tfio
print("tensorflow-io version: {}".format(tfio.__version__))
print("tensorflow version: {}".format(tf.__version__))
tensorflow-io version: 0.16.0 tensorflow version: 2.3.0
Pobierz i skonfiguruj instancję Elasticsearch
Do celów demonstracyjnych używana jest wersja open-source pakietu elasticsearch.
wget -q https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gzwget -q https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512tar -xzf elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gzsudo chown -R daemon:daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz: OK
Uruchom instancję jako proces demona
sudo -H -u daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/bin/elasticsearch
Starting job # 0 in a separate thread.
# Sleep for few seconds to let the instance start.
time.sleep(20)
Gdy instancja została rozpoczęta, grep dla elasticsearch w procesach listy w celu potwierdzenia dostępności.
ps -ef | grep elasticsearch
root 144 142 0 21:24 ? 00:00:00 sudo -H -u daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/bin/elasticsearch daemon 145 144 86 21:24 ? 00:00:17 /content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/jdk/bin/java -Xshare:auto -Des.networkaddress.cache.ttl=60 -Des.networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10 -XX:+AlwaysPreTouch -Xss1m -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Djna.nosys=true -XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow -XX:+ShowCodeDetailsInExceptionMessages -Dio.netty.noUnsafe=true -Dio.netty.noKeySetOptimization=true -Dio.netty.recycler.maxCapacityPerThread=0 -Dio.netty.allocator.numDirectArenas=0 -Dlog4j.shutdownHookEnabled=false -Dlog4j2.disable.jmx=true -Djava.locale.providers=SPI,COMPAT -Xms1g -Xmx1g -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:G1ReservePercent=25 -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=30 -Djava.io.tmpdir=/tmp/elasticsearch-16913031424109346409 -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=data -XX:ErrorFile=logs/hs_err_pid%p.log -Xlog:gc*,gc+age=trace,safepoint:file=logs/gc.log:utctime,pid,tags:filecount=32,filesize=64m -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=536870912 -Des.path.home=/content/elasticsearch-7.9.2 -Des.path.conf=/content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/config -Des.distribution.flavor=oss -Des.distribution.type=tar -Des.bundled_jdk=true -cp /content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/lib/* org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch root 382 380 0 21:24 ? 00:00:00 grep elasticsearch
wysyła zapytanie do podstawowego punktu końcowego, aby pobrać informacje o klastrze.
curl -sX GET "localhost:9200/"
{
"name" : "d1bc7d054c69",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "P8YXfKqYS-OS3k9CdMmlsw",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.9.2",
"build_flavor" : "oss",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "d34da0ea4a966c4e49417f2da2f244e3e97b4e6e",
"build_date" : "2020-09-23T00:45:33.626720Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.6.2",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Przeglądaj zbiór danych
Na potrzeby tego tutoriala, pozwala pobrać PetFinder zbiór danych i paszy dane do elasticsearch ręcznie. Celem tego problemu klasyfikacyjnego jest przewidzenie, czy zwierzę zostanie adoptowane, czy nie.
dataset_url = 'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip'
csv_file = 'datasets/petfinder-mini/petfinder-mini.csv'
tf.keras.utils.get_file('petfinder_mini.zip', dataset_url,
extract=True, cache_dir='.')
pf_df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
Downloading data from http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip 1671168/1668792 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
pf_df.head()
Na potrzeby samouczka w kolumnie etykiety wprowadzono modyfikacje. 0 oznacza, że zwierzę nie zostało adoptowane, a 1, że było.
# In the original dataset "4" indicates the pet was not adopted.
pf_df['target'] = np.where(pf_df['AdoptionSpeed']==4, 0, 1)
# Drop un-used columns.
pf_df = pf_df.drop(columns=['AdoptionSpeed', 'Description'])
# Number of datapoints and columns
len(pf_df), len(pf_df.columns)
(11537, 14)
Podziel zbiór danych
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(pf_df, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True)
print("Number of training samples: ",len(train_df))
print("Number of testing sample: ",len(test_df))
Number of training samples: 8075 Number of testing sample: 3462
Przechowuj dane pociągu i testu w indeksach elasticsearch
Przechowywanie danych w lokalnym klastrze elasticsearch symuluje środowisko do ciągłego zdalnego pobierania danych do celów uczenia i wnioskowania.
ES_NODES = "http://localhost:9200"
def prepare_es_data(index, doc_type, df):
records = df.to_dict(orient="records")
es_data = []
for idx, record in enumerate(records):
meta_dict = {
"index": {
"_index": index,
"_type": doc_type,
"_id": idx
}
}
es_data.append(meta_dict)
es_data.append(record)
return es_data
def index_es_data(index, es_data):
es_client = Elasticsearch(hosts = [ES_NODES])
if es_client.indices.exists(index):
print("deleting the '{}' index.".format(index))
res = es_client.indices.delete(index=index)
print("Response from server: {}".format(res))
print("creating the '{}' index.".format(index))
res = es_client.indices.create(index=index)
print("Response from server: {}".format(res))
print("bulk index the data")
res = es_client.bulk(index=index, body=es_data, refresh = True)
print("Errors: {}, Num of records indexed: {}".format(res["errors"], len(res["items"])))
train_es_data = prepare_es_data(index="train", doc_type="pet", df=train_df)
test_es_data = prepare_es_data(index="test", doc_type="pet", df=test_df)
index_es_data(index="train", es_data=train_es_data)
time.sleep(3)
index_es_data(index="test", es_data=test_es_data)
creating the 'train' index.
Response from server: {'acknowledged': True, 'shards_acknowledged': True, 'index': 'train'}
bulk index the data
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/elasticsearch/connection/base.py:190: ElasticsearchDeprecationWarning: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
warnings.warn(message, category=ElasticsearchDeprecationWarning)
Errors: False, Num of records indexed: 8075
creating the 'test' index.
Response from server: {'acknowledged': True, 'shards_acknowledged': True, 'index': 'test'}
bulk index the data
Errors: False, Num of records indexed: 3462
Przygotuj zbiory danych tfio
Gdy dane są dostępne w klastrze tylko tensorflow-io jest wymagana do przesyłania danych z tych wskaźników. elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset klasa jest wykorzystywana do tego celu. Klasa dziedziczy z tf.data.Dataset a tym samym naraża wszystkich użytecznych funkcjonalności tf.data.Dataset po wyjęciu z pudełka.
Zbiór danych szkoleniowych
BATCH_SIZE=32
HEADERS = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
train_ds = tfio.experimental.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset(
nodes=[ES_NODES],
index="train",
doc_type="pet",
headers=HEADERS
)
# Prepare a tuple of (features, label)
train_ds = train_ds.map(lambda v: (v, v.pop("target")))
train_ds = train_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
Connection successful: http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health
Testowanie zbioru danych
test_ds = tfio.experimental.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset(
nodes=[ES_NODES],
index="test",
doc_type="pet",
headers=HEADERS
)
# Prepare a tuple of (features, label)
test_ds = test_ds.map(lambda v: (v, v.pop("target")))
test_ds = test_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
Connection successful: http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health
Zdefiniuj warstwy wstępnego przetwarzania keras
Zgodnie z uporządkowanego tutorialu danych , zaleca się korzystanie z warstw Keras przerób , ponieważ są one bardziej intuicyjne i można łatwo zintegrować z modelami. Jednak standardowe feature_columns może być również używany.
Dla lepszego zrozumienia preprocessing_layers w klasyfikacji danych strukturalnych, proszę odnieść się do strukturalnego tutorialu danych
def get_normalization_layer(name, dataset):
# Create a Normalization layer for our feature.
normalizer = preprocessing.Normalization()
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature.
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the statistics of the data.
normalizer.adapt(feature_ds)
return normalizer
def get_category_encoding_layer(name, dataset, dtype, max_tokens=None):
# Create a StringLookup layer which will turn strings into integer indices
if dtype == 'string':
index = preprocessing.StringLookup(max_tokens=max_tokens)
else:
index = preprocessing.IntegerLookup(max_values=max_tokens)
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the set of possible values and assign them a fixed integer index.
index.adapt(feature_ds)
# Create a Discretization for our integer indices.
encoder = preprocessing.CategoryEncoding(max_tokens=index.vocab_size())
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature.
feature_ds = feature_ds.map(index)
# Learn the space of possible indices.
encoder.adapt(feature_ds)
# Apply one-hot encoding to our indices. The lambda function captures the
# layer so you can use them, or include them in the functional model later.
return lambda feature: encoder(index(feature))
Pobierz partię i obserwuj cechy przykładowego rekordu. Pomoże to w określeniu Keras przerób warstw na szkolenie tf.keras model.
ds_iter = iter(train_ds)
features, label = next(ds_iter)
{key: value.numpy()[0] for key,value in features.items()}
{'Age': 2,
'Breed1': b'Tabby',
'Color1': b'Black',
'Color2': b'Cream',
'Fee': 0,
'FurLength': b'Short',
'Gender': b'Male',
'Health': b'Healthy',
'MaturitySize': b'Small',
'PhotoAmt': 4,
'Sterilized': b'No',
'Type': b'Cat',
'Vaccinated': b'No'}
Wybierz podzbiór funkcji.
all_inputs = []
encoded_features = []
# Numeric features.
for header in ['PhotoAmt', 'Fee']:
numeric_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header)
normalization_layer = get_normalization_layer(header, train_ds)
encoded_numeric_col = normalization_layer(numeric_col)
all_inputs.append(numeric_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_numeric_col)
# Categorical features encoded as string.
categorical_cols = ['Type', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'Gender', 'MaturitySize',
'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Breed1']
for header in categorical_cols:
categorical_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header, dtype='string')
encoding_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(header, train_ds, dtype='string',
max_tokens=5)
encoded_categorical_col = encoding_layer(categorical_col)
all_inputs.append(categorical_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_categorical_col)
Buduj, kompiluj i trenuj model
# Set the parameters
OPTIMIZER="adam"
LOSS=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
METRICS=['accuracy']
EPOCHS=10
# Convert the feature columns into a tf.keras layer
all_features = tf.keras.layers.concatenate(encoded_features)
# design/build the model
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation="relu")(all_features)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation="relu")(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
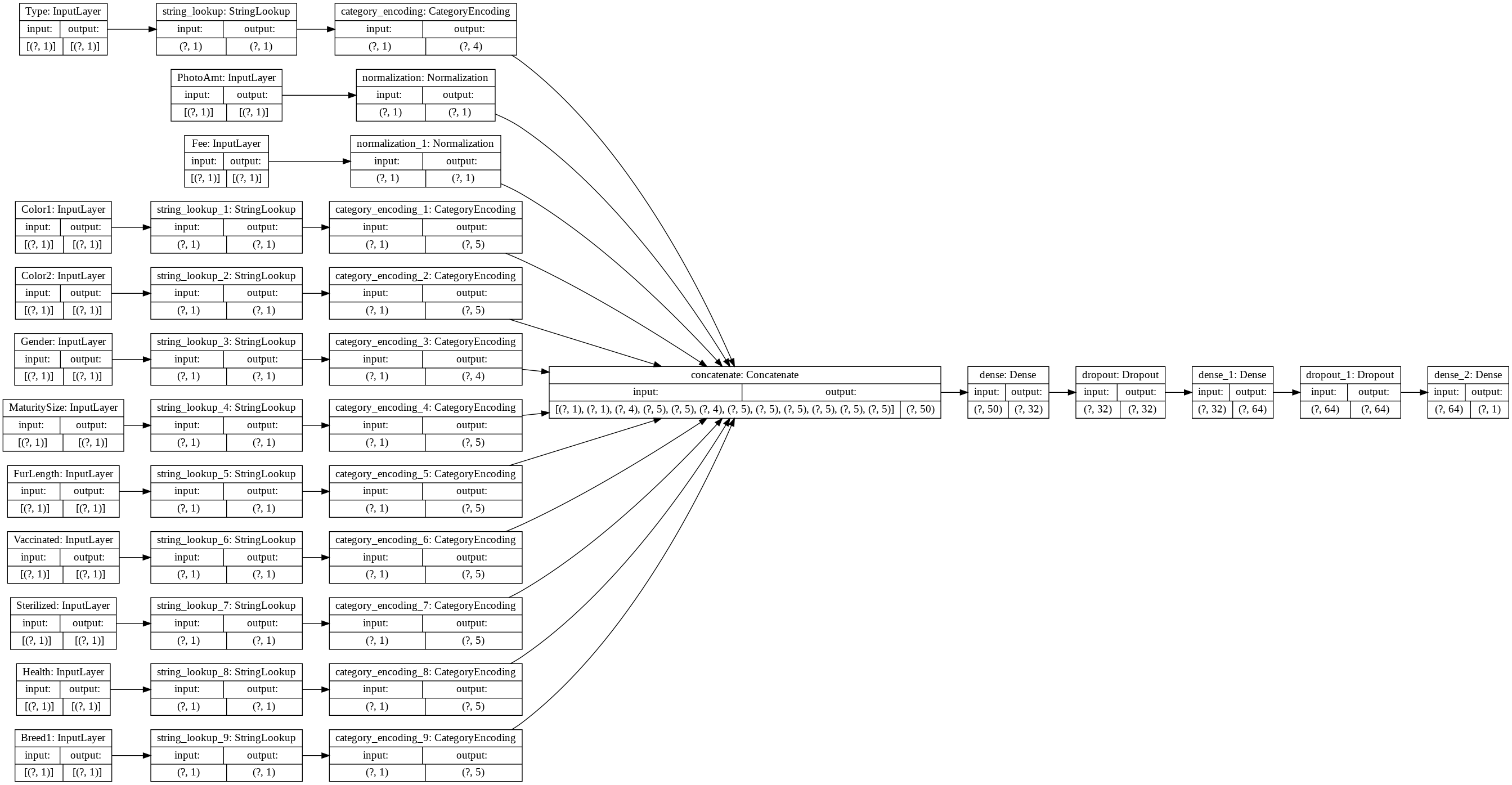
model = tf.keras.Model(all_inputs, output)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, rankdir='LR', show_shapes=True)
# compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=OPTIMIZER, loss=LOSS, metrics=METRICS)
# fit the model
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=EPOCHS)
Epoch 1/10 /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/keras/engine/functional.py:543: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['Age'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model. [n for n in tensors.keys() if n not in ref_input_names]) 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6169 - accuracy: 0.6042 Epoch 2/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5634 - accuracy: 0.6937 Epoch 3/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5573 - accuracy: 0.6981 Epoch 4/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5528 - accuracy: 0.7087 Epoch 5/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5512 - accuracy: 0.7173 Epoch 6/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5456 - accuracy: 0.7219 Epoch 7/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5397 - accuracy: 0.7283 Epoch 8/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5385 - accuracy: 0.7331 Epoch 9/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5355 - accuracy: 0.7326 Epoch 10/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5412 - accuracy: 0.7321 <tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f5c235112e8>
Wnioskuj na temat danych testowych
res = model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("test loss, test acc:", res)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/keras/engine/functional.py:543: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['Age'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model. [n for n in tensors.keys() if n not in ref_input_names]) 109/109 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5344 - accuracy: 0.7421 test loss, test acc: [0.534355640411377, 0.7420566082000732]
