 Visualizza su TensorFlow.org Visualizza su TensorFlow.org |  Esegui in Google Colab Esegui in Google Colab |  Visualizza su GitHub Visualizza su GitHub |  Scarica taccuino Scarica taccuino |  Vedi modello TF Hub Vedi modello TF Hub |
Questo Colab illustra come utilizzare l'Universal Sentence Encoder-Lite per il compito di somiglianza delle frasi. Questo modulo è molto simile a universale Frase Encoder con l'unica differenza che è necessario eseguire SentencePiece trattamento sulle vostre frasi di ingresso.
L'Universal Sentence Encoder rende facile ottenere incorporamenti a livello di frase come è stato storicamente cercare gli incorporamenti per singole parole. Gli incorporamenti di frasi possono quindi essere banalmente utilizzati per calcolare la somiglianza del significato a livello di frase e per consentire prestazioni migliori nelle attività di classificazione a valle utilizzando dati di addestramento meno supervisionati.
Iniziare
Impostare
# Install seaborn for pretty visualizationspip3 install --quiet seaborn# Install SentencePiece package# SentencePiece package is needed for Universal Sentence Encoder Lite. We'll# use it for all the text processing and sentence feature ID lookup.pip3 install --quiet sentencepiece
from absl import logging
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import sentencepiece as spm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
import seaborn as sns
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/compat/v2_compat.py:111: disable_resource_variables (from tensorflow.python.ops.variable_scope) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: non-resource variables are not supported in the long term
Carica il modulo da TF-Hub
module = hub.Module("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder-lite/2")
input_placeholder = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None, None])
encodings = module(
inputs=dict(
values=input_placeholder.values,
indices=input_placeholder.indices,
dense_shape=input_placeholder.dense_shape))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Carica il modello Frase dal modulo TF-Hub
Il modello FrasePiece è comodamente memorizzato all'interno delle risorse del modulo. Deve essere caricato per inizializzare il processore.
with tf.Session() as sess:
spm_path = sess.run(module(signature="spm_path"))
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(spm_path, mode="rb") as f:
sp.LoadFromSerializedProto(f.read())
print("SentencePiece model loaded at {}.".format(spm_path))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore SentencePiece model loaded at b'/tmp/tfhub_modules/539544f0a997d91c327c23285ea00c37588d92cc/assets/universal_encoder_8k_spm.model'.
def process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, sentences):
# An utility method that processes sentences with the sentence piece processor
# 'sp' and returns the results in tf.SparseTensor-similar format:
# (values, indices, dense_shape)
ids = [sp.EncodeAsIds(x) for x in sentences]
max_len = max(len(x) for x in ids)
dense_shape=(len(ids), max_len)
values=[item for sublist in ids for item in sublist]
indices=[[row,col] for row in range(len(ids)) for col in range(len(ids[row]))]
return (values, indices, dense_shape)
Prova il modulo con alcuni esempi
# Compute a representation for each message, showing various lengths supported.
word = "Elephant"
sentence = "I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding."
paragraph = (
"Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. "
"There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer "
"the more 'diluted' the embedding will be.")
messages = [word, sentence, paragraph]
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, messages)
# Reduce logging output.
logging.set_verbosity(logging.ERROR)
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run([tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.tables_initializer()])
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
for i, message_embedding in enumerate(np.array(message_embeddings).tolist()):
print("Message: {}".format(messages[i]))
print("Embedding size: {}".format(len(message_embedding)))
message_embedding_snippet = ", ".join(
(str(x) for x in message_embedding[:3]))
print("Embedding: [{}, ...]\n".format(message_embedding_snippet))
Message: Elephant Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.053387489169836044, 0.053194381296634674, -0.052356015890836716, ...] Message: I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.03533298149704933, -0.04714975506067276, 0.012305550277233124, ...] Message: Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer the more 'diluted' the embedding will be. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [-0.004081667400896549, -0.08954868465662003, 0.03737196698784828, ...]
Esempio di attività di somiglianza testuale semantica (STS)
Gli embedding prodotti dall'Universal Sentence Encoder sono approssimativamente normalizzati. La somiglianza semantica di due frasi può essere banalmente calcolata come il prodotto interno delle codifiche.
def plot_similarity(labels, features, rotation):
corr = np.inner(features, features)
sns.set(font_scale=1.2)
g = sns.heatmap(
corr,
xticklabels=labels,
yticklabels=labels,
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
cmap="YlOrRd")
g.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=rotation)
g.set_title("Semantic Textual Similarity")
def run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages):
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp,messages)
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
plot_similarity(messages, message_embeddings, 90)
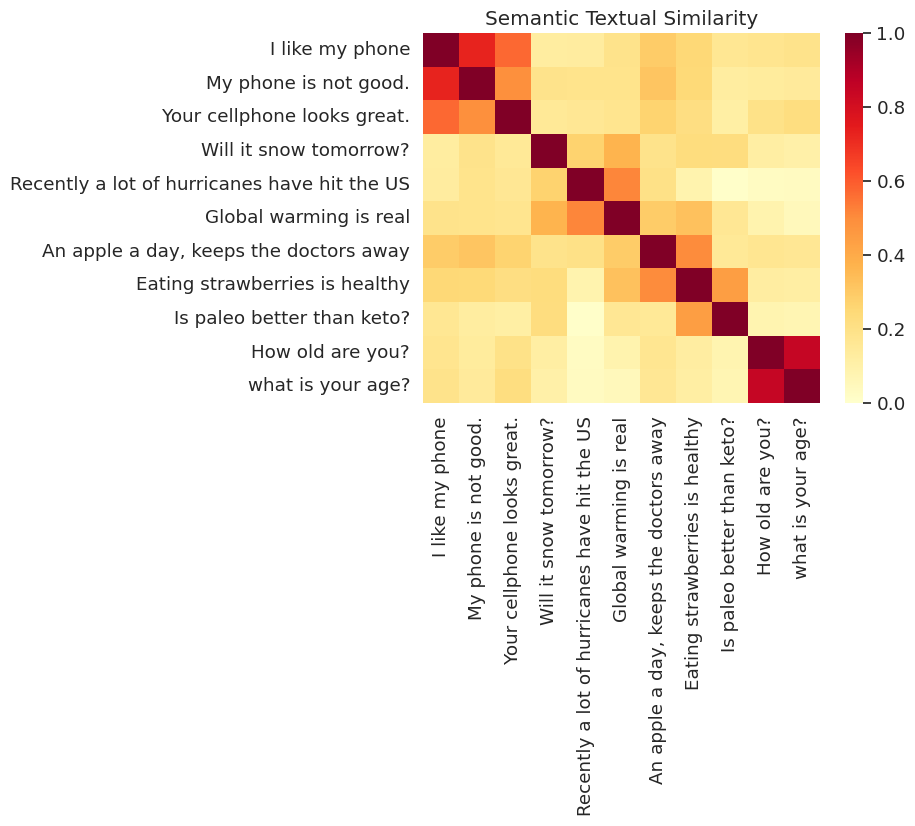
Somiglianza visualizzata
Qui mostriamo la somiglianza in una mappa di calore. Il grafico finale è una matrice 9x9 in cui ogni voce [i, j] è colorato in base al prodotto interno delle codifiche per frase i e j .
messages = [
# Smartphones
"I like my phone",
"My phone is not good.",
"Your cellphone looks great.",
# Weather
"Will it snow tomorrow?",
"Recently a lot of hurricanes have hit the US",
"Global warming is real",
# Food and health
"An apple a day, keeps the doctors away",
"Eating strawberries is healthy",
"Is paleo better than keto?",
# Asking about age
"How old are you?",
"what is your age?",
]
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages)
Valutazione: benchmark STS (somiglianza testuale semantica)
La STS Benchmark fornisce una valutazione intristic del grado in cui i punteggi di similitudine calcolato usando frase embeddings allineamento con giudizio umano. Il benchmark richiede che i sistemi restituiscano punteggi di somiglianza per una selezione diversificata di coppie di frasi. Correlazione di Pearson viene poi utilizzato per valutare la qualità dei punteggi macchina somiglianza contro giudizi umani.
Scarica i dati
import pandas
import scipy
import math
def load_sts_dataset(filename):
# Loads a subset of the STS dataset into a DataFrame. In particular both
# sentences and their human rated similarity score.
sent_pairs = []
with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
for line in f:
ts = line.strip().split("\t")
# (sent_1, sent_2, similarity_score)
sent_pairs.append((ts[5], ts[6], float(ts[4])))
return pandas.DataFrame(sent_pairs, columns=["sent_1", "sent_2", "sim"])
def download_and_load_sts_data():
sts_dataset = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname="Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
origin="http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
extract=True)
sts_dev = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-dev.csv"))
sts_test = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-test.csv"))
return sts_dev, sts_test
sts_dev, sts_test = download_and_load_sts_data()
Downloading data from http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz 417792/409630 [==============================] - 2s 5us/step 425984/409630 [===============================] - 2s 5us/step
Crea grafico di valutazione
sts_input1 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
sts_input2 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
# For evaluation we use exactly normalized rather than
# approximately normalized.
sts_encode1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input1.values,
indices=sts_input1.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input1.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sts_encode2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input2.values,
indices=sts_input2.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input2.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sim_scores = -tf.acos(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(sts_encode1, sts_encode2), axis=1))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Valuta gli incorporamenti di frasi
Scegli il set di dati per il benchmark
dataset = sts_dev
values1, indices1, dense_shape1 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_1'].tolist())
values2, indices2, dense_shape2 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_2'].tolist())
similarity_scores = dataset['sim'].tolist()
def run_sts_benchmark(session):
"""Returns the similarity scores"""
scores = session.run(
sim_scores,
feed_dict={
sts_input1.values: values1,
sts_input1.indices: indices1,
sts_input1.dense_shape: dense_shape1,
sts_input2.values: values2,
sts_input2.indices: indices2,
sts_input2.dense_shape: dense_shape2,
})
return scores
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
scores = run_sts_benchmark(session)
pearson_correlation = scipy.stats.pearsonr(scores, similarity_scores)
print('Pearson correlation coefficient = {0}\np-value = {1}'.format(
pearson_correlation[0], pearson_correlation[1]))
Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.7856484874001958 p-value = 1.065794746e-314
