 TensorFlow.org पर देखें TensorFlow.org पर देखें |  Google Colab में चलाएं Google Colab में चलाएं |  गिटहब पर देखें गिटहब पर देखें |  नोटबुक डाउनलोड करें नोटबुक डाउनलोड करें |  टीएफ हब मॉडल देखें टीएफ हब मॉडल देखें |
यह कोलाब आपको दिखाएगा कि TensorFlow हब से डाउनलोड किए गए SPICE मॉडल का उपयोग कैसे करें।
sudo apt-get install -q -y timidity libsndfile1
Reading package lists... Building dependency tree... Reading state information... The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: linux-gcp-5.4-headers-5.4.0-1040 linux-gcp-5.4-headers-5.4.0-1043 linux-gcp-5.4-headers-5.4.0-1044 linux-gcp-5.4-headers-5.4.0-1049 linux-headers-5.4.0-1049-gcp linux-image-5.4.0-1049-gcp linux-modules-5.4.0-1049-gcp linux-modules-extra-5.4.0-1049-gcp Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following additional packages will be installed: freepats libaudio2 libflac8 libjack-jackd2-0 libogg0 libsamplerate0 libvorbis0a libvorbisenc2 timidity-daemon Suggested packages: nas jackd2 fluid-soundfont-gm fluid-soundfont-gs pmidi The following NEW packages will be installed: freepats libaudio2 libflac8 libjack-jackd2-0 libogg0 libsamplerate0 libsndfile1 libvorbis0a libvorbisenc2 timidity timidity-daemon 0 upgraded, 11 newly installed, 0 to remove and 143 not upgraded. Need to get 31.4 MB of archives. After this operation, 40.4 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libogg0 amd64 1.3.2-1 [17.2 kB] Get:2 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/universe amd64 freepats all 20060219-1 [29.0 MB] Get:3 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libaudio2 amd64 1.9.4-6 [50.3 kB] Get:4 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libflac8 amd64 1.3.2-1 [213 kB] Get:5 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libsamplerate0 amd64 0.1.9-1 [938 kB] Get:6 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libjack-jackd2-0 amd64 1.9.12~dfsg-2 [263 kB] Get:7 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libvorbis0a amd64 1.3.5-4.2 [86.4 kB] Get:8 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 libvorbisenc2 amd64 1.3.5-4.2 [70.7 kB] Get:9 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main amd64 libsndfile1 amd64 1.0.28-4ubuntu0.18.04.2 [170 kB] Get:10 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/universe amd64 timidity amd64 2.13.2-41 [585 kB] Get:11 http://asia-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/universe amd64 timidity-daemon all 2.13.2-41 [5984 B] Fetched 31.4 MB in 2s (14.5 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libogg0:amd64. (Reading database ... 281949 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../00-libogg0_1.3.2-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libogg0:amd64 (1.3.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package freepats. Preparing to unpack .../01-freepats_20060219-1_all.deb ... Unpacking freepats (20060219-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libaudio2:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../02-libaudio2_1.9.4-6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libaudio2:amd64 (1.9.4-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package libflac8:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../03-libflac8_1.3.2-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libflac8:amd64 (1.3.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsamplerate0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../04-libsamplerate0_0.1.9-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsamplerate0:amd64 (0.1.9-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjack-jackd2-0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../05-libjack-jackd2-0_1.9.12~dfsg-2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libjack-jackd2-0:amd64 (1.9.12~dfsg-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libvorbis0a:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../06-libvorbis0a_1.3.5-4.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libvorbis0a:amd64 (1.3.5-4.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libvorbisenc2:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../07-libvorbisenc2_1.3.5-4.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libvorbisenc2:amd64 (1.3.5-4.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsndfile1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../08-libsndfile1_1.0.28-4ubuntu0.18.04.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsndfile1:amd64 (1.0.28-4ubuntu0.18.04.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package timidity. Preparing to unpack .../09-timidity_2.13.2-41_amd64.deb ... Unpacking timidity (2.13.2-41) ... Selecting previously unselected package timidity-daemon. Preparing to unpack .../10-timidity-daemon_2.13.2-41_all.deb ... Unpacking timidity-daemon (2.13.2-41) ... Setting up libogg0:amd64 (1.3.2-1) ... Setting up libsamplerate0:amd64 (0.1.9-1) ... Setting up freepats (20060219-1) ... Setting up libvorbis0a:amd64 (1.3.5-4.2) ... Setting up libaudio2:amd64 (1.9.4-6) ... Setting up libflac8:amd64 (1.3.2-1) ... Setting up libjack-jackd2-0:amd64 (1.9.12~dfsg-2) ... Setting up libvorbisenc2:amd64 (1.3.5-4.2) ... Setting up timidity (2.13.2-41) ... Setting up libsndfile1:amd64 (1.0.28-4ubuntu0.18.04.2) ... Setting up timidity-daemon (2.13.2-41) ... Adding group timidity....done Adding system user timidity....done Adding user `timidity' to group `audio' ... Adding user timidity to group audio Done. Processing triggers for man-db (2.8.3-2ubuntu0.1) ... Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-21) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.27-3ubuntu1.2) ... Processing triggers for systemd (237-3ubuntu10.50) ...
# All the imports to deal with sound datapip install pydub numba==0.48 librosa music21
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import librosa
from librosa import display as librosadisplay
import logging
import math
import statistics
import sys
from IPython.display import Audio, Javascript
from scipy.io import wavfile
from base64 import b64decode
import music21
from pydub import AudioSegment
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
print("tensorflow: %s" % tf.__version__)
#print("librosa: %s" % librosa.__version__)
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numba/errors.py:137: UserWarning: Insufficiently recent colorama version found. Numba requires colorama >= 0.3.9
warnings.warn(msg)
tensorflow: 2.7.0
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pydub/utils.py:170: RuntimeWarning: Couldn't find ffmpeg or avconv - defaulting to ffmpeg, but may not work
warn("Couldn't find ffmpeg or avconv - defaulting to ffmpeg, but may not work", RuntimeWarning)
ऑडियो इनपुट फ़ाइल
अब सबसे कठिन हिस्सा: अपना गायन रिकॉर्ड करें! :)
हम ऑडियो फ़ाइल प्राप्त करने के लिए चार तरीके प्रदान करते हैं:
- सीधे कोलाब में ऑडियो रिकॉर्ड करें
- अपने कंप्यूटर से अपलोड करें
- Google डिस्क पर सहेजी गई फ़ाइल का उपयोग करें
- वेब से फ़ाइल डाउनलोड करें
नीचे दी गई चार विधियों में से एक चुनें।
[इसे चलाएं] सीधे ब्राउज़र से ऑडियो रिकॉर्ड करने के लिए जेएस कोड की परिभाषा
RECORD = """
const sleep = time => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, time))
const b2text = blob => new Promise(resolve => {
const reader = new FileReader()
reader.onloadend = e => resolve(e.srcElement.result)
reader.readAsDataURL(blob)
})
var record = time => new Promise(async resolve => {
stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: true })
recorder = new MediaRecorder(stream)
chunks = []
recorder.ondataavailable = e => chunks.push(e.data)
recorder.start()
await sleep(time)
recorder.onstop = async ()=>{
blob = new Blob(chunks)
text = await b2text(blob)
resolve(text)
}
recorder.stop()
})
"""
def record(sec=5):
try:
from google.colab import output
except ImportError:
print('No possible to import output from google.colab')
return ''
else:
print('Recording')
display(Javascript(RECORD))
s = output.eval_js('record(%d)' % (sec*1000))
fname = 'recorded_audio.wav'
print('Saving to', fname)
b = b64decode(s.split(',')[1])
with open(fname, 'wb') as f:
f.write(b)
return fname
अपना ऑडियो इनपुट करने का तरीका चुनें
INPUT_SOURCE = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav'
print('You selected', INPUT_SOURCE)
if INPUT_SOURCE == 'RECORD':
uploaded_file_name = record(5)
elif INPUT_SOURCE == 'UPLOAD':
try:
from google.colab import files
except ImportError:
print("ImportError: files from google.colab seems to not be available")
else:
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(
name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
uploaded_file_name = next(iter(uploaded))
print('Uploaded file: ' + uploaded_file_name)
elif INPUT_SOURCE.startswith('./drive/'):
try:
from google.colab import drive
except ImportError:
print("ImportError: files from google.colab seems to not be available")
else:
drive.mount('/content/drive')
# don't forget to change the name of the file you
# will you here!
gdrive_audio_file = 'YOUR_MUSIC_FILE.wav'
uploaded_file_name = INPUT_SOURCE
elif INPUT_SOURCE.startswith('http'):
!wget --no-check-certificate 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav' -O c-scale.wav
uploaded_file_name = 'c-scale.wav'
else:
print('Unrecognized input format!')
print('Please select "RECORD", "UPLOAD", or specify a file hosted on Google Drive or a file from the web to download file to download')
You selected https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav --2021-11-05 11:10:55-- https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav Resolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 108.177.97.128, 64.233.189.128, 74.125.203.128, ... Connecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|108.177.97.128|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 384728 (376K) [audio/wav] Saving to: ‘c-scale.wav’ c-scale.wav 100%[===================>] 375.71K --.-KB/s in 0.006s 2021-11-05 11:10:56 (65.4 MB/s) - ‘c-scale.wav’ saved [384728/384728]
ऑडियो डेटा तैयार करना
अब हमारे पास ऑडियो है, आइए इसे अपेक्षित प्रारूप में बदलें और फिर इसे सुनें!
SPICE मॉडल को इनपुट के रूप में 16kHz की नमूना दर और केवल एक चैनल (मोनो) के साथ एक ऑडियो फ़ाइल की आवश्यकता होती है।
इस भाग में आपकी मदद के लिए, हम एक समारोह (बनाया convert_audio_for_model मॉडल की उम्मीद प्रारूप करने के लिए किसी भी wav फ़ाइल आप परिवर्तित करने के लिए):
# Function that converts the user-created audio to the format that the model
# expects: bitrate 16kHz and only one channel (mono).
EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE = 16000
def convert_audio_for_model(user_file, output_file='converted_audio_file.wav'):
audio = AudioSegment.from_file(user_file)
audio = audio.set_frame_rate(EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE).set_channels(1)
audio.export(output_file, format="wav")
return output_file
# Converting to the expected format for the model
# in all the input 4 input method before, the uploaded file name is at
# the variable uploaded_file_name
converted_audio_file = convert_audio_for_model(uploaded_file_name)
# Loading audio samples from the wav file:
sample_rate, audio_samples = wavfile.read(converted_audio_file, 'rb')
# Show some basic information about the audio.
duration = len(audio_samples)/sample_rate
print(f'Sample rate: {sample_rate} Hz')
print(f'Total duration: {duration:.2f}s')
print(f'Size of the input: {len(audio_samples)}')
# Let's listen to the wav file.
Audio(audio_samples, rate=sample_rate)
Sample rate: 16000 Hz Total duration: 11.89s Size of the input: 190316
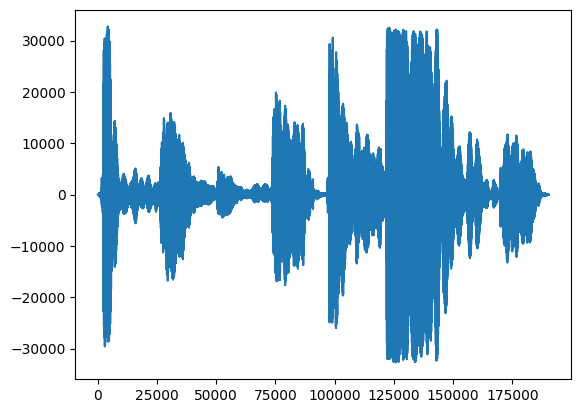
सबसे पहले, आइए हमारे गायन की तरंग पर एक नजर डालते हैं।
# We can visualize the audio as a waveform.
_ = plt.plot(audio_samples)
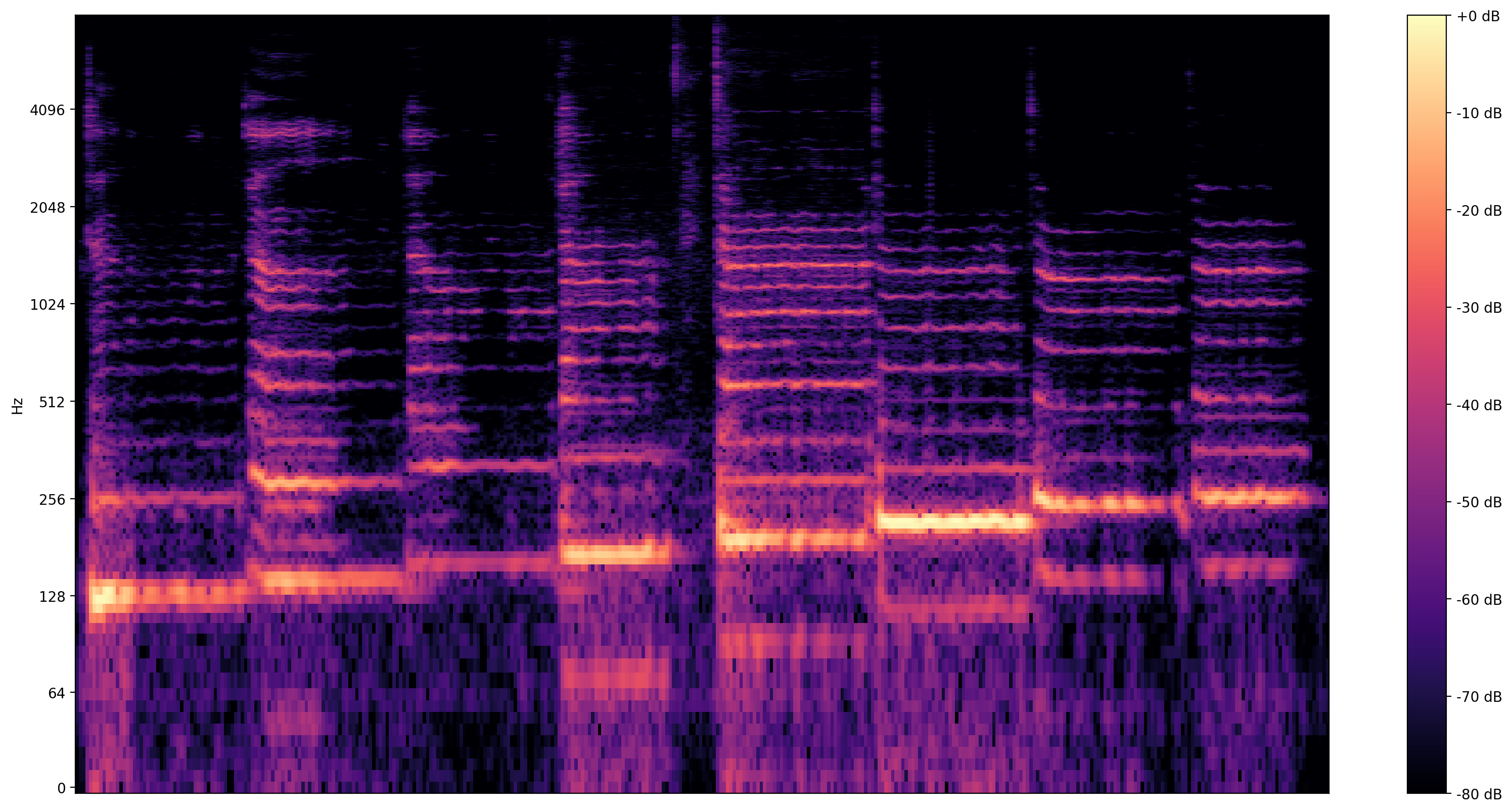
एक अधिक सूचनात्मक दृश्य है spectrogram , जो शो आवृत्तियों समय के साथ प्रस्तुत करते हैं।
यहाँ, हम गायन को अधिक स्पष्ट रूप से दृश्यमान बनाने के लिए एक लघुगणक आवृत्ति पैमाने का उपयोग करते हैं।
MAX_ABS_INT16 = 32768.0
def plot_stft(x, sample_rate, show_black_and_white=False):
x_stft = np.abs(librosa.stft(x, n_fft=2048))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
x_stft_db = librosa.amplitude_to_db(x_stft, ref=np.max)
if(show_black_and_white):
librosadisplay.specshow(data=x_stft_db, y_axis='log',
sr=sample_rate, cmap='gray_r')
else:
librosadisplay.specshow(data=x_stft_db, y_axis='log', sr=sample_rate)
plt.colorbar(format='%+2.0f dB')
plot_stft(audio_samples / MAX_ABS_INT16 , sample_rate=EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE)
plt.show()
हमें यहां एक आखिरी रूपांतरण की जरूरत है। ऑडियो नमूने int16 प्रारूप में हैं। उन्हें -1 और 1 के बीच तैरने के लिए सामान्यीकृत करने की आवश्यकता है।
audio_samples = audio_samples / float(MAX_ABS_INT16)
मॉडल का निष्पादन
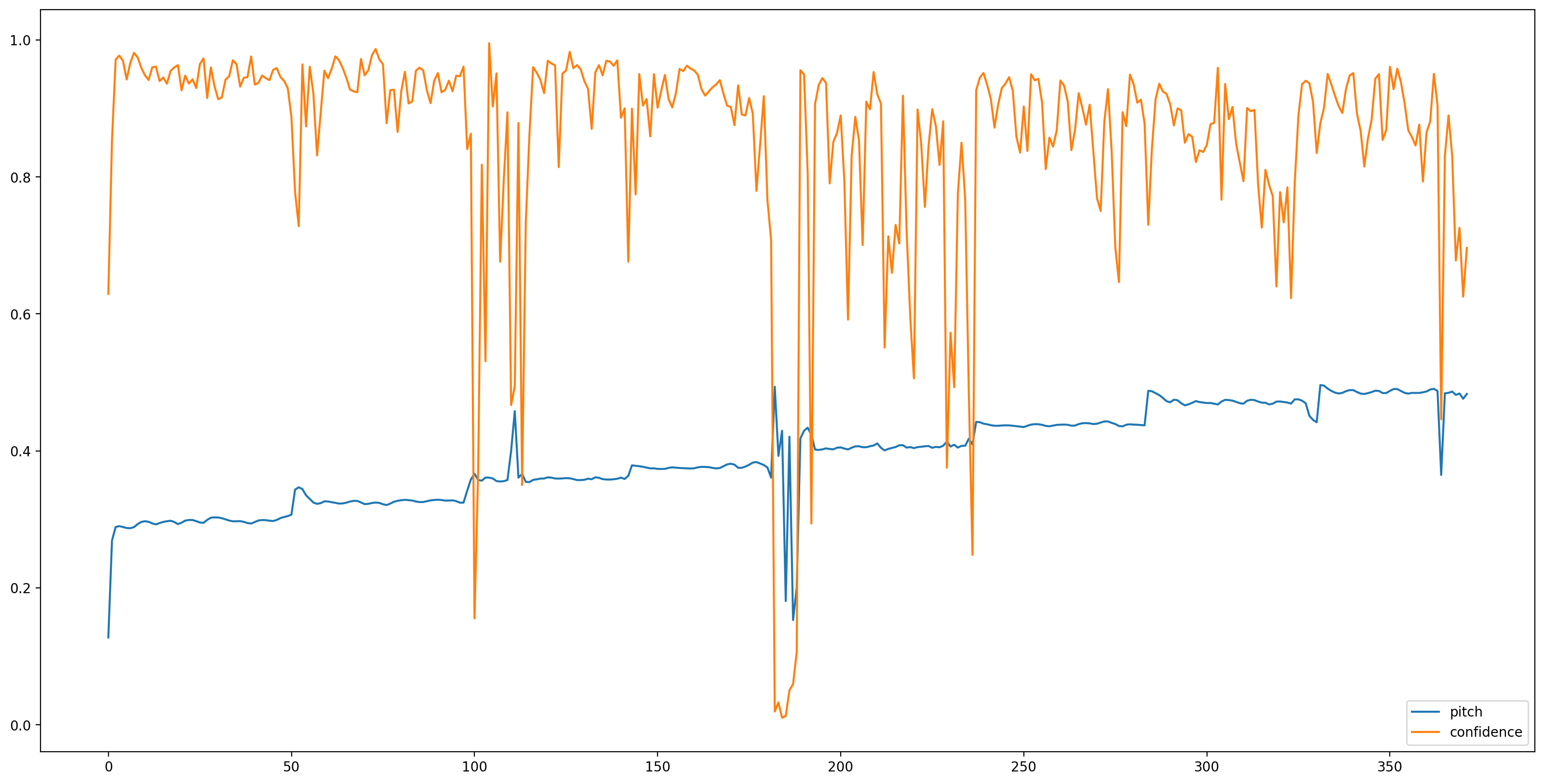
अब आसान हिस्सा है, के TensorFlow हब के साथ मॉडल लोड करते हैं, और यह करने के लिए ऑडियो फ़ीड। SPICE हमें दो आउटपुट देगा: पिच और अनिश्चितता
TensorFlow हब प्रकाशन, खोज, और मशीन लर्निंग मॉडल का पुन: प्रयोज्य भागों की खपत के लिए एक पुस्तकालय है। यह आपकी चुनौतियों को हल करने के लिए मशीन लर्निंग का उपयोग करना आसान बनाता है।
मॉडल को लोड करने के लिए आपको बस हब मॉड्यूल और मॉडल की ओर इशारा करने वाले URL की आवश्यकता है:
# Loading the SPICE model is easy:
model = hub.load("https://tfhub.dev/google/spice/2")
WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables().
मॉडल लोड होने के साथ, डेटा तैयार होने पर, हमें परिणाम प्राप्त करने के लिए 3 लाइनों की आवश्यकता होती है:
# We now feed the audio to the SPICE tf.hub model to obtain pitch and uncertainty outputs as tensors.
model_output = model.signatures["serving_default"](tf.constant(audio_samples, tf.float32))
pitch_outputs = model_output["pitch"]
uncertainty_outputs = model_output["uncertainty"]
# 'Uncertainty' basically means the inverse of confidence.
confidence_outputs = 1.0 - uncertainty_outputs
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
plt.plot(pitch_outputs, label='pitch')
plt.plot(confidence_outputs, label='confidence')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
आइए कम आत्मविश्वास (आत्मविश्वास <0.9) के साथ सभी पिच अनुमानों को हटाकर परिणामों को समझना आसान बनाते हैं और शेष को प्लॉट करते हैं।
confidence_outputs = list(confidence_outputs)
pitch_outputs = [ float(x) for x in pitch_outputs]
indices = range(len (pitch_outputs))
confident_pitch_outputs = [ (i,p)
for i, p, c in zip(indices, pitch_outputs, confidence_outputs) if c >= 0.9 ]
confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y = zip(*confident_pitch_outputs)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y, )
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y, c="r")
plt.show()
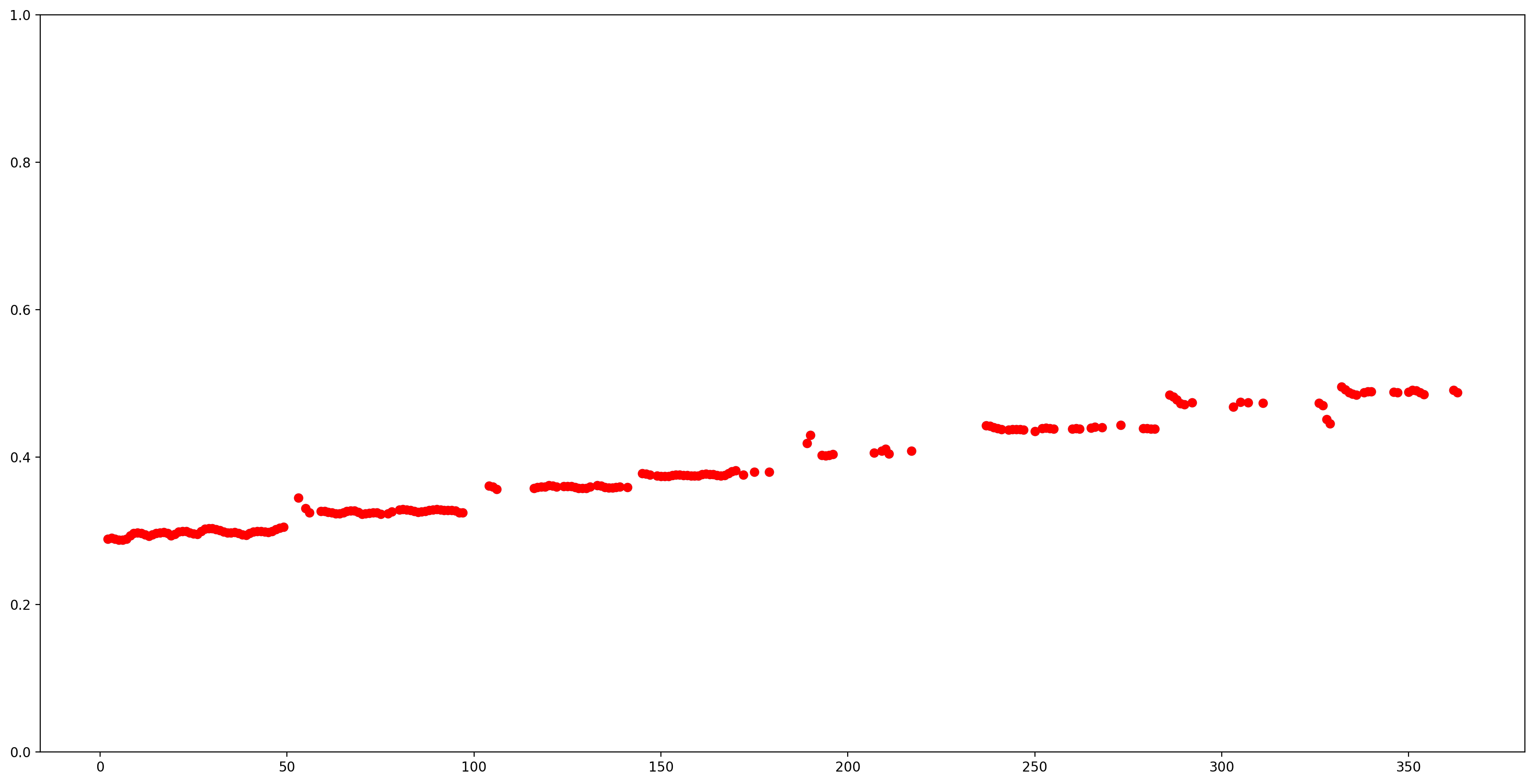
SPICE द्वारा लौटाए गए पिच मान 0 से 1 की सीमा में हैं। आइए उन्हें Hz में पूर्ण पिच मानों में परिवर्तित करें।
def output2hz(pitch_output):
# Constants taken from https://tfhub.dev/google/spice/2
PT_OFFSET = 25.58
PT_SLOPE = 63.07
FMIN = 10.0;
BINS_PER_OCTAVE = 12.0;
cqt_bin = pitch_output * PT_SLOPE + PT_OFFSET;
return FMIN * 2.0 ** (1.0 * cqt_bin / BINS_PER_OCTAVE)
confident_pitch_values_hz = [ output2hz(p) for p in confident_pitch_outputs_y ]
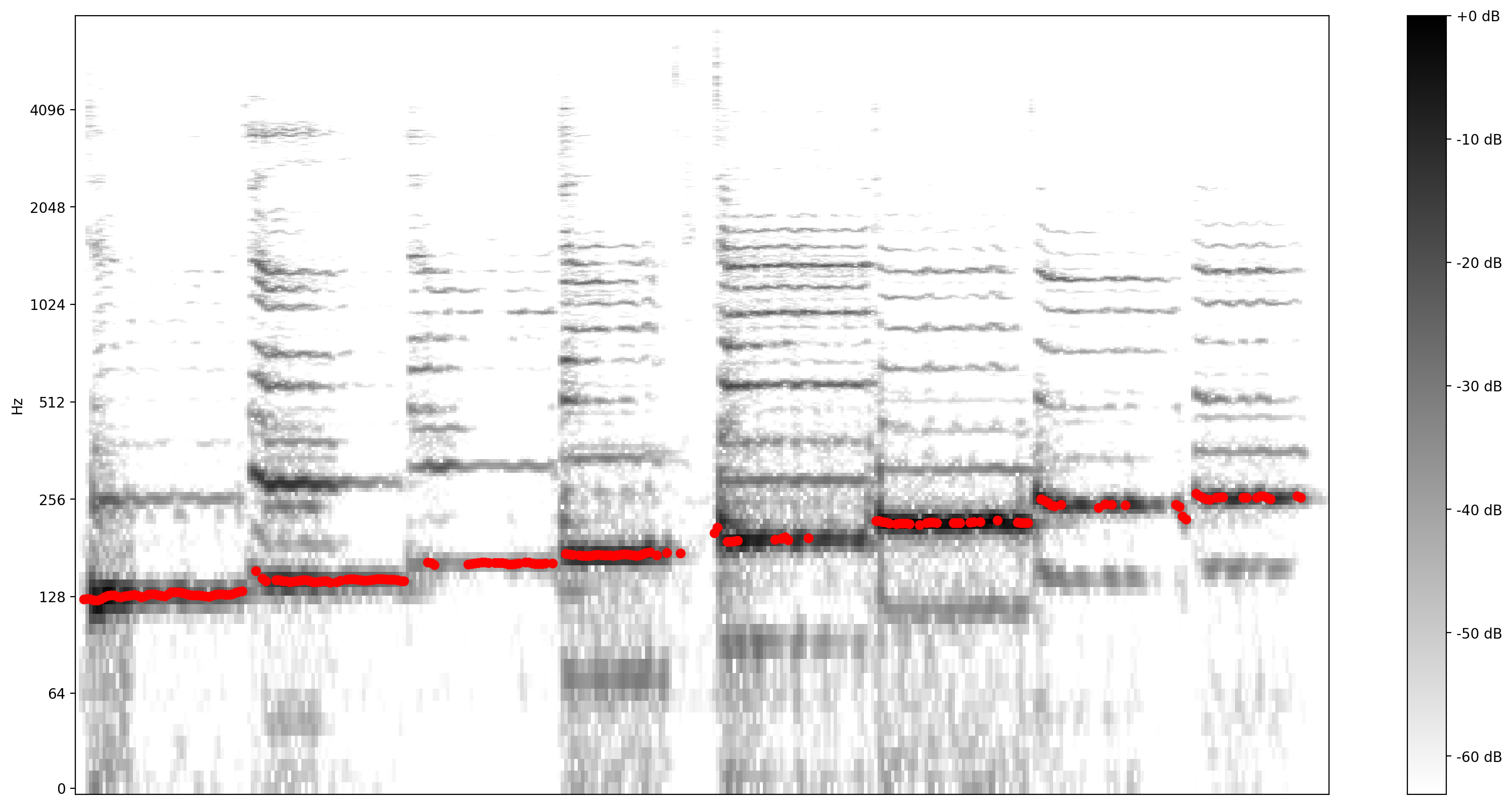
अब, देखते हैं कि भविष्यवाणी कितनी अच्छी है: हम मूल स्पेक्ट्रोग्राम पर अनुमानित पिचों को ओवरले करेंगे। पिच की भविष्यवाणियों को और अधिक दृश्यमान बनाने के लिए, हमने स्पेक्ट्रोग्राम को ब्लैक एंड व्हाइट में बदल दिया।
plot_stft(audio_samples / MAX_ABS_INT16 ,
sample_rate=EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE, show_black_and_white=True)
# Note: conveniently, since the plot is in log scale, the pitch outputs
# also get converted to the log scale automatically by matplotlib.
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_values_hz, c="r")
plt.show()
संगीत नोट्स में कनवर्ट करना
अब जब हमारे पास पिच मान हैं, तो आइए उन्हें नोट्स में बदलें! यह हिस्सा अपने आप में चुनौतीपूर्ण है। हमें दो बातों का ध्यान रखना होगा:
- बाकी (जब कोई गायन नहीं है)
- प्रत्येक नोट का आकार (ऑफ़सेट)
1: जब कोई गायन नहीं होता है तो यह इंगित करने के लिए आउटपुट में शून्य जोड़ना
pitch_outputs_and_rests = [
output2hz(p) if c >= 0.9 else 0
for i, p, c in zip(indices, pitch_outputs, confidence_outputs)
]
2: नोट ऑफ़सेट जोड़ना
जब कोई व्यक्ति स्वतंत्र रूप से गाता है, तो माधुर्य में निरपेक्ष पिच मूल्यों की भरपाई हो सकती है जो नोट्स का प्रतिनिधित्व कर सकते हैं। इसलिए, भविष्यवाणियों को नोट्स में बदलने के लिए, इस संभावित ऑफसेट को सही करने की आवश्यकता है। यह निम्नलिखित कोड गणना करता है।
A4 = 440
C0 = A4 * pow(2, -4.75)
note_names = ["C", "C#", "D", "D#", "E", "F", "F#", "G", "G#", "A", "A#", "B"]
def hz2offset(freq):
# This measures the quantization error for a single note.
if freq == 0: # Rests always have zero error.
return None
# Quantized note.
h = round(12 * math.log2(freq / C0))
return 12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - h
# The ideal offset is the mean quantization error for all the notes
# (excluding rests):
offsets = [hz2offset(p) for p in pitch_outputs_and_rests if p != 0]
print("offsets: ", offsets)
ideal_offset = statistics.mean(offsets)
print("ideal offset: ", ideal_offset)
offsets: [0.2851075707500712, 0.3700368844097355, 0.2861639241998972, 0.19609005646164235, 0.17851737247163868, 0.27334483073408933, -0.4475316266590852, -0.24651997073237908, -0.1796558047706398, -0.23060136331860548, -0.3782634107643901, -0.4725100625926686, -0.3457194541269999, -0.2436666886383776, -0.1818906877810207, -0.1348077739650435, -0.24551812662426897, -0.4454903457934165, -0.3126792745167535, -0.12241723670307181, -0.06614479972665066, -0.06702634735648871, -0.1744135098034576, -0.29365551425759406, -0.32520890458170726, -0.056438377636119696, 0.1470525135224534, 0.17167006002122775, 0.16529246704037348, 0.09569531546290477, -0.006323616641203955, -0.11799822075907684, -0.18835098459069144, -0.17934754504506145, -0.17215419157092526, -0.23695828034226452, -0.34594501002376177, -0.39380045278613807, -0.2528674895936689, -0.11009248657768467, -0.07118597401920113, -0.08042248799149121, -0.12799598588293293, -0.16227484329287023, -0.05931985421721464, 0.10667800800259641, 0.21044687793906292, 0.2931939382975841, -0.22329278631751492, -0.12365553720538003, -0.4571117360765271, -0.34864566459005175, -0.35947798653189267, -0.4313175396496476, -0.4818928106004421, 0.44220950977261, 0.45883109973128455, -0.47095522924010425, -0.3674495078498552, -0.3047186536962201, -0.31075979246441676, -0.4501382996017185, 0.3966096259778311, 0.4238116671269694, 0.4982676686471237, -0.45932030423227843, -0.4890504510576079, 0.3836871527260044, 0.4441304941600137, -0.38787359430138935, -0.24855899466817277, -0.20666386647764057, -0.23811575664822726, -0.2760223047310504, -0.3641714288169524, -0.41670903606955534, -0.41009272976462086, -0.3340427999073796, -0.26122959716860805, -0.2232610212141708, -0.19940660549943345, -0.22528914465252825, -0.2780899004513415, -0.2744434134537457, -0.25654931231085953, -0.33068201704567457, -0.4678933079416083, -0.4695135511333177, -0.1648153518015647, -0.24618840082233362, -0.48052406086269883, -0.3771743489677135, -0.32261801643912236, -0.25560347987954657, -0.24629741950576545, -0.14035005553309787, -0.16659160448853783, -0.2442749349648139, -0.236978201704666, -0.20882506652418442, -0.22637331529204374, -0.29836135937516417, -0.39081484182421633, -0.3909877680117404, -0.3650093676025108, -0.2642347521955202, -0.13023199393098395, -0.18214744283501716, -0.3020867909366345, -0.33754229827467697, -0.34391801162306024, -0.31454499496763333, -0.26713502510135356, -0.2910439501578139, -0.11686573876684037, -0.1673094354445226, -0.24345334692542053, -0.30852998240535356, -0.35647376789395935, -0.37154654069487236, -0.3600149954730796, -0.2667062802488047, -0.21902000440899627, -0.2484456507736752, -0.2774107871825038, -0.2941432754570741, -0.31118778272216474, -0.32662896348779213, -0.3053947554403962, -0.2160201109821145, -0.17343703730647775, -0.17792559965198507, -0.19880643679444177, -0.2725068260604502, -0.3152120758468442, -0.28217377586905457, -0.11595223738495974, 0.0541902144377957, 0.11488166735824024, -0.2559698195630773, 0.01930235610660702, -0.002236352401425279, 0.4468796487277231, 0.15514959977323883, 0.4207694853966899, 0.3854474319642236, 0.4373497234409598, -0.4694994504625001, -0.3662719146782649, -0.20354085369650932, -0.015043790774988963, -0.4185651697093675, -0.17896653874461066, -0.032896162706066434, -0.061098168330843805, -0.1953772325689087, -0.2545198683315988, -0.3363741032654488, -0.39191536320988973, -0.36531668408458984, -0.3489657612020167, -0.35455202891175475, -0.38925192399566555, 0.48781635300571935, -0.2820884378129733, -0.241939488189864, -0.24987341685836384, -0.3034880535179809, -0.2910712014014081, -0.2783103765422581, -0.30017802073304267, -0.23735882385318519, -0.15802705569807785, -0.1688725350672513, 0.00533368216211727, -0.2545762573057857, -0.28210347487274845, -0.29791870250051034, -0.3228369901949648, -0.3895802937323367, 0.4323827980583488, 0.17439196334535723, -0.12961039467398905, -0.2236296109730489, -0.04022635205333813, -0.4264043621594098, -0.0019025255615048309, -0.07466309859101727, -0.08665327413623203, -0.08169104440753472, -0.31617519541327965, -0.47420548422877573, 0.1502044753855003, 0.30507923857624064, 0.031032583278971515, -0.17852388186996393, -0.3371347884709195, -0.41780861421172233, -0.2023933346444835, -0.10604901297633518, -0.10771248771493447, -0.16037790997569346, -0.18698410763089868, -0.17355977250879562, -0.008242337244190878, -0.011401999431292609, -0.1876701734835322, -0.3601715640598968, 0.011681766969516616, -0.1931417836124183] ideal offset: -0.16889341450193418
अब हम गाए गए नोटों के सबसे संभावित अनुक्रम का अनुमान लगाने और अनुमान लगाने के लिए कुछ अनुमानों का उपयोग कर सकते हैं। ऊपर गणना की गई आदर्श ऑफसेट एक घटक है - लेकिन हमें गति (कितनी भविष्यवाणियां, कहते हैं, आठवां?) इसे सरल रखने के लिए, हम बस अलग-अलग गति और समय ऑफसेट का प्रयास करेंगे और अंत में इस त्रुटि को कम करने वाले मानों का उपयोग करके परिमाणीकरण त्रुटि को मापेंगे।
def quantize_predictions(group, ideal_offset):
# Group values are either 0, or a pitch in Hz.
non_zero_values = [v for v in group if v != 0]
zero_values_count = len(group) - len(non_zero_values)
# Create a rest if 80% is silent, otherwise create a note.
if zero_values_count > 0.8 * len(group):
# Interpret as a rest. Count each dropped note as an error, weighted a bit
# worse than a badly sung note (which would 'cost' 0.5).
return 0.51 * len(non_zero_values), "Rest"
else:
# Interpret as note, estimating as mean of non-rest predictions.
h = round(
statistics.mean([
12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - ideal_offset for freq in non_zero_values
]))
octave = h // 12
n = h % 12
note = note_names[n] + str(octave)
# Quantization error is the total difference from the quantized note.
error = sum([
abs(12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - ideal_offset - h)
for freq in non_zero_values
])
return error, note
def get_quantization_and_error(pitch_outputs_and_rests, predictions_per_eighth,
prediction_start_offset, ideal_offset):
# Apply the start offset - we can just add the offset as rests.
pitch_outputs_and_rests = [0] * prediction_start_offset + \
pitch_outputs_and_rests
# Collect the predictions for each note (or rest).
groups = [
pitch_outputs_and_rests[i:i + predictions_per_eighth]
for i in range(0, len(pitch_outputs_and_rests), predictions_per_eighth)
]
quantization_error = 0
notes_and_rests = []
for group in groups:
error, note_or_rest = quantize_predictions(group, ideal_offset)
quantization_error += error
notes_and_rests.append(note_or_rest)
return quantization_error, notes_and_rests
best_error = float("inf")
best_notes_and_rests = None
best_predictions_per_note = None
for predictions_per_note in range(20, 65, 1):
for prediction_start_offset in range(predictions_per_note):
error, notes_and_rests = get_quantization_and_error(
pitch_outputs_and_rests, predictions_per_note,
prediction_start_offset, ideal_offset)
if error < best_error:
best_error = error
best_notes_and_rests = notes_and_rests
best_predictions_per_note = predictions_per_note
# At this point, best_notes_and_rests contains the best quantization.
# Since we don't need to have rests at the beginning, let's remove these:
while best_notes_and_rests[0] == 'Rest':
best_notes_and_rests = best_notes_and_rests[1:]
# Also remove silence at the end.
while best_notes_and_rests[-1] == 'Rest':
best_notes_and_rests = best_notes_and_rests[:-1]
अब परिमाणित नोट्स को शीट संगीत स्कोर के रूप में लिखते हैं!
यह ऐसा करने के लिए हम दो पुस्तकालयों का उपयोग करेगा: music21 और ओपन शीट संगीत प्रदर्शन
# Creating the sheet music score.
sc = music21.stream.Score()
# Adjust the speed to match the actual singing.
bpm = 60 * 60 / best_predictions_per_note
print ('bpm: ', bpm)
a = music21.tempo.MetronomeMark(number=bpm)
sc.insert(0,a)
for snote in best_notes_and_rests:
d = 'half'
if snote == 'Rest':
sc.append(music21.note.Rest(type=d))
else:
sc.append(music21.note.Note(snote, type=d))
bpm: 78.26086956521739
[इसे चलाएं] एक संगीत स्कोर दिखाने के लिए ओपन शीट म्यूजिक डिस्प्ले (जेएस कोड) का उपयोग करने के लिए हेल्पर फ़ंक्शन
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML, Javascript
import json, random
def showScore(score):
xml = open(score.write('musicxml')).read()
showMusicXML(xml)
def showMusicXML(xml):
DIV_ID = "OSMD_div"
display(HTML('<div id="'+DIV_ID+'">loading OpenSheetMusicDisplay</div>'))
script = """
var div_id = { {DIV_ID} };
function loadOSMD() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
if (window.opensheetmusicdisplay) {
return resolve(window.opensheetmusicdisplay)
}
// OSMD script has a 'define' call which conflicts with requirejs
var _define = window.define // save the define object
window.define = undefined // now the loaded script will ignore requirejs
var s = document.createElement( 'script' );
s.setAttribute( 'src', "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/opensheetmusicdisplay@0.7.6/build/opensheetmusicdisplay.min.js" );
//s.setAttribute( 'src', "/custom/opensheetmusicdisplay.js" );
s.onload=function(){
window.define = _define
resolve(opensheetmusicdisplay);
};
document.body.appendChild( s ); // browser will try to load the new script tag
})
}
loadOSMD().then((OSMD)=>{
window.openSheetMusicDisplay = new OSMD.OpenSheetMusicDisplay(div_id, {
drawingParameters: "compacttight"
});
openSheetMusicDisplay
.load({ {data} })
.then(
function() {
openSheetMusicDisplay.render();
}
);
})
""".replace('{ {DIV_ID} }',DIV_ID).replace('{ {data} }',json.dumps(xml))
display(Javascript(script))
return
# rendering the music score
showScore(sc)
print(best_notes_and_rests)
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/music21/musicxml/m21ToXml.py:465: MusicXMLWarning: <music21.stream.Score 0x7f276c652190> is not well-formed; see isWellFormedNotation() category=MusicXMLWarning)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object> ['C3', 'D3', 'E3', 'F3', 'G3', 'A3', 'B3', 'C4']
आइए संगीत नोट्स को एक MIDI फ़ाइल में बदलें और इसे सुनें।
इस फ़ाइल को बनाने के लिए, हम पहले बनाई गई स्ट्रीम का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
# Saving the recognized musical notes as a MIDI file
converted_audio_file_as_midi = converted_audio_file[:-4] + '.mid'
fp = sc.write('midi', fp=converted_audio_file_as_midi)
wav_from_created_midi = converted_audio_file_as_midi.replace(' ', '_') + "_midioutput.wav"
print(wav_from_created_midi)
converted_audio_file.mid_midioutput.wav
इसे कोलाब पर सुनने के लिए, हमें इसे वापस wav में बदलना होगा। ऐसा करने का एक आसान तरीका टिमिडिटी का उपयोग करना है।
timidity $converted_audio_file_as_midi -Ow -o $wav_from_created_midi
Playing converted_audio_file.mid MIDI file: converted_audio_file.mid Format: 1 Tracks: 2 Divisions: 1024 Track name: Playing time: ~16 seconds Notes cut: 0 Notes lost totally: 0
और अंत में, मॉडल द्वारा अनुमानित अनुमानित पिचों से MIDI के माध्यम से बनाए गए नोट्स से बनाए गए ऑडियो को सुनें!
Audio(wav_from_created_midi)
