Mục đích của máy tính xách tay này là giúp TFP 0.13.0 "trở nên sống động" thông qua một số đoạn trích nhỏ - bản trình diễn nhỏ về những điều bạn có thể đạt được với TFP.
 Xem trên TensorFlow.org Xem trên TensorFlow.org |  Chạy trong Google Colab Chạy trong Google Colab |  Xem nguồn trên GitHub Xem nguồn trên GitHub | 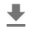 Tải xuống sổ ghi chép Tải xuống sổ ghi chép |
Cài đặt và nhập
!pip3 install -qU tensorflow==2.5.0 tensorflow_probability==0.13.0 tensorflow-datasets inference_gym
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
assert '0.13' in tfp.__version__, tfp.__version__
assert '2.5' in tf.__version__, tf.__version__
physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('CPU')
tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
physical_devices[0],
[tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration()])
tfd = tfp.distributions
tfb = tfp.bijectors
tfpk = tfp.math.psd_kernels
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.interpolate
import IPython
import seaborn as sns
import logging
[K |████████████████████████████████| 5.4MB 8.8MB/s [K |████████████████████████████████| 3.9MB 37.1MB/s [K |████████████████████████████████| 296kB 31.6MB/s [?25h
Phân phối [toán học cốt lõi]
BetaQuotient
Tỷ lệ của hai biến ngẫu nhiên có phân phối Beta độc lập
plt.hist(tfd.BetaQuotient(concentration1_numerator=5.,
concentration0_numerator=2.,
concentration1_denominator=3.,
concentration0_denominator=8.).sample(1_000, seed=(1, 23)),
bins='auto');
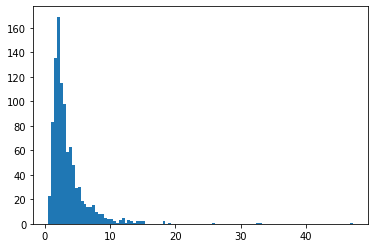
DeterminantalPointProcess
Phân phối trên các tập hợp con (được biểu diễn dưới dạng một nóng) của một tập hợp nhất định. Các mẫu tuân theo thuộc tính tính đẩy lùi (xác suất tỷ lệ với khối lượng được bao quanh bởi các vectơ tương ứng với tập con điểm đã chọn), có xu hướng lấy mẫu các tập con đa dạng. [So sánh với các mẫu Bernoulli iid.]
grid_size = 16
# Generate grid_size**2 pts on the unit square.
grid = np.arange(0, 1, 1./grid_size).astype(np.float32)
import itertools
points = np.array(list(itertools.product(grid, grid)))
# Create the kernel L that parameterizes the DPP.
kernel_amplitude = 2.
kernel_lengthscale = [.1, .15, .2, .25] # Increasing length scale indicates more points are "nearby", tending toward smaller subsets.
kernel = tfpk.ExponentiatedQuadratic(kernel_amplitude, kernel_lengthscale)
kernel_matrix = kernel.matrix(points, points)
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = tf.linalg.eigh(kernel_matrix)
dpp = tfd.DeterminantalPointProcess(eigenvalues, eigenvectors)
print(dpp)
# The inner-most dimension of the result of `dpp.sample` is a multi-hot
# encoding of a subset of {1, ..., ground_set_size}.
# We will compare against a bernoulli distribution.
samps_dpp = dpp.sample(seed=(1, 2)) # 4 x grid_size**2
logits = tf.broadcast_to([[-1.], [-1.5], [-2], [-2.5]], [4, grid_size**2])
samps_bern = tfd.Bernoulli(logits=logits).sample(seed=(2, 3))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
for i, (samp, samp_bern) in enumerate(zip(samps_dpp, samps_bern)):
plt.subplot(241 + i)
plt.scatter(*points[np.where(samp)].T)
plt.title(f'DPP, length scale={kernel_lengthscale[i]}')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.gca().set_aspect(1.)
plt.subplot(241 + i + 4)
plt.scatter(*points[np.where(samp_bern)].T)
plt.title(f'bernoulli, logit={logits[i,0]}')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.gca().set_aspect(1.)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
tfp.distributions.DeterminantalPointProcess("DeterminantalPointProcess", batch_shape=[4], event_shape=[256], dtype=int32)
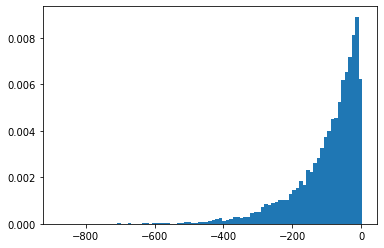
SigmoidBeta
Tỷ lệ đăng nhập của hai phân phối gamma. Số lượng nhiều không gian mẫu ổn định hơn Beta .
plt.hist(tfd.SigmoidBeta(concentration1=.01, concentration0=2.).sample(10_000, seed=(1, 23)),
bins='auto', density=True);
plt.show()
print('Old way, fractions non-finite:')
print(np.sum(~tf.math.is_finite(
tfb.Invert(tfb.Sigmoid())(tfd.Beta(concentration1=.01, concentration0=2.)).sample(10_000, seed=(1, 23)))) / 10_000)
print(np.sum(~tf.math.is_finite(
tfb.Invert(tfb.Sigmoid())(tfd.Beta(concentration1=2., concentration0=.01)).sample(10_000, seed=(2, 34)))) / 10_000)
Old way, fractions non-finite: 0.4215 0.8624
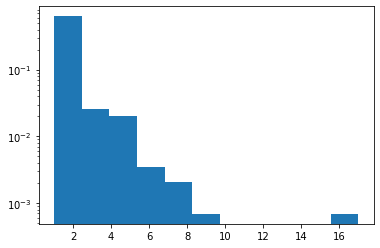
Zipf
Đã thêm hỗ trợ JAX.
plt.hist(tfd.Zipf(3.).sample(1_000, seed=(12, 34)).numpy(), bins='auto', density=True, log=True);
NormalInverseGaussian
Họ tham số linh hoạt hỗ trợ đuôi nặng, lệch và vani Bình thường.
MatrixNormalLinearOperator
Ma trận Phân phối chuẩn.
# Initialize a single 2 x 3 Matrix Normal.
mu = [[1., 2, 3], [3., 4, 5]]
col_cov = [[ 0.36, 0.12, 0.06],
[ 0.12, 0.29, -0.13],
[ 0.06, -0.13, 0.26]]
scale_column = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorLowerTriangular(tf.linalg.cholesky(col_cov))
scale_row = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorDiag([0.9, 0.8])
mvn = tfd.MatrixNormalLinearOperator(loc=mu, scale_row=scale_row, scale_column=scale_column)
mvn.sample()
WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/linalg/linear_operator_kronecker.py:224: LinearOperator.graph_parents (from tensorflow.python.ops.linalg.linear_operator) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Do not call `graph_parents`.
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1.2495145, 1.549366 , 3.2748342],
[3.7330258, 4.3413105, 4.83423 ]], dtype=float32)>
MatrixStudentTLinearOperator
Ma trận T phân phối.
mu = [[1., 2, 3], [3., 4, 5]]
col_cov = [[ 0.36, 0.12, 0.06],
[ 0.12, 0.29, -0.13],
[ 0.06, -0.13, 0.26]]
scale_column = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorLowerTriangular(tf.linalg.cholesky(col_cov))
scale_row = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorDiag([0.9, 0.8])
mvn = tfd.MatrixTLinearOperator(
df=2.,
loc=mu,
scale_row=scale_row,
scale_column=scale_column)
mvn.sample()
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1.6549466, 2.6708362, 2.8629923],
[2.1222284, 3.6904747, 5.08014 ]], dtype=float32)>
Phân phối [phần mềm / wrappers]
Sharded
Chia nhỏ các phần sự kiện độc lập của một bản phân phối trên nhiều bộ xử lý. Uẩn log_prob giữa các thiết bị, xử lý gradient phối hợp với tfp.experimental.distribute.JointDistribution* . Nhiều hơn nữa trong suy luận Distributed máy tính xách tay.
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
@tf.function
def sample_and_lp(seed):
d = tfp.experimental.distribute.Sharded(tfd.Normal(0, 1))
s = d.sample(seed=seed)
return s, d.log_prob(s)
strategy.run(sample_and_lp, args=(tf.constant([12,34]),))
WARNING:tensorflow:There are non-GPU devices in `tf.distribute.Strategy`, not using nccl allreduce.
WARNING:tensorflow:Collective ops is not configured at program startup. Some performance features may not be enabled.
INFO:tensorflow:Using MirroredStrategy with devices ('/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0', '/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:1')
INFO:tensorflow:Reduce to /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0 then broadcast to ('/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0', '/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:1').
(PerReplica:{
0: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.0051413667>,
1: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=-0.3393052>
}, PerReplica:{
0: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=-1.8954543>,
1: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=-1.8954543>
})
BatchBroadcast
Ngầm phát sóng kích thước hàng loạt của một phân phối tiềm ẩn với hoặc một hình dạng batch nhất định.
underlying = tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(tf.zeros([7, 1, 5]), tf.ones([5]))
print('underlying:', underlying)
d = tfd.BatchBroadcast(underlying, [8, 1, 6])
print('broadcast [7, 1] *with* [8, 1, 6]:', d)
try:
tfd.BatchBroadcast(underlying, to_shape=[8, 1, 6])
except ValueError as e:
print('broadcast [7, 1] *to* [8, 1, 6] is invalid:', e)
d = tfd.BatchBroadcast(underlying, to_shape=[8, 7, 6])
print('broadcast [7, 1] *to* [8, 7, 6]:', d)
underlying: tfp.distributions.MultivariateNormalDiag("MultivariateNormalDiag", batch_shape=[7, 1], event_shape=[5], dtype=float32)
broadcast [7, 1] *with* [8, 1, 6]: tfp.distributions.BatchBroadcast("BatchBroadcastMultivariateNormalDiag", batch_shape=[8, 7, 6], event_shape=[5], dtype=float32)
broadcast [7, 1] *to* [8, 1, 6] is invalid: Argument `to_shape` ([8 1 6]) is incompatible with underlying distribution batch shape ((7, 1)).
broadcast [7, 1] *to* [8, 7, 6]: tfp.distributions.BatchBroadcast("BatchBroadcastMultivariateNormalDiag", batch_shape=[8, 7, 6], event_shape=[5], dtype=float32)
Masked
Đối với đơn chương trình / nhiều dữ liệu hoặc trường hợp sử dụng thưa thớt-as-che-dày đặc, một phân phối mặt nạ ra log_prob bản phân phối cơ bản không hợp lệ.
d = tfd.Masked(tfd.Normal(tf.zeros([7]), 1),
validity_mask=tf.sequence_mask([3, 4], 7))
print(d.log_prob(d.sample(seed=(1, 1))))
d = tfd.Masked(tfd.Normal(0, 1),
validity_mask=[False, True, False],
safe_sample_fn=tfd.Distribution.mode)
print(d.log_prob(d.sample(seed=(2, 2))))
tf.Tensor( [[-2.3054113 -1.8524303 -1.2220721 0. 0. 0. 0. ] [-1.118623 -1.1370811 -1.1574132 -5.884986 0. 0. 0. ]], shape=(2, 7), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([ 0. -0.93683904 0. ], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
Bijector
- Bijector
- Thêm bijectors để bắt chước
tf.nest.flatten(tfb.tree_flatten) vàtf.nest.pack_sequence_as(tfb.pack_sequence_as). - Thêm
tfp.experimental.bijectors.Sharded - Remove phản
tfb.ScaleTrilL. Sử dụngtfb.FillScaleTriLđể thay thế. - Thêm
cls.parameter_properties()chú thích cho Bijectors. - Mở rộng phạm vi
tfb.Powercho tất cả các số thực cho sức mạnh số nguyên lẻ. - Suy ra log-deg-jacobian của bijectar vô hướng sử dụng autodiff, nếu không được chỉ định khác.
- Thêm bijectors để bắt chước
Tái cấu trúc các máy phát sinh
ex = (tf.constant(1.), dict(b=tf.constant(2.), c=tf.constant(3.)))
b = tfb.tree_flatten(ex)
print(b.forward(ex))
print(b.inverse(list(tf.constant([1., 2, 3]))))
b = tfb.pack_sequence_as(ex)
print(b.forward(list(tf.constant([1., 2, 3]))))
print(b.inverse(ex))
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.0>]
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>, {'b': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>, 'c': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.0>})
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>, {'b': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>, 'c': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.0>})
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.0>]
Sharded
Giảm SPMD trong yếu tố quyết định log. Xem Sharded trong phân phối, bên dưới.
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
def sample_lp_logdet(seed):
d = tfd.TransformedDistribution(tfp.experimental.distribute.Sharded(tfd.Normal(0, 1), shard_axis_name='i'),
tfp.experimental.bijectors.Sharded(tfb.Sigmoid(), shard_axis_name='i'))
s = d.sample(seed=seed)
return s, d.log_prob(s), d.bijector.inverse_log_det_jacobian(s)
strategy.run(sample_lp_logdet, (tf.constant([1, 2]),))
WARNING:tensorflow:There are non-GPU devices in `tf.distribute.Strategy`, not using nccl allreduce.
WARNING:tensorflow:Collective ops is not configured at program startup. Some performance features may not be enabled.
INFO:tensorflow:Using MirroredStrategy with devices ('/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0', '/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:1')
WARNING:tensorflow:Using MirroredStrategy eagerly has significant overhead currently. We will be working on improving this in the future, but for now please wrap `call_for_each_replica` or `experimental_run` or `run` inside a tf.function to get the best performance.
INFO:tensorflow:Reduce to /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0 then broadcast to ('/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0', '/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:1').
INFO:tensorflow:Reduce to /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0 then broadcast to ('/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0', '/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:1').
(PerReplica:{
0: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.87746525>,
1: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.24580425>
}, PerReplica:{
0: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=-0.48870325>,
1: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=-0.48870325>
}, PerReplica:{
0: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.9154015>,
1: <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.9154015>
})
VI
- Thêm
build_split_flow_surrogate_posteriorđểtfp.experimental.viđể xây dựng cấu trúc VI posteriors thay thế từ chảy bình thường. - Thêm
build_affine_surrogate_posteriorđểtfp.experimental.vixây dựng posteriors thay thế ADVI từ một hình dạng sự kiện. - Thêm
build_affine_surrogate_posterior_from_base_distributionđểtfp.experimental.viđể cho phép xây dựng posteriors ADVI thay thế với các cấu trúc tương quan gây ra bởi biến đổi afin.
VI / MAP / MLE
- Bổ sung phương pháp thuận tiện
tfp.experimental.util.make_trainable(cls)để tạo ra các trường hợp khả năng huấn luyện của các bản phân phối và bijectors.
d = tfp.experimental.util.make_trainable(tfd.Gamma)
print(d.trainable_variables)
print(d)
(<tf.Variable 'Gamma_trainable_variables/concentration:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=1.0296053>, <tf.Variable 'Gamma_trainable_variables/log_rate:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=-0.3465951>)
tfp.distributions.Gamma("Gamma", batch_shape=[], event_shape=[], dtype=float32)
MCMC
- Chẩn đoán MCMC hỗ trợ cấu trúc trạng thái tùy ý, không chỉ danh sách.
-
remc_thermodynamic_integralsthêm vàotfp.experimental.mcmc - Thêm
tfp.experimental.mcmc.windowed_adaptive_hmc - Thêm một API thử nghiệm để khởi tạo chuỗi Markov từ một phân phối đồng nhất gần như bằng không trong không gian không bị giới hạn.
tfp.experimental.mcmc.init_near_unconstrained_zero - Thêm tiện ích thử nghiệm để thử lại quá trình khởi tạo Chuỗi Markov cho đến khi tìm thấy điểm chấp nhận được.
tfp.experimental.mcmc.retry_init - Trộn API MCMC phát trực tuyến thử nghiệm sang vị trí vào tfp.mcmc với mức gián đoạn tối thiểu.
- Thêm
ThinningKernelđểexperimental.mcmc. - Thêm
experimental.mcmc.run_kernellái xe như một ứng cử viên streaming-dựa thay thế đểmcmc.sample_chain
init_near_unconstrained_zero , retry_init
@tfd.JointDistributionCoroutine
def model():
Root = tfd.JointDistributionCoroutine.Root
c0 = yield Root(tfd.Gamma(2, 2, name='c0'))
c1 = yield Root(tfd.Gamma(2, 2, name='c1'))
counts = yield tfd.Sample(tfd.BetaBinomial(23, c1, c0), 10, name='counts')
jd = model.experimental_pin(counts=model.sample(seed=[20, 30]).counts)
init_dist = tfp.experimental.mcmc.init_near_unconstrained_zero(jd)
print(init_dist)
tfp.experimental.mcmc.retry_init(init_dist.sample, jd.unnormalized_log_prob)
tfp.distributions.TransformedDistribution("default_joint_bijectorrestructureJointDistributionSequential", batch_shape=StructTuple(
c0=[],
c1=[]
), event_shape=StructTuple(
c0=[],
c1=[]
), dtype=StructTuple(
c0=float32,
c1=float32
))
StructTuple(
c0=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.7879653>,
c1=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.34548905>
)
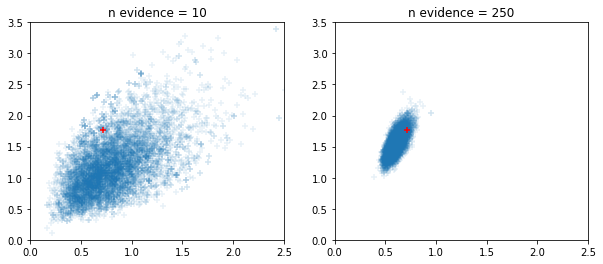
Bộ lấy mẫu HMC và NUTS thích ứng có cửa sổ
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
for i, n_evidence in enumerate((10, 250)):
ax[i].set_title(f'n evidence = {n_evidence}')
ax[i].set_xlim(0, 2.5); ax[i].set_ylim(0, 3.5)
@tfd.JointDistributionCoroutine
def model():
Root = tfd.JointDistributionCoroutine.Root
c0 = yield Root(tfd.Gamma(2, 2, name='c0'))
c1 = yield Root(tfd.Gamma(2, 2, name='c1'))
counts = yield tfd.Sample(tfd.BetaBinomial(23, c1, c0), n_evidence, name='counts')
s = model.sample(seed=[20, 30])
print(s)
jd = model.experimental_pin(counts=s.counts)
states, trace = tf.function(tfp.experimental.mcmc.windowed_adaptive_hmc)(
100, jd, num_leapfrog_steps=5, seed=[100, 200])
ax[i].scatter(states.c0.numpy().reshape(-1), states.c1.numpy().reshape(-1),
marker='+', alpha=.1)
ax[i].scatter(s.c0, s.c1, marker='+', color='r')
StructTuple(
c0=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.7161876>,
c1=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.7696666>,
counts=<tf.Tensor: shape=(10,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([ 6., 10., 23., 7., 2., 20., 14., 16., 22., 17.], dtype=float32)>
)
WARNING:tensorflow:6 out of the last 6 calls to <function windowed_adaptive_hmc at 0x7fda42bed8c0> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
StructTuple(
c0=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.7161876>,
c1=<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.7696666>,
counts=<tf.Tensor: shape=(250,), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([ 6., 10., 23., 7., 2., 20., 14., 16., 22., 17., 22., 21., 6.,
21., 12., 22., 23., 16., 18., 21., 16., 17., 17., 16., 21., 14.,
23., 15., 10., 19., 8., 23., 23., 14., 1., 23., 16., 22., 20.,
20., 22., 15., 16., 20., 20., 21., 23., 22., 21., 15., 18., 23.,
12., 16., 19., 23., 18., 5., 22., 22., 22., 18., 12., 17., 17.,
16., 8., 22., 20., 23., 3., 12., 14., 18., 7., 19., 19., 9.,
10., 23., 14., 22., 22., 21., 13., 23., 14., 23., 10., 17., 23.,
17., 20., 16., 20., 19., 14., 0., 17., 22., 12., 2., 17., 15.,
14., 23., 19., 15., 23., 2., 21., 23., 21., 7., 21., 12., 23.,
17., 17., 4., 22., 16., 14., 19., 19., 20., 6., 16., 14., 18.,
21., 12., 21., 21., 22., 2., 19., 11., 6., 19., 1., 23., 23.,
14., 6., 23., 18., 8., 20., 23., 13., 20., 18., 23., 17., 22.,
23., 20., 18., 22., 16., 23., 9., 22., 21., 16., 20., 21., 16.,
23., 7., 13., 23., 19., 3., 13., 23., 23., 13., 19., 23., 20.,
18., 8., 19., 14., 12., 6., 8., 23., 3., 13., 21., 23., 22.,
23., 19., 22., 21., 15., 22., 21., 21., 23., 9., 19., 20., 23.,
11., 23., 14., 23., 14., 21., 21., 10., 23., 9., 13., 1., 8.,
8., 20., 21., 21., 21., 14., 16., 16., 9., 23., 22., 11., 23.,
12., 18., 1., 23., 9., 3., 21., 21., 23., 22., 18., 23., 16.,
3., 11., 16.], dtype=float32)>
)
Toán học, số liệu thống kê
Math / linalg
- Thêm
tfp.math.trapzlồng ghép hình thang. - Thêm
tfp.math.log_bessel_kve. - Thêm
no_pivot_ldlđểexperimental.linalg. - Thêm
marginal_fnlập luận đểGaussianProcess(xemno_pivot_ldl). - Thêm
tfp.math.atan_difference(x, y) - Thêm
tfp.math.erfcx,tfp.math.logerfcvàtfp.math.logerfcx - Thêm
tfp.math.dawsncho Integral Dawson của. - Thêm
tfp.math.igammaincinv,tfp.math.igammacinv. - Thêm
tfp.math.sqrt1pm1. - Thêm
LogitNormal.stddev_approxvàLogitNormal.variance_approx - Thêm
tfp.math.owens_tcho chức năng T của Owen. - Thêm
bracket_rootphương pháp để giới hạn tự động khởi tạo cho một tìm kiếm gốc. - Thêm phương pháp của Chandrupatla để tìm gốc của các hàm vô hướng.
- Thêm
Số liệu thống kê
-
tfp.stats.windowed_meanphương tiện hiệu quả tính cửa sổ. -
tfp.stats.windowed_variancemột cách hiệu quả và chính xác tính cửa sổ chênh lệch. -
tfp.stats.cumulative_variancemột cách hiệu quả và tính chính xác chênh lệch tích lũy. -
RunningCovariancevà bạn bè bây giờ có thể được khởi tạo từ một ví dụ tensor, không chỉ từ hình dạng rõ ràng và dtype. - Cleaner API cho
RunningCentralMoments,RunningMean,RunningPotentialScaleReduction.
-
Các hàm Owen's T, Erfcx, Logerfc, Logerfcx, Dawson
# Owen's T gives the probability that X > h, 0 < Y < a * X. Let's check that
# with random sampling.
h = np.array([1., 2.]).astype(np.float32)
a = np.array([10., 11.5]).astype(np.float32)
probs = tfp.math.owens_t(h, a)
x = tfd.Normal(0., 1.).sample(int(1e5), seed=(6, 245)).numpy()
y = tfd.Normal(0., 1.).sample(int(1e5), seed=(7, 245)).numpy()
true_values = (
(x[..., np.newaxis] > h) &
(0. < y[..., np.newaxis]) &
(y[..., np.newaxis] < a * x[..., np.newaxis]))
print('Calculated values: {}'.format(
np.count_nonzero(true_values, axis=0) / 1e5))
print('Expected values: {}'.format(probs))
Calculated values: [0.07896 0.01134] Expected values: [0.07932763 0.01137507]
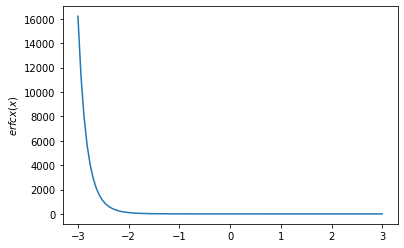
x = np.linspace(-3., 3., 100)
plt.plot(x, tfp.math.erfcx(x))
plt.ylabel('$erfcx(x)$')
plt.show()
plt.plot(x, tfp.math.logerfcx(x))
plt.ylabel('$logerfcx(x)$')
plt.show()
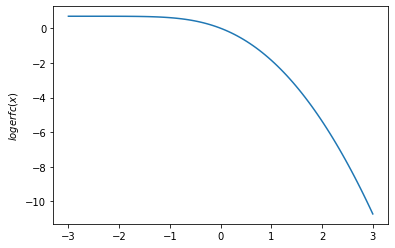
plt.plot(x, tfp.math.logerfc(x))
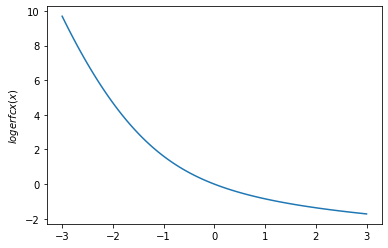
plt.ylabel('$logerfc(x)$')
plt.show()
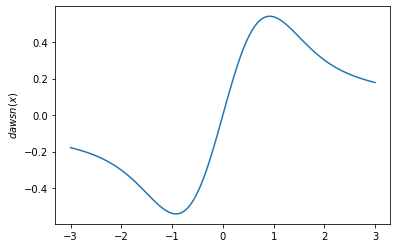
plt.plot(x, tfp.math.dawsn(x))
plt.ylabel('$dawsn(x)$')
plt.show()
igammainv / igammacinv
# Igammainv and Igammacinv are inverses to Igamma and Igammac
x = np.linspace(1., 10., 10)
y = tf.math.igamma(0.3, x)
x_prime = tfp.math.igammainv(0.3, y)
print('x: {}'.format(x))
print('igammainv(igamma(a, x)):\n {}'.format(x_prime))
y = tf.math.igammac(0.3, x)
x_prime = tfp.math.igammacinv(0.3, y)
print('\n')
print('x: {}'.format(x))
print('igammacinv(igammac(a, x)):\n {}'.format(x_prime))
x: [ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.] igammainv(igamma(a, x)): [1. 1.9999992 3.000003 4.0000024 5.0000257 5.999887 7.0002484 7.999243 8.99872 9.994673 ] x: [ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.] igammacinv(igammac(a, x)): [1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.000001 9. 9.999999]
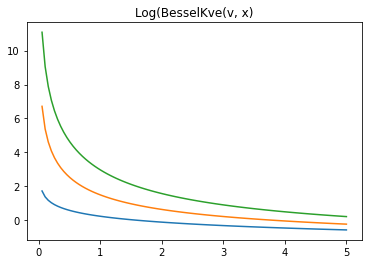
log-kve
x = np.linspace(0., 5., 100)
for v in [0.5, 2., 3]:
plt.plot(x, tfp.math.log_bessel_kve(v, x).numpy())
plt.title('Log(BesselKve(v, x)')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Log(BesselKve(v, x)')
Khác
STS
- Đẩy nhanh tiến độ STS dự báo và phân hủy sử dụng nội
tf.functiongói. - Thêm tùy chọn để tăng tốc độ lọc trong
LinearGaussianSSMkhi kết quả chỉ là bước cuối cùng của là bắt buộc. - Variational Suy luận với các bản phân phối chung: ví dụ máy tính xách tay với mô hình Radon .
- Thêm hỗ trợ thử nghiệm để chuyển đổi bất kỳ phân phối nào thành một bijector điều hòa trước.
- Đẩy nhanh tiến độ STS dự báo và phân hủy sử dụng nội
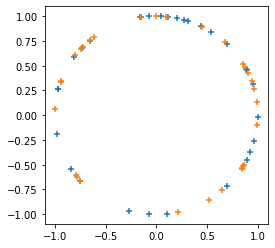
Thêm
tfp.random.sanitize_seed.Thêm
tfp.random.spherical_uniform.
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
seed = tfp.random.sanitize_seed(123)
seed1, seed2 = tfp.random.split_seed(seed)
samps = tfp.random.spherical_uniform([30], dimension=2, seed=seed1)
plt.scatter(*samps.numpy().T, marker='+')
samps = tfp.random.spherical_uniform([30], dimension=2, seed=seed2)
plt.scatter(*samps.numpy().T, marker='+');