 View on TensorFlow.org View on TensorFlow.org
|
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
 View source on GitHub View source on GitHub
|
 Download notebook Download notebook
|
This tutorial demonstrates two ways to load and preprocess text.
- First, you will use Keras utilities and preprocessing layers. These include
tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directoryto turn data into atf.data.Datasetandtf.keras.layers.TextVectorizationfor data standardization, tokenization, and vectorization. If you are new to TensorFlow, you should start with these. - Then, you will use lower-level utilities like
tf.data.TextLineDatasetto load text files,tf.lookupfor custom in-model lookup tables, and TensorFlow Text APIs, such astext.UnicodeScriptTokenizerandtext.case_fold_utf8, to preprocess the data for finer-grain control.
pip install "tensorflow-text==2.13.*"import collections
import pathlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow.keras import utils
from tensorflow.keras.layers import TextVectorization
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow_text as tf_text
Example 1: Predict the tag for a Stack Overflow question
As a first example, you will download a dataset of programming questions from Stack Overflow. Each question ("How do I sort a dictionary by value?") is labeled with exactly one tag (Python, CSharp, JavaScript, or Java). Your task is to develop a model that predicts the tag for a question. This is an example of multi-class classification—an important and widely applicable kind of machine learning problem.
To implement this task, you'll start with the simplest tools:
keras.utils.text_datasaet_from_directory: for loading text-file examples.keras.layers.TextVectorization: for converting strings to token indices.
Download and explore the dataset
Begin by downloading the Stack Overflow dataset using tf.keras.utils.get_file, and exploring the directory structure:
data_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/stack_overflow_16k.tar.gz'
dataset_dir = utils.get_file(
origin=data_url,
untar=True,
cache_dir='stack_overflow',
cache_subdir='')
dataset_dir = pathlib.Path(dataset_dir).parent
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/stack_overflow_16k.tar.gz 6053168/6053168 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
list(dataset_dir.iterdir())
[PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/stack_overflow_16k.tar.gz'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/README.md'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/train'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/test')]
train_dir = dataset_dir/'train'
list(train_dir.iterdir())
[PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/train/java'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/train/csharp'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/train/python'),
PosixPath('/tmp/.keras/train/javascript')]
The train/csharp, train/java, train/python and train/javascript directories contain many text files, each of which is a Stack Overflow question.
Print an example file and inspect the data:
sample_file = train_dir/'python/1755.txt'
with open(sample_file) as f:
print(f.read())
why does this blank program print true x=true.def stupid():. x=false.stupid().print x
Load the dataset
Next, you will load the data off-disk and prepare it into a format suitable for training. To do so, you will use the tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directory utility to create a labeled tf.data.Dataset. If you're new to tf.data, it's a powerful collection of tools for building input pipelines. (Learn more in the tf.data: Build TensorFlow input pipelines guide.)
The tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directory API expects a directory structure as follows:
train/
...csharp/
......1.txt
......2.txt
...java/
......1.txt
......2.txt
...javascript/
......1.txt
......2.txt
...python/
......1.txt
......2.txt
When running a machine learning experiment, it is a best practice to divide your dataset into three splits: training, validation, and test.
The Stack Overflow dataset has already been divided into training and test sets, but it lacks a validation set.
Create a validation set using an 80:20 split of the training data by using tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directory with validation_split set to 0.2 (i.e. 20%):
batch_size = 32
seed = 42
raw_train_ds = utils.text_dataset_from_directory(
train_dir,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_split=0.2,
subset='training',
seed=seed)
Found 8000 files belonging to 4 classes. Using 6400 files for training. 2024-08-16 07:38:27.487373: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1960] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform. Skipping registering GPU devices...
As the previous cell output suggests, there are 8,000 examples in the training folder, of which you will use 80% (or 6,400) for training. You will learn in a moment that you can train a model by passing a tf.data.Dataset directly to Model.fit.
First, iterate over the dataset and print out a few examples, to get a feel for the data.
for text_batch, label_batch in raw_train_ds.take(1):
for i in range(10):
print("Question: ", text_batch.numpy()[i])
print("Label:", label_batch.numpy()[i])
Question: b'"my tester is going to the wrong constructor i am new to programming so if i ask a question that can be easily fixed, please forgive me. my program has a tester class with a main. when i send that to my regularpolygon class, it sends it to the wrong constructor. i have two constructors. 1 without perameters..public regularpolygon(). {. mynumsides = 5;. mysidelength = 30;. }//end default constructor...and my second, with perameters. ..public regularpolygon(int numsides, double sidelength). {. mynumsides = numsides;. mysidelength = sidelength;. }// end constructor...in my tester class i have these two lines:..regularpolygon shape = new regularpolygon(numsides, sidelength);. shape.menu();...numsides and sidelength were declared and initialized earlier in the testing class...so what i want to happen, is the tester class sends numsides and sidelength to the second constructor and use it in that class. but it only uses the default constructor, which therefor ruins the whole rest of the program. can somebody help me?..for those of you who want to see more of my code: here you go..public double vertexangle(). {. system.out.println(""the vertex angle method: "" + mynumsides);// prints out 5. system.out.println(""the vertex angle method: "" + mysidelength); // prints out 30.. double vertexangle;. vertexangle = ((mynumsides - 2.0) / mynumsides) * 180.0;. return vertexangle;. }//end method vertexangle..public void menu().{. system.out.println(mynumsides); // prints out what the user puts in. system.out.println(mysidelength); // prints out what the user puts in. gotographic();. calcr(mynumsides, mysidelength);. calcr(mynumsides, mysidelength);. print(); .}// end menu...this is my entire tester class:..public static void main(string[] arg).{. int numsides;. double sidelength;. scanner keyboard = new scanner(system.in);.. system.out.println(""welcome to the regular polygon program!"");. system.out.println();.. system.out.print(""enter the number of sides of the polygon ==> "");. numsides = keyboard.nextint();. system.out.println();.. system.out.print(""enter the side length of each side ==> "");. sidelength = keyboard.nextdouble();. system.out.println();.. regularpolygon shape = new regularpolygon(numsides, sidelength);. shape.menu();.}//end main...for testing it i sent it numsides 4 and sidelength 100."\n'
Label: 1
Question: b'"blank code slow skin detection this code changes the color space to lab and using a threshold finds the skin area of an image. but it\'s ridiculously slow. i don\'t know how to make it faster ? ..from colormath.color_objects import *..def skindetection(img, treshold=80, color=[255,20,147]):.. print img.shape. res=img.copy(). for x in range(img.shape[0]):. for y in range(img.shape[1]):. rgbimg=rgbcolor(img[x,y,0],img[x,y,1],img[x,y,2]). labimg=rgbimg.convert_to(\'lab\', debug=false). if (labimg.lab_l > treshold):. res[x,y,:]=color. else: . res[x,y,:]=img[x,y,:].. return res"\n'
Label: 3
Question: b'"option and validation in blank i want to add a new option on my system where i want to add two text files, both rental.txt and customer.txt. inside each text are id numbers of the customer, the videotape they need and the price...i want to place it as an option on my code. right now i have:...add customer.rent return.view list.search.exit...i want to add this as my sixth option. say for example i ordered a video, it would display the price and would let me confirm the price and if i am going to buy it or not...here is my current code:.. import blank.io.*;. import blank.util.arraylist;. import static blank.lang.system.out;.. public class rentalsystem{. static bufferedreader input = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(system.in));. static file file = new file(""file.txt"");. static arraylist<string> list = new arraylist<string>();. static int rows;.. public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{. introduction();. system.out.print(""nn"");. login();. system.out.print(""nnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnn"");. introduction();. string repeat;. do{. loadfile();. system.out.print(""nwhat do you want to do?nn"");. system.out.print(""n - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -"");. system.out.print(""nn | 1. add customer | 2. rent return |n"");. system.out.print(""n - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -"");. system.out.print(""nn | 3. view list | 4. search |n"");. system.out.print(""n - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -"");. system.out.print(""nn | 5. exit |n"");. system.out.print(""n - - - - - - - - - -"");. system.out.print(""nnchoice:"");. int choice = integer.parseint(input.readline());. switch(choice){. case 1:. writedata();. break;. case 2:. rentdata();. break;. case 3:. viewlist();. break;. case 4:. search();. break;. case 5:. system.out.println(""goodbye!"");. system.exit(0);. default:. system.out.print(""invalid choice: "");. break;. }. system.out.print(""ndo another task? [y/n] "");. repeat = input.readline();. }while(repeat.equals(""y""));.. if(repeat!=""y"") system.out.println(""ngoodbye!"");.. }.. public static void writedata() throws exception{. system.out.print(""nname: "");. string cname = input.readline();. system.out.print(""address: "");. string add = input.readline();. system.out.print(""phone no.: "");. string pno = input.readline();. system.out.print(""rental amount: "");. string ramount = input.readline();. system.out.print(""tapenumber: "");. string tno = input.readline();. system.out.print(""title: "");. string title = input.readline();. system.out.print(""date borrowed: "");. string dborrowed = input.readline();. system.out.print(""due date: "");. string ddate = input.readline();. createline(cname, add, pno, ramount,tno, title, dborrowed, ddate);. rentdata();. }.. public static void createline(string name, string address, string phone , string rental, string tapenumber, string title, string borrowed, string due) throws exception{. filewriter fw = new filewriter(file, true);. fw.write(""nname: ""+name + ""naddress: "" + address +""nphone no.: ""+ phone+""nrentalamount: ""+rental+""ntape no.: ""+ tapenumber+""ntitle: ""+ title+""ndate borrowed: ""+borrowed +""ndue date: ""+ due+"":rn"");. fw.close();. }.. public static void loadfile() throws exception{. try{. list.clear();. fileinputstream fstream = new fileinputstream(file);. bufferedreader br = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(fstream));. rows = 0;. while( br.ready()). {. list.add(br.readline());. rows++;. }. br.close();. } catch(exception e){. system.out.println(""list not yet loaded."");. }. }.. public static void viewlist(){. system.out.print(""n~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. system.out.print("" |list of all costumers|"");. system.out.print(""~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. for(int i = 0; i <rows; i++){. system.out.println(list.get(i));. }. }. public static void rentdata()throws exception. { system.out.print(""n~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. system.out.print("" |rent data list|"");. system.out.print(""~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. system.out.print(""nenter customer name: "");. string cname = input.readline();. system.out.print(""date borrowed: "");. string dborrowed = input.readline();. system.out.print(""due date: "");. string ddate = input.readline();. system.out.print(""return date: "");. string rdate = input.readline();. system.out.print(""rent amount: "");. string ramount = input.readline();.. system.out.print(""you pay:""+ramount);... }. public static void search()throws exception. { system.out.print(""n~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. system.out.print("" |search costumers|"");. system.out.print(""~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~"");. system.out.print(""nenter costumer name: "");. string cname = input.readline();. boolean found = false;.. for(int i=0; i < rows; i++){. string temp[] = list.get(i).split("","");.. if(cname.equals(temp[0])){. system.out.println(""search result:nyou are "" + temp[0] + "" from "" + temp[1] + "".""+ temp[2] + "".""+ temp[3] + "".""+ temp[4] + "".""+ temp[5] + "" is "" + temp[6] + "".""+ temp[7] + "" is "" + temp[8] + ""."");. found = true;. }. }.. if(!found){. system.out.print(""no results."");. }.. }.. public static boolean evaluate(string uname, string pass){. if (uname.equals(""admin"")&&pass.equals(""12345"")) return true;. else return false;. }.. public static string login()throws exception{. bufferedreader input=new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(system.in));. int counter=0;. do{. system.out.print(""username:"");. string uname =input.readline();. system.out.print(""password:"");. string pass =input.readline();.. boolean accept= evaluate(uname,pass);.. if(accept){. break;. }else{. system.out.println(""incorrect username or password!"");. counter ++;. }. }while(counter<3);.. if(counter !=3) return ""login successful"";. else return ""login failed"";. }. public static void introduction() throws exception{.. system.out.println("" - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -"");. system.out.println("" ! r e n t a l !"");. system.out.println("" ! ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ! ================= ! ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ !"");. system.out.println("" ! s y s t e m !"");. system.out.println("" - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -"");. }..}"\n'
Label: 1
Question: b'"exception: dynamic sql generation for the updatecommand is not supported against a selectcommand that does not return any key i dont know what is the problem this my code : ..string nomtable;..datatable listeetablissementtable = new datatable();.datatable listeinteretstable = new datatable();.dataset ds = new dataset();.sqldataadapter da;.sqlcommandbuilder cmdb;..private void listeinterets_click(object sender, eventargs e).{. nomtable = ""listeinteretstable"";. d.cnx.open();. da = new sqldataadapter(""select nome from offices"", d.cnx);. ds = new dataset();. da.fill(ds, nomtable);. datagridview1.datasource = ds.tables[nomtable];.}..private void sauvgarder_click(object sender, eventargs e).{. d.cnx.open();. cmdb = new sqlcommandbuilder(da);. da.update(ds, nomtable);. d.cnx.close();.}"\n'
Label: 0
Question: b'"parameter with question mark and super in blank, i\'ve come across a method that is formatted like this:..public final subscription subscribe(final action1<? super t> onnext, final action1<throwable> onerror) {.}...in the first parameter, what does the question mark and super mean?"\n'
Label: 1
Question: b'call two objects wsdl the first time i got a very strange wsdl. ..i would like to call the object (interface - invoicecheck_out) do you know how?....i would like to call the object (variable) do you know how?..try to call (it`s ok)....try to call (how call this?)\n'
Label: 0
Question: b"how to correctly make the icon for systemtray in blank using icon sizes of any dimension for systemtray doesn't look good overall. .what is the correct way of making icons for windows system tray?..screenshots: http://imgur.com/zsibwn9..icon: http://imgur.com/vsh4zo8\n"
Label: 0
Question: b'"is there a way to check a variable that exists in a different script than the original one? i\'m trying to check if a variable, which was previously set to true in 2.py in 1.py, as 1.py is only supposed to continue if the variable is true...2.py..import os..completed = false..#some stuff here..completed = true...1.py..import 2 ..if completed == true. #do things...however i get a syntax error at ..if completed == true"\n'
Label: 3
Question: b'"blank control flow i made a number which asks for 2 numbers with blank and responds with the corresponding message for the case. how come it doesnt work for the second number ? .regardless what i enter for the second number , i am getting the message ""your number is in the range 0-10""...using system;.using system.collections.generic;.using system.linq;.using system.text;..namespace consoleapplication1.{. class program. {. static void main(string[] args). {. string myinput; // declaring the type of the variables. int myint;.. string number1;. int number;... console.writeline(""enter a number"");. myinput = console.readline(); //muyinput is a string which is entry input. myint = int32.parse(myinput); // myint converts the string into an integer.. if (myint > 0). console.writeline(""your number {0} is greater than zero."", myint);. else if (myint < 0). console.writeline(""your number {0} is less than zero."", myint);. else. console.writeline(""your number {0} is equal zero."", myint);.. console.writeline(""enter another number"");. number1 = console.readline(); . number = int32.parse(myinput); .. if (number < 0 || number == 0). console.writeline(""your number {0} is less than zero or equal zero."", number);. else if (number > 0 && number <= 10). console.writeline(""your number {0} is in the range from 0 to 10."", number);. else. console.writeline(""your number {0} is greater than 10."", number);.. console.writeline(""enter another number"");.. }. } .}"\n'
Label: 0
Question: b'"credentials cannot be used for ntlm authentication i am getting org.apache.commons.httpclient.auth.invalidcredentialsexception: credentials cannot be used for ntlm authentication: exception in eclipse..whether it is possible mention eclipse to take system proxy settings directly?..public class httpgetproxy {. private static final string proxy_host = ""proxy.****.com"";. private static final int proxy_port = 6050;.. public static void main(string[] args) {. httpclient client = new httpclient();. httpmethod method = new getmethod(""https://kodeblank.org"");.. hostconfiguration config = client.gethostconfiguration();. config.setproxy(proxy_host, proxy_port);.. string username = ""*****"";. string password = ""*****"";. credentials credentials = new usernamepasswordcredentials(username, password);. authscope authscope = new authscope(proxy_host, proxy_port);.. client.getstate().setproxycredentials(authscope, credentials);.. try {. client.executemethod(method);.. if (method.getstatuscode() == httpstatus.sc_ok) {. string response = method.getresponsebodyasstring();. system.out.println(""response = "" + response);. }. } catch (ioexception e) {. e.printstacktrace();. } finally {. method.releaseconnection();. }. }.}...exception:... dec 08, 2017 1:41:39 pm . org.apache.commons.httpclient.auth.authchallengeprocessor selectauthscheme. info: ntlm authentication scheme selected. dec 08, 2017 1:41:39 pm org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector executeconnect. severe: credentials cannot be used for ntlm authentication: . org.apache.commons.httpclient.usernamepasswordcredentials. org.apache.commons.httpclient.auth.invalidcredentialsexception: credentials . cannot be used for ntlm authentication: . enter code here . org.apache.commons.httpclient.usernamepasswordcredentials. at org.apache.commons.httpclient.auth.ntlmscheme.authenticate(ntlmscheme.blank:332). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector.authenticateproxy(httpmethoddirector.blank:320). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector.executeconnect(httpmethoddirector.blank:491). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector.executewithretry(httpmethoddirector.blank:391). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector.executemethod(httpmethoddirector.blank:171). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpclient.executemethod(httpclient.blank:397). at org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpclient.executemethod(httpclient.blank:323). at httpgetproxy.main(httpgetproxy.blank:31). dec 08, 2017 1:41:39 pm org.apache.commons.httpclient.httpmethoddirector processproxyauthchallenge. info: failure authenticating with ntlm @proxy.****.com:6050"\n'
Label: 1
The labels are 0, 1, 2 or 3. To check which of these correspond to which string label, you can inspect the class_names property on the dataset:
for i, label in enumerate(raw_train_ds.class_names):
print("Label", i, "corresponds to", label)
Label 0 corresponds to csharp Label 1 corresponds to java Label 2 corresponds to javascript Label 3 corresponds to python
Next, you will create a validation and a test set using tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directory. You will use the remaining 1,600 reviews from the training set for validation.
# Create a validation set.
raw_val_ds = utils.text_dataset_from_directory(
train_dir,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_split=0.2,
subset='validation',
seed=seed)
Found 8000 files belonging to 4 classes. Using 1600 files for validation.
test_dir = dataset_dir/'test'
# Create a test set.
raw_test_ds = utils.text_dataset_from_directory(
test_dir,
batch_size=batch_size)
Found 8000 files belonging to 4 classes.
Configure the datasets for performance
These are two important methods you should use when loading data to make sure that I/O does not become blocking.
Dataset.cachekeeps data in memory after it's loaded off-disk. This will ensure the dataset does not become a bottleneck while training your model. If your dataset is too large to fit into memory, you can also use this method to create a performant on-disk cache, which is more efficient to read than many small files.Dataset.prefetchoverlaps data preprocessing and model execution while training.
You can learn more about both methods, as well as how to cache data to disk in the Prefetching section of the Better performance with the tf.data API guide.
raw_train_ds = raw_train_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
raw_val_ds = raw_val_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
raw_test_ds = raw_test_ds.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
This first example will keep things simple by integrating the text processing into the model. But you may be able to increase performance by moving the text processing into the dataset pipeline, this is demonstrated in Example 2
Prepare the dataset for training
Next, you will standardize, tokenize, and vectorize the data using the tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization layer.
- Standardization refers to preprocessing the text, typically to remove punctuation or HTML elements to simplify the dataset.
- Tokenization refers to splitting strings into tokens (for example, splitting a sentence into individual words by splitting on whitespace).
- Vectorization refers to converting tokens into numbers so they can be fed into a neural network.
All of these tasks can be accomplished with this layer. (You can learn more about each of these in the tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization API docs.)
Note that:
- The default standardization converts text to lowercase and removes punctuation (
standardize='lower_and_strip_punctuation'). - The default tokenizer splits on whitespace (
split='whitespace'). - The default vectorization mode is
'int'(output_mode='int'). This outputs integer indices (one per token). This mode can be used to build models that take word order into account. You can also use other modes—like'binary'—to build bag-of-words models.
You will build two models to learn more about standardization, tokenization, and vectorization with TextVectorization:
- First, you will use the
'binary'vectorization mode to build a bag-of-words model. - Then, you will use the
'int'mode with a 1D ConvNet.
VOCAB_SIZE = 10000
binary_vectorize_layer = TextVectorization(
max_tokens=VOCAB_SIZE,
output_mode='binary')
For the 'int' mode, in addition to maximum vocabulary size, you need to set an explicit maximum sequence length (MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH), which will cause the layer to pad or truncate sequences to exactly output_sequence_length values:
MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 250
int_vectorize_layer = TextVectorization(
max_tokens=VOCAB_SIZE,
output_mode='int',
output_sequence_length=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
Next, call TextVectorization.adapt to fit the state of the preprocessing layer to the dataset. This will cause the model to build an index of strings to integers.
# Make a text-only dataset (without labels), then call `TextVectorization.adapt`.
train_text = raw_train_ds.map(lambda text, labels: text)
binary_vectorize_layer.adapt(train_text)
int_vectorize_layer.adapt(train_text)
Print the result of using these layers to preprocess data:
# Retrieve a batch (of 32 reviews and labels) from the dataset.
text_batch, label_batch = next(iter(raw_train_ds))
first_question, first_label = text_batch[0], label_batch[0]
print("Question:", first_question)
print("Label:", first_label)
Question: tf.Tensor(b'"unit testing of setters and getters teacher wanted us to do a comprehensive unit test. for me, this will be the first time that i use junit. i am confused about testing set and get methods. do you think should i test them? if the answer is yes; is this code enough for testing?.. public void testsetandget(){. int a = 10;. class firstclass = new class();. firstclass.setvalue(10);. int value = firstclass.getvalue();. assert.asserttrue(""error"", value==a);. }...in my code, i think if there is an error, we can\'t know that the error is deriving because of setter or getter."\n', shape=(), dtype=string)
Label: tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
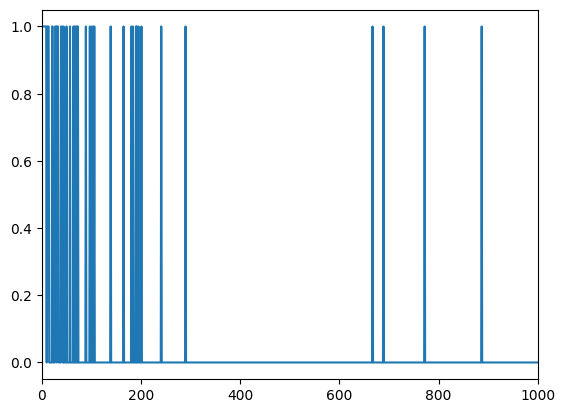
The binary vectorization layer returns a multi-hot vector, with a 1 in the location for each token that was in the input string.
print("'binary' vectorized question:",
list(binary_vectorize_layer(first_question).numpy()))
plt.plot(binary_vectorize_layer(first_question).numpy())
plt.xlim(0,1000)
'binary' vectorized question: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] (0.0, 1000.0)
print("'int' vectorized question:",
int_vectorize_layer(first_question).numpy())
'int' vectorized question: [1011 773 9 2456 8 1863 2362 690 1267 4 40 5 1 1011
196 12 74 13 72 33 2 98 105 14 3 70 9611 3
34 888 202 773 107 8 41 242 40 58 291 90 3 196
191 10 2 182 6 668 6 13 30 1187 12 773 22 42
1 28 5 140 29 5213 15 29 1 28 51 1 1 1
7 23 30 3 291 10 67 6 32 65 185 166 102 14
2 65 6 1 193 9 2784 45 2410 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
As shown above, TextVectorization's 'binary' mode returns an array denoting which tokens exist at least once in the input, while the 'int' mode replaces each token by an integer, thus preserving their order.
You can lookup the token (string) that each integer corresponds to by calling TextVectorization.get_vocabulary on the layer:
print("1289 ---> ", int_vectorize_layer.get_vocabulary()[1289])
print("313 ---> ", int_vectorize_layer.get_vocabulary()[313])
print("Vocabulary size: {}".format(len(int_vectorize_layer.get_vocabulary())))
1289 ---> roman 313 ---> source Vocabulary size: 10000
Train the model
It's time to create your neural network.
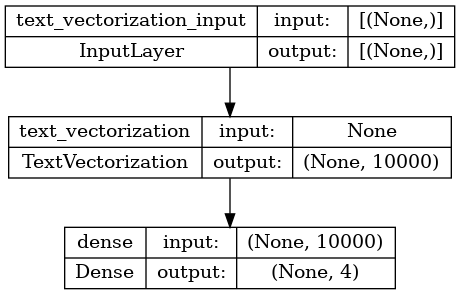
For the 'binary' vectorized data, define a simple bag-of-words linear model, then configure and train it:
binary_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
binary_vectorize_layer,
layers.Dense(4)])
binary_model.compile(
loss=losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(binary_model, show_shapes=True)
bin_history = binary_model.fit(
raw_train_ds, validation_data=raw_val_ds, epochs=10)
print()
Epoch 1/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 1.1224 - accuracy: 0.6353 - val_loss: 0.9172 - val_accuracy: 0.7806 Epoch 2/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.7810 - accuracy: 0.8166 - val_loss: 0.7519 - val_accuracy: 0.8037 Epoch 3/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.6289 - accuracy: 0.8564 - val_loss: 0.6655 - val_accuracy: 0.8181 Epoch 4/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.5351 - accuracy: 0.8878 - val_loss: 0.6117 - val_accuracy: 0.8288 Epoch 5/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4689 - accuracy: 0.9031 - val_loss: 0.5748 - val_accuracy: 0.8350 Epoch 6/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4184 - accuracy: 0.9177 - val_loss: 0.5480 - val_accuracy: 0.8356 Epoch 7/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3781 - accuracy: 0.9275 - val_loss: 0.5278 - val_accuracy: 0.8388 Epoch 8/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3447 - accuracy: 0.9358 - val_loss: 0.5122 - val_accuracy: 0.8406 Epoch 9/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3165 - accuracy: 0.9417 - val_loss: 0.5000 - val_accuracy: 0.8419 Epoch 10/10 200/200 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.2921 - accuracy: 0.9500 - val_loss: 0.4903 - val_accuracy: 0.8431
Next, you will use the 'int' vectorized layer to build a 1D ConvNet:
def create_model(vocab_size, num_labels, vectorizer=None):
my_layers =[]
if vectorizer is not None:
my_layers = [vectorizer]
my_layers.extend([
layers.Embedding(vocab_size, 64, mask_zero=True),
layers.Dropout(0.5),
layers.Conv1D(64, 5, padding="valid", activation="relu", strides=2),
layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D(),
layers.Dense(num_labels)
])
model = tf.keras.Sequential(my_layers)
return model
# `vocab_size` is `VOCAB_SIZE + 1` since `0` is used additionally for padding.
int_model = create_model(vocab_size=VOCAB_SIZE + 1, num_labels=4, vectorizer=int_vectorize_layer)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(int_model, show_shapes=True)
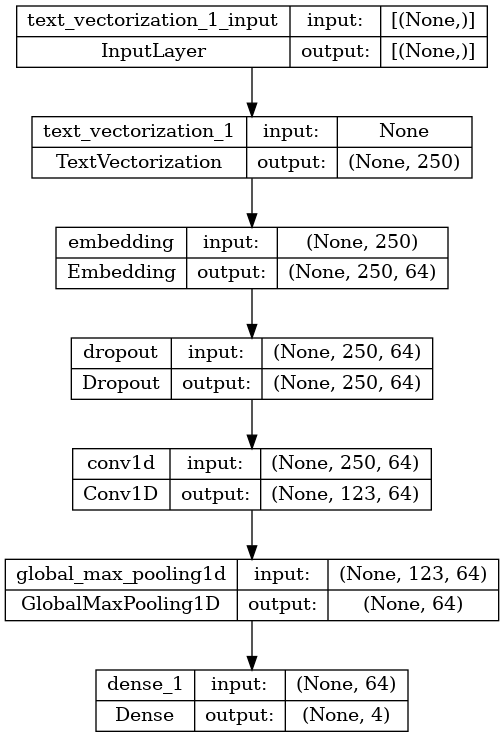
int_model.compile(
loss=losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
int_history = int_model.fit(raw_train_ds, validation_data=raw_val_ds, epochs=10)
Epoch 1/10 200/200 [==============================] - 3s 11ms/step - loss: 1.2680 - accuracy: 0.4155 - val_loss: 0.9306 - val_accuracy: 0.6119 Epoch 2/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.7792 - accuracy: 0.6737 - val_loss: 0.6409 - val_accuracy: 0.7419 Epoch 3/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.5617 - accuracy: 0.7848 - val_loss: 0.5409 - val_accuracy: 0.8025 Epoch 4/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.4142 - accuracy: 0.8589 - val_loss: 0.4931 - val_accuracy: 0.8125 Epoch 5/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.2987 - accuracy: 0.9044 - val_loss: 0.4819 - val_accuracy: 0.8206 Epoch 6/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.2133 - accuracy: 0.9369 - val_loss: 0.5010 - val_accuracy: 0.8112 Epoch 7/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.1571 - accuracy: 0.9588 - val_loss: 0.5368 - val_accuracy: 0.8069 Epoch 8/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.1126 - accuracy: 0.9702 - val_loss: 0.5629 - val_accuracy: 0.8069 Epoch 9/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.0780 - accuracy: 0.9805 - val_loss: 0.6029 - val_accuracy: 0.8031 Epoch 10/10 200/200 [==============================] - 2s 10ms/step - loss: 0.0563 - accuracy: 0.9881 - val_loss: 0.6394 - val_accuracy: 0.8037
loss = plt.plot(bin_history.epoch, bin_history.history['loss'], label='bin-loss')
plt.plot(bin_history.epoch, bin_history.history['val_loss'], '--', color=loss[0].get_color(), label='bin-val_loss')
loss = plt.plot(int_history.epoch, int_history.history['loss'], label='int-loss')
plt.plot(int_history.epoch, int_history.history['val_loss'], '--', color=loss[0].get_color(), label='int-val_loss')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('CE/token')
Text(0, 0.5, 'CE/token')
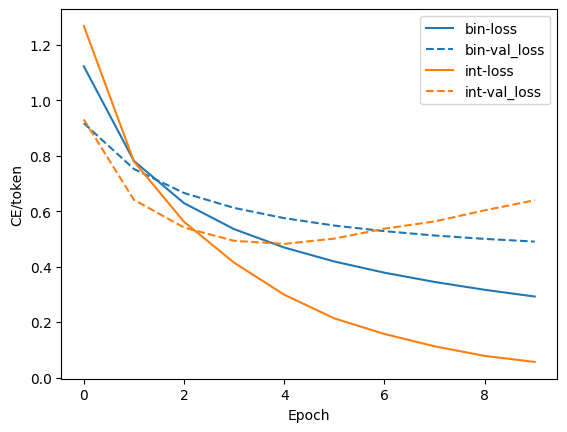
You are nearly ready to train your model.
As a final preprocessing step, you will apply the TextVectorization layers you created earlier to the training, validation, and test sets:
binary_train_ds = raw_train_ds.map(lambda x,y: (binary_vectorize_layer(x), y))
binary_val_ds = raw_val_ds.map(lambda x,y: (binary_vectorize_layer(x), y))
binary_test_ds = raw_test_ds.map(lambda x,y: (binary_vectorize_layer(x), y))
int_train_ds = raw_train_ds.map(lambda x,y: (int_vectorize_layer(x), y))
int_val_ds = raw_val_ds.map(lambda x,y: (int_vectorize_layer(x), y))
int_test_ds = raw_test_ds.map(lambda x,y: (int_vectorize_layer(x), y))
Export the model
binary_model.export('bin.tf')
INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: bin.tf/assets
INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: bin.tf/assets
Saved artifact at 'bin.tf'. The following endpoints are available:
* Endpoint 'serve'
Args:
args_0: string Tensor, shape=(None,)
Returns:
float32 Tensor, shape=(None, 4)
loaded = tf.saved_model.load('bin.tf')
binary_model.predict(['How do you sort a list?'])
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 114ms/step
array([[-0.11534691, 0.01791038, -0.58859897, 0.3795665 ]],
dtype=float32)
loaded.serve(tf.constant(['How do you sort a list?'])).numpy()
array([[-0.11534691, 0.01791038, -0.58859897, 0.3795665 ]],
dtype=float32)
Including the text preprocessing logic inside your model enables you to export a model for production that simplifies deployment, and reduces the potential for train/test skew.
There is a performance difference to keep in mind when choosing where to apply tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization. Using it outside of your model enables you to do asynchronous CPU processing and buffering of your data when training on GPU. So, if you're training your model on the GPU, you probably want to go with this option to get the best performance while developing your model, then switch to including the TextVectorization layer inside your model when you're ready to prepare for deployment.
Visit the Save and load models tutorial to learn more about saving models.
Example 2: Predict the author of Iliad translations
The following provides an example of using tf.data.TextLineDataset to load examples from text files, and TensorFlow Text to preprocess the data. You will use three different English translations of the same work, Homer's Iliad, and train a model to identify the translator given a single line of text.
To implement this task you'll use some lower level tools.
- You'll use
tf.data.TextLineDatasetto load text-lines from files. - You'll implement your own version of
keras.layers.TextVectorizationusing:text.UnicodeScriptTokenizer- to convert strings to tokens.tf.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable- to convert tokens to integer ids.
- You'll maximize performance by placing the text processing in the dataset pipeline, so it can run in parallel with the model training.
Download and explore the dataset
The texts of the three translations are by:
The text files used in this tutorial have undergone some typical preprocessing tasks like removing document header and footer, line numbers and chapter titles.
Download these lightly munged files locally:
DIRECTORY_URL = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/illiad/'
FILE_NAMES = ['cowper.txt', 'derby.txt', 'butler.txt']
for name in FILE_NAMES:
text_dir = utils.get_file(name, origin=DIRECTORY_URL + name)
parent_dir = pathlib.Path(text_dir).parent
list(parent_dir.iterdir())
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/illiad/cowper.txt
815980/815980 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/illiad/derby.txt
809730/809730 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/illiad/butler.txt
807992/807992 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
[PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/flower_photos.tar'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/butler.txt'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/fashion-mnist'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/cowper.txt'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/flower_photos.tgz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/mnist.npz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/HIGGS.csv.gz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/derby.txt'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/facades.tar.gz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/train.csv'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/iris_test.csv'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/cats_and_dogs_filtered'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/heart.csv'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/facades'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/kandinsky5.jpg'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/320px-Felis_catus-cat_on_snow.jpg'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/iris_training.csv'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/cats_and_dogs.zip'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/194px-New_East_River_Bridge_from_Brooklyn_det.4a09796u.jpg'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/Red_sunflower'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py.tar.gz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/flower_photos')]
Load the dataset
Previously, with tf.keras.utils.text_dataset_from_directory all contents of a file were treated as a single example. Here, you will use tf.data.TextLineDataset, which is designed to create a tf.data.Dataset from a text file where each example is a line of text from the original file. TextLineDataset is useful for text data that is primarily line-based (for example, poetry or error logs).
Iterate through these files, loading each one into its own dataset. Each example needs to be individually labeled, so use Dataset.map to apply a labeler function to each one. This will iterate over every example in the dataset, returning (example, label) pairs.
def labeler(example, index):
return example, tf.cast(index, tf.int64)
labeled_data_sets = []
for i, file_name in enumerate(FILE_NAMES):
lines_dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset(str(parent_dir/file_name))
labeled_dataset = lines_dataset.map(lambda ex: labeler(ex, i))
labeled_data_sets.append(labeled_dataset)
Next, you'll combine these labeled datasets into a single dataset using Dataset.concatenate, and shuffle it with Dataset.shuffle:
BUFFER_SIZE = 50000
BATCH_SIZE = 64
VALIDATION_SIZE = 5000
all_labeled_data = labeled_data_sets[0]
for labeled_dataset in labeled_data_sets[1:]:
all_labeled_data = all_labeled_data.concatenate(labeled_dataset)
all_labeled_data = all_labeled_data.shuffle(
BUFFER_SIZE, reshuffle_each_iteration=False)
Print out a few examples as before. The dataset hasn't been batched yet, hence each entry in all_labeled_data corresponds to one data point:
for text, label in all_labeled_data.take(10):
print("Sentence: ", text.numpy())
print("Label:", label.numpy())
Sentence: b'and Proto, Pherusa and Dynamene, Dexamene, Amphinome and Callianeira,' Label: 2 Sentence: b"Far from my sire and friends, in Lemnos' isle." Label: 1 Sentence: b'Sarpedon, as a lion on a herd:' Label: 1 Sentence: b'shook the dust from out of their manes, and bore their chariot swiftly' Label: 2 Sentence: b'with ease, had not Phoebus Apollo been angry, and in the guise of' Label: 2 Sentence: b'As may assuage Achilles, and prevail' Label: 0 Sentence: b'should have been hurled in vain, and withdrew under cover of his men.' Label: 2 Sentence: b'drove straight at Patroclus. Patroclus then sprang from his chariot to' Label: 2 Sentence: b"Me, Menela\xc3\xbcs, by Minerva's aid," Label: 0 Sentence: b'As he spoke Patroclus put on his armour. First he greaved his legs with' Label: 2
Prepare the dataset for training
Instead of using tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization to preprocess the text dataset, you will now use the lower-level TensorFlow Text APIs to standardize and tokenize the data, build a vocabulary and use tf.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable to map tokens to integers to feed to the model. (Learn more about TensorFlow Text).
Define a function to convert the text to lower-case and tokenize it:
- TensorFlow Text provides various tokenizers. In this example, you will use the
text.UnicodeScriptTokenizerto tokenize the dataset. - You will use
Dataset.mapto apply the tokenization to the dataset.
class MyTokenizer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.tokenizer = tf_text.UnicodeScriptTokenizer()
def call(self, text):
lower_case = tf_text.case_fold_utf8(text)
result = self.tokenizer.tokenize(lower_case)
# If you pass a batch of strings, it will return a RaggedTensor.
if isinstance(result, tf.RaggedTensor):
# Convert to dense 0-padded.
result = result.to_tensor()
return result
tokenizer = MyTokenizer()
tokenized_ds = all_labeled_data.map(lambda text, label: (tokenizer(text), label))
tokenized_ds
<_MapDataset element_spec=(TensorSpec(shape=(None,), dtype=tf.string, name=None), TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.int64, name=None))>
You can iterate over the dataset and print out a few tokenized examples:
for tokens, label in tokenized_ds.take(1):
break
print(tokens)
print()
print(label)
tf.Tensor( [b'and' b'proto' b',' b'pherusa' b'and' b'dynamene' b',' b'dexamene' b',' b'amphinome' b'and' b'callianeira' b','], shape=(13,), dtype=string) tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int64)
Next, you will build a vocabulary by sorting tokens by frequency and keeping the top VOCAB_SIZE tokens:
tokenized_ds = tokenized_ds.cache().prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
vocab_count = collections.Counter()
for toks, labels in tokenized_ds.ragged_batch(1000):
toks = tf.reshape(toks, [-1])
for tok in toks.numpy():
vocab_count[tok] += 1
vocab = [tok for tok, count in vocab_count.most_common(VOCAB_SIZE)]
print("First five vocab entries:", vocab[:5])
print()
First five vocab entries: [b',', b'the', b'and', b"'", b'of']
To convert the tokens into integers, use the vocab set to create a tf.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable. You will map tokens to integers with 0 reserved for padding, and n+1 reserved to denote an out-of-vocabulary (OOV) token.
class MyVocabTable(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, vocab):
super().__init__()
self.keys = [''] + vocab
self.values = range(len(self.keys))
self.init = tf.lookup.KeyValueTensorInitializer(
self.keys, self.values, key_dtype=tf.string, value_dtype=tf.int64)
num_oov_buckets = 1
self.table = tf.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable(self.init, num_oov_buckets)
def call(self, x):
result = self.table.lookup(x)
return result
Try it on a dummy vocabulary:
vocab_table = MyVocabTable(['a','b','c'])
vocab_table(tf.constant([''] + list('abcdefghi')))
<tf.Tensor: shape=(10,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4])>
Create one for the real vocabulary:
vocab_table = MyVocabTable(vocab)
Finally, define a layer to standardize, tokenize and vectorize the dataset using the tokenizer and lookup table:
preprocess_text = tf.keras.Sequential([
tokenizer,
vocab_table
])
You can try this on a single example to print the output:
example_text, example_label = next(iter(all_labeled_data))
print("Sentence: ", example_text.numpy())
vectorized_text = preprocess_text(example_text)
print("Vectorized sentence: ", vectorized_text.numpy())
Sentence: b'and Proto, Pherusa and Dynamene, Dexamene, Amphinome and Callianeira,' Vectorized sentence: [ 3 7805 1 7806 3 7807 1 7808 1 7809 3 9790 1]
Now create a dataset pipeline that will process the text on the fly using Dataset.map:
all_encoded_data = all_labeled_data.map(lambda text, labels:(preprocess_text(text), labels))
for ids, label in all_encoded_data.take(1):
break
print("Ids: ", ids.numpy())
print("Label: ", label.numpy())
Ids: [ 3 7805 1 7806 3 7807 1 7808 1 7809 3 9790 1] Label: 2
Split the dataset into training and test sets
The Keras TextVectorization layer also batches and pads the vectorized data. Padding is required because the examples inside of a batch need to be the same size and shape, but the examples in these datasets are not all the same size—each line of text has a different number of words.
tf.data.Dataset supports splitting and padded-batching datasets:
train_data = all_encoded_data.skip(VALIDATION_SIZE).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).padded_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
validation_data = all_encoded_data.take(VALIDATION_SIZE).padded_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
Now, validation_data and train_data are not collections of (example, label) pairs, but collections of batches. Each batch is a pair of (many examples, many labels) represented as arrays.
To illustrate this:
sample_text, sample_labels = next(iter(validation_data))
print("Text batch shape: ", sample_text.shape)
print("Label batch shape: ", sample_labels.shape)
print("First text example: ", sample_text[0])
print("First label example: ", sample_labels[0])
Text batch shape: (64, 18)
Label batch shape: (64,)
First text example: tf.Tensor(
[ 3 7805 1 7806 3 7807 1 7808 1 7809 3 9790 1 0
0 0 0 0], shape=(18,), dtype=int64)
First label example: tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int64)
Configure the datasets for better performance as before:
train_data = train_data.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
validation_data = validation_data.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
Train the model
You can train a model on this dataset as before:
Since this text vectorization adds 0 for padding and n+1 for out-of-vocabulary (OOV) tokens, the vocabulary size has increased by two:
model = create_model(vocab_size=VOCAB_SIZE+2, num_labels=3)
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss=losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, show_shapes=True)
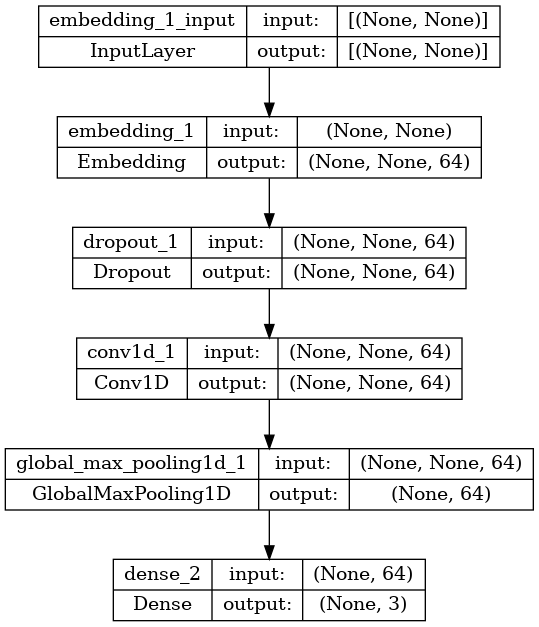
history = model.fit(train_data, validation_data=validation_data, epochs=3)
Epoch 1/3 697/697 [==============================] - 30s 10ms/step - loss: 0.5868 - accuracy: 0.7339 - val_loss: 0.4017 - val_accuracy: 0.8302 Epoch 2/3 697/697 [==============================] - 28s 10ms/step - loss: 0.3642 - accuracy: 0.8489 - val_loss: 0.3574 - val_accuracy: 0.8472 Epoch 3/3 697/697 [==============================] - 29s 9ms/step - loss: 0.2910 - accuracy: 0.8808 - val_loss: 0.3527 - val_accuracy: 0.8506
metrics = model.evaluate(validation_data, return_dict=True)
print("Loss: ", metrics['loss'])
print("Accuracy: {:2.2%}".format(metrics['accuracy']))
79/79 [==============================] - 3s 29ms/step - loss: 0.3527 - accuracy: 0.8506 Loss: 0.35271939635276794 Accuracy: 85.06%
Export the model
To make the model capable of taking raw strings as input, pack both the text processor and the model into a keras.Sequential:
export_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
preprocess_text,
model
])
export_model.compile(
loss=losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
This model you can run directly on batches of strings:
# Create a test dataset of raw strings.
test_ds = all_labeled_data.take(VALIDATION_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
test_ds = test_ds.cache().prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
test_ds
<_PrefetchDataset element_spec=(TensorSpec(shape=(None,), dtype=tf.string, name=None), TensorSpec(shape=(None,), dtype=tf.int64, name=None))>
loss, accuracy = export_model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("Loss: ", loss)
print("Accuracy: {:2.2%}".format(accuracy))
79/79 [==============================] - 5s 9ms/step - loss: 1.0300 - accuracy: 0.8506 Loss: 1.0299931764602661 Accuracy: 85.06%
Use saved_model.save to export it.
tf.saved_model.save(export_model, 'export.tf')
INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: export.tf/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: export.tf/assets
loaded = tf.saved_model.load('export.tf')
export_model(tf.constant(['The field bristled with the long and deadly spears which they bore.'])).numpy()
array([[-3.2765586 , -0.37794957, 3.0517902 ]], dtype=float32)
loaded(tf.constant(['The field bristled with the long and deadly spears which they bore.'])).numpy()
2024-08-16 07:41:04.103166: W tensorflow/core/grappler/optimizers/loop_optimizer.cc:933] Skipping loop optimization for Merge node with control input: StatefulPartitionedCall/StatefulPartitionedCall/sequential_2/StatefulPartitionedCall/my_tokenizer/UnicodeScriptTokenize/RaggedConcat/assert_equal_1/Assert/AssertGuard/branch_executed/_42 array([[-3.2765586 , -0.37794957, 3.0517902 ]], dtype=float32)
The loss and accuracy for the model on encoded validation set and the exported model on the raw validation set are the same, as expected.
Run inference on new data
inputs = [
"Join'd to th' Ionians with their flowing robes,", # Label: 1
"the allies, and his armour flashed about him so that he seemed to all", # Label: 2
"And with loud clangor of his arms he fell.", # Label: 0
]
predicted_scores = export_model.predict(inputs)
predicted_labels = tf.math.argmax(predicted_scores, axis=1)
for input, label in zip(inputs, predicted_labels):
print("Question: ", input)
print("Predicted label: ", label.numpy())
1/1 [==============================] - 2s 2s/step Question: Join'd to th' Ionians with their flowing robes, Predicted label: 1 Question: the allies, and his armour flashed about him so that he seemed to all Predicted label: 2 Question: And with loud clangor of his arms he fell. Predicted label: 0
Download more datasets using TensorFlow Datasets (TFDS)
You can download many more datasets from TensorFlow Datasets.
In this example, you will use the IMDB Large Movie Review dataset to train a model for sentiment classification:
# Training set.
train_ds = tfds.load(
'imdb_reviews',
split='train[:80%]',
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle_files=True,
as_supervised=True)
# Validation set.
val_ds = tfds.load(
'imdb_reviews',
split='train[80%:]',
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle_files=True,
as_supervised=True)
Print a few examples:
for review_batch, label_batch in val_ds.take(1):
for i in range(5):
print("Review: ", review_batch[i].numpy())
print("Label: ", label_batch[i].numpy())
Review: b"Instead, go to the zoo, buy some peanuts and feed 'em to the monkeys. Monkeys are funny. People with amnesia who don't say much, just sit there with vacant eyes are not all that funny.<br /><br />Black comedy? There isn't a black person in it, and there isn't one funny thing in it either.<br /><br />Walmart buys these things up somehow and puts them on their dollar rack. It's labeled Unrated. I think they took out the topless scene. They may have taken out other stuff too, who knows? All we know is that whatever they took out, isn't there any more.<br /><br />The acting seemed OK to me. There's a lot of unfathomables tho. It's supposed to be a city? It's supposed to be a big lake? If it's so hot in the church people are fanning themselves, why are they all wearing coats?" Label: 0 Review: b'Well, was Morgan Freeman any more unusual as God than George Burns? This film sure was better than that bore, "Oh, God". I was totally engrossed and LMAO all the way through. Carrey was perfect as the out of sorts anchorman wannabe, and Aniston carried off her part as the frustrated girlfriend in her usual well played performance. I, for one, don\'t consider her to be either ugly or untalented. I think my favorite scene was when Carrey opened up the file cabinet thinking it could never hold his life history. See if you can spot the file in the cabinet that holds the events of his bathroom humor: I was rolling over this one. Well written and even better played out, this comedy will go down as one of this funnyman\'s best.' Label: 1 Review: b'I remember stumbling upon this special while channel-surfing in 1965. I had never heard of Barbra before. When the show was over, I thought "This is probably the best thing on TV I will ever see in my life." 42 years later, that has held true. There is still nothing so amazing, so honestly astonishing as the talent that was displayed here. You can talk about all the super-stars you want to, this is the most superlative of them all!<br /><br />You name it, she can do it. Comedy, pathos, sultry seduction, ballads, Barbra is truly a story-teller. Her ability to pull off anything she attempts is legendary. But this special was made in the beginning, and helped to create the legend that she quickly became. In spite of rising so far in such a short time, she has fulfilled the promise, revealing more of her talents as she went along. But they are all here from the very beginning. You will not be disappointed in viewing this.' Label: 1 Review: b"Firstly, I would like to point out that people who have criticised this film have made some glaring errors. Anything that has a rating below 6/10 is clearly utter nonsense.<br /><br />Creep is an absolutely fantastic film with amazing film effects. The actors are highly believable, the narrative thought provoking and the horror and graphical content extremely disturbing. <br /><br />There is much mystique in this film. Many questions arise as the audience are revealed to the strange and freakish creature that makes habitat in the dark rat ridden tunnels. How was 'Craig' created and what happened to him?<br /><br />A fantastic film with a large chill factor. A film with so many unanswered questions and a film that needs to be appreciated along with others like 28 Days Later, The Bunker, Dog Soldiers and Deathwatch.<br /><br />Look forward to more of these fantastic films!!" Label: 1 Review: b"I'm sorry but I didn't like this doc very much. I can think of a million ways it could have been better. The people who made it obviously don't have much imagination. The interviews aren't very interesting and no real insight is offered. The footage isn't assembled in a very informative way, either. It's too bad because this is a movie that really deserves spellbinding special features. One thing I'll say is that Isabella Rosselini gets more beautiful the older she gets. All considered, this only gets a '4.'" Label: 0
You can now preprocess the data and train a model as before.
Prepare the dataset for training
vectorize_layer = TextVectorization(
max_tokens=VOCAB_SIZE,
output_mode='int',
output_sequence_length=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
# Make a text-only dataset (without labels), then call `TextVectorization.adapt`.
train_text = train_ds.map(lambda text, labels: text)
vectorize_layer.adapt(train_text)
def vectorize_text(text, label):
text = tf.expand_dims(text, -1)
return vectorize_layer(text), label
train_ds = train_ds.map(vectorize_text)
val_ds = val_ds.map(vectorize_text)
# Configure datasets for performance as before.
train_ds = train_ds.cache().prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
val_ds = val_ds.cache().prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
Create, configure and train the model
model = create_model(vocab_size=VOCAB_SIZE, num_labels=1)
model.summary()
Model: "sequential_5"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_2 (Embedding) (None, None, 64) 640000
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, None, 64) 0
conv1d_2 (Conv1D) (None, None, 64) 20544
global_max_pooling1d_2 (Gl (None, 64) 0
obalMaxPooling1D)
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 65
=================================================================
Total params: 660609 (2.52 MB)
Trainable params: 660609 (2.52 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
model.compile(
loss=losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(train_ds, validation_data=val_ds, epochs=3)
Epoch 1/3 313/313 [==============================] - 5s 12ms/step - loss: 0.5965 - accuracy: 0.6120 - val_loss: 0.4267 - val_accuracy: 0.7970 Epoch 2/3 313/313 [==============================] - 3s 10ms/step - loss: 0.3725 - accuracy: 0.8299 - val_loss: 0.3418 - val_accuracy: 0.8454 Epoch 3/3 313/313 [==============================] - 3s 10ms/step - loss: 0.2846 - accuracy: 0.8781 - val_loss: 0.3165 - val_accuracy: 0.8584
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(val_ds)
print("Loss: ", loss)
print("Accuracy: {:2.2%}".format(accuracy))
79/79 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3165 - accuracy: 0.8584 Loss: 0.3165397047996521 Accuracy: 85.84%
Export the model
export_model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[vectorize_layer, model,
layers.Activation('sigmoid')])
export_model.compile(
loss=losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 0 --> negative review
# 1 --> positive review
inputs = [
"This is a fantastic movie.",
"This is a bad movie.",
"This movie was so bad that it was good.",
"I will never say yes to watching this movie.",
]
predicted_scores = export_model.predict(inputs)
predicted_labels = [int(round(x[0])) for x in predicted_scores]
for input, label in zip(inputs, predicted_labels):
print("Question: ", input)
print("Predicted label: ", label)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 100ms/step Question: This is a fantastic movie. Predicted label: 1 Question: This is a bad movie. Predicted label: 0 Question: This movie was so bad that it was good. Predicted label: 0 Question: I will never say yes to watching this movie. Predicted label: 1
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated several ways to load and preprocess text. As a next step, you can explore additional text preprocessing TensorFlow Text tutorials, such as:
You can also find new datasets on TensorFlow Datasets. And, to learn more about tf.data, check out the guide on building input pipelines.
