 Посмотреть на TensorFlow.org Посмотреть на TensorFlow.org |  Запускаем в Google Colab Запускаем в Google Colab |  Посмотреть на GitHub Посмотреть на GitHub |  Скачать блокнот Скачать блокнот |  См. Модель TF Hub См. Модель TF Hub |
Этот Colab показывает, как использовать универсальный кодировщик предложений Lite для задачи схожести предложений. Этот модуль очень похож на универсальный Предложению кодировщик с той лишь разницей , что вам нужно запустить SentencePiece обработки ваших входных предложений.
Универсальный кодировщик предложений делает получение вложений на уровне предложения таким же простым, как это было исторически при поиске вложений для отдельных слов. Вложения предложений затем можно тривиально использовать для вычисления уровня предложения, означающего сходство, а также для обеспечения лучшей производительности в последующих задачах классификации с использованием менее контролируемых обучающих данных.
Начиная
Настраивать
# Install seaborn for pretty visualizationspip3 install --quiet seaborn# Install SentencePiece package# SentencePiece package is needed for Universal Sentence Encoder Lite. We'll# use it for all the text processing and sentence feature ID lookup.pip3 install --quiet sentencepiece
from absl import logging
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import sentencepiece as spm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
import seaborn as sns
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/compat/v2_compat.py:111: disable_resource_variables (from tensorflow.python.ops.variable_scope) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: non-resource variables are not supported in the long term
Загрузите модуль из TF-Hub
module = hub.Module("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder-lite/2")
input_placeholder = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None, None])
encodings = module(
inputs=dict(
values=input_placeholder.values,
indices=input_placeholder.indices,
dense_shape=input_placeholder.dense_shape))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Загрузить модель SentencePiece из модуля TF-Hub
Модель SentencePiece удобно хранится в активах модуля. Он должен быть загружен для инициализации процессора.
with tf.Session() as sess:
spm_path = sess.run(module(signature="spm_path"))
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(spm_path, mode="rb") as f:
sp.LoadFromSerializedProto(f.read())
print("SentencePiece model loaded at {}.".format(spm_path))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore SentencePiece model loaded at b'/tmp/tfhub_modules/539544f0a997d91c327c23285ea00c37588d92cc/assets/universal_encoder_8k_spm.model'.
def process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, sentences):
# An utility method that processes sentences with the sentence piece processor
# 'sp' and returns the results in tf.SparseTensor-similar format:
# (values, indices, dense_shape)
ids = [sp.EncodeAsIds(x) for x in sentences]
max_len = max(len(x) for x in ids)
dense_shape=(len(ids), max_len)
values=[item for sublist in ids for item in sublist]
indices=[[row,col] for row in range(len(ids)) for col in range(len(ids[row]))]
return (values, indices, dense_shape)
Протестируйте модуль на нескольких примерах
# Compute a representation for each message, showing various lengths supported.
word = "Elephant"
sentence = "I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding."
paragraph = (
"Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. "
"There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer "
"the more 'diluted' the embedding will be.")
messages = [word, sentence, paragraph]
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, messages)
# Reduce logging output.
logging.set_verbosity(logging.ERROR)
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run([tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.tables_initializer()])
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
for i, message_embedding in enumerate(np.array(message_embeddings).tolist()):
print("Message: {}".format(messages[i]))
print("Embedding size: {}".format(len(message_embedding)))
message_embedding_snippet = ", ".join(
(str(x) for x in message_embedding[:3]))
print("Embedding: [{}, ...]\n".format(message_embedding_snippet))
Message: Elephant Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.053387489169836044, 0.053194381296634674, -0.052356015890836716, ...] Message: I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.03533298149704933, -0.04714975506067276, 0.012305550277233124, ...] Message: Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer the more 'diluted' the embedding will be. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [-0.004081667400896549, -0.08954868465662003, 0.03737196698784828, ...]
Пример задачи семантического текстового сходства (STS)
Вложения, производимые универсальным кодировщиком предложений, приблизительно нормализованы. Семантическое сходство двух предложений можно тривиально вычислить как внутренний продукт кодировок.
def plot_similarity(labels, features, rotation):
corr = np.inner(features, features)
sns.set(font_scale=1.2)
g = sns.heatmap(
corr,
xticklabels=labels,
yticklabels=labels,
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
cmap="YlOrRd")
g.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=rotation)
g.set_title("Semantic Textual Similarity")
def run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages):
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp,messages)
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
plot_similarity(messages, message_embeddings, 90)
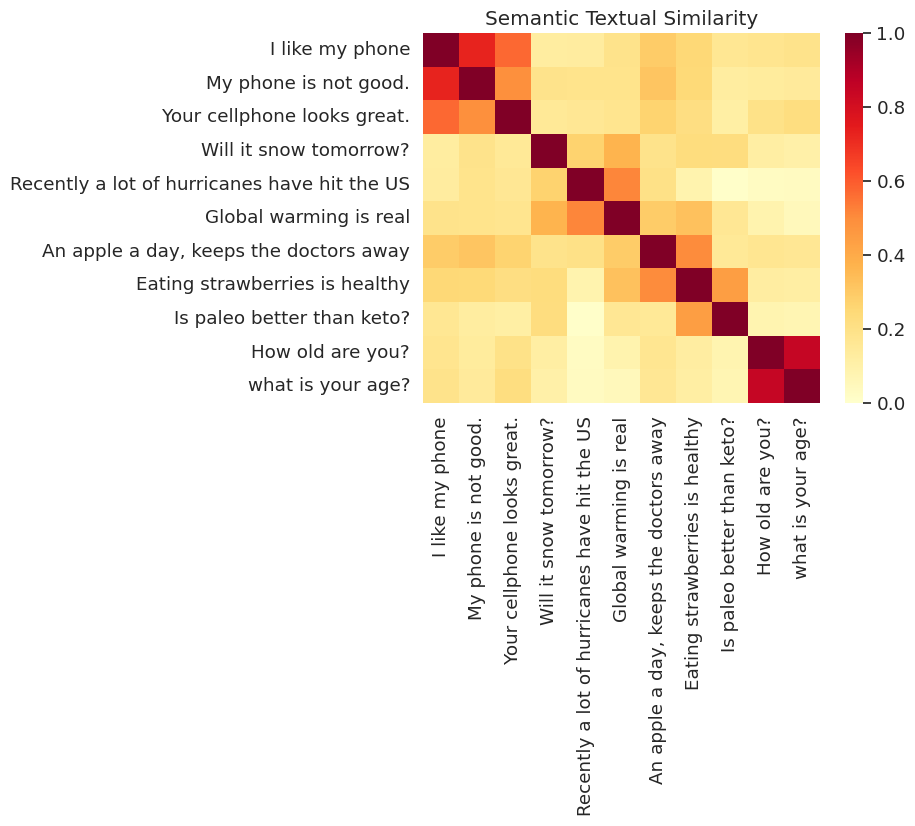
Визуализированное сходство
Здесь мы показываем сходство на тепловой карте. Окончательный график представляет собой матрицу 9х9 , где каждая запись [i, j] окрашен на основе скалярного произведения кодировок для предложения i и j .
messages = [
# Smartphones
"I like my phone",
"My phone is not good.",
"Your cellphone looks great.",
# Weather
"Will it snow tomorrow?",
"Recently a lot of hurricanes have hit the US",
"Global warming is real",
# Food and health
"An apple a day, keeps the doctors away",
"Eating strawberries is healthy",
"Is paleo better than keto?",
# Asking about age
"How old are you?",
"what is your age?",
]
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages)
Оценка: тест STS (семантическое текстовое сходство)
СТС Тест обеспечивает intristic оценки степени , в которой подобие оценка вычисляется с использованием высказыванием вложений совпадают с человеческими суждениями. Тест требует, чтобы системы возвращали оценки сходства для разнообразного выбора пар предложений. Корреляция Пирсона затем используется для оценки качества машины подобия баллов против человеческих суждений.
Скачать данные
import pandas
import scipy
import math
def load_sts_dataset(filename):
# Loads a subset of the STS dataset into a DataFrame. In particular both
# sentences and their human rated similarity score.
sent_pairs = []
with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
for line in f:
ts = line.strip().split("\t")
# (sent_1, sent_2, similarity_score)
sent_pairs.append((ts[5], ts[6], float(ts[4])))
return pandas.DataFrame(sent_pairs, columns=["sent_1", "sent_2", "sim"])
def download_and_load_sts_data():
sts_dataset = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname="Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
origin="http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
extract=True)
sts_dev = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-dev.csv"))
sts_test = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-test.csv"))
return sts_dev, sts_test
sts_dev, sts_test = download_and_load_sts_data()
Downloading data from http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz 417792/409630 [==============================] - 2s 5us/step 425984/409630 [===============================] - 2s 5us/step
Построить оценочный график
sts_input1 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
sts_input2 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
# For evaluation we use exactly normalized rather than
# approximately normalized.
sts_encode1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input1.values,
indices=sts_input1.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input1.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sts_encode2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input2.values,
indices=sts_input2.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input2.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sim_scores = -tf.acos(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(sts_encode1, sts_encode2), axis=1))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Оцените вложения предложений
Выберите набор данных для теста
dataset = sts_dev
values1, indices1, dense_shape1 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_1'].tolist())
values2, indices2, dense_shape2 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_2'].tolist())
similarity_scores = dataset['sim'].tolist()
def run_sts_benchmark(session):
"""Returns the similarity scores"""
scores = session.run(
sim_scores,
feed_dict={
sts_input1.values: values1,
sts_input1.indices: indices1,
sts_input1.dense_shape: dense_shape1,
sts_input2.values: values2,
sts_input2.indices: indices2,
sts_input2.dense_shape: dense_shape2,
})
return scores
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
scores = run_sts_benchmark(session)
pearson_correlation = scipy.stats.pearsonr(scores, similarity_scores)
print('Pearson correlation coefficient = {0}\np-value = {1}'.format(
pearson_correlation[0], pearson_correlation[1]))
Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.7856484874001958 p-value = 1.065794746e-314
