 Lihat di TensorFlow.org Lihat di TensorFlow.org |  Jalankan di Google Colab Jalankan di Google Colab |  Lihat sumber di GitHub Lihat sumber di GitHub |  Unduh buku catatan Unduh buku catatan |
Tutorial ini memberikan contoh cara memuat panda DataFrames ke TensorFlow.
Anda akan menggunakan kumpulan data penyakit jantung kecil yang disediakan oleh UCI Machine Learning Repository. Ada beberapa ratus baris di CSV. Setiap baris menggambarkan pasien, dan setiap kolom menggambarkan atribut. Anda akan menggunakan informasi ini untuk memprediksi apakah pasien memiliki penyakit jantung, yang merupakan tugas klasifikasi biner.
Baca data menggunakan panda
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
SHUFFLE_BUFFER = 500
BATCH_SIZE = 2
Unduh file CSV yang berisi kumpulan data penyakit jantung:
csv_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file('heart.csv', 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv')
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/heart.csv 16384/13273 [=====================================] - 0s 0us/step 24576/13273 [=======================================================] - 0s 0us/step
Baca file CSV menggunakan panda:
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
Berikut tampilan datanya:
df.head()
df.dtypes
age int64 sex int64 cp int64 trestbps int64 chol int64 fbs int64 restecg int64 thalach int64 exang int64 oldpeak float64 slope int64 ca int64 thal object target int64 dtype: object
Anda akan membangun model untuk memprediksi label yang terdapat di kolom target .
target = df.pop('target')
DataFrame sebagai array
Jika data Anda memiliki tipe data yang seragam, atau dtype , Anda dapat menggunakan pandas DataFrame di mana pun Anda dapat menggunakan array NumPy. Ini berfungsi karena kelas pandas.DataFrame mendukung protokol __array__ , dan fungsi tf.convert_to_tensor menerima objek yang mendukung protokol.
Ambil fitur numerik dari kumpulan data (lewati fitur kategoris untuk saat ini):
numeric_feature_names = ['age', 'thalach', 'trestbps', 'chol', 'oldpeak']
numeric_features = df[numeric_feature_names]
numeric_features.head()
DataFrame dapat dikonversi ke array NumPy menggunakan properti DataFrame.values atau numpy.array(df) . Untuk mengubahnya menjadi tensor, gunakan tf.convert_to_tensor :
tf.convert_to_tensor(numeric_features)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(303, 5), dtype=float64, numpy=
array([[ 63. , 150. , 145. , 233. , 2.3],
[ 67. , 108. , 160. , 286. , 1.5],
[ 67. , 129. , 120. , 229. , 2.6],
...,
[ 65. , 127. , 135. , 254. , 2.8],
[ 48. , 150. , 130. , 256. , 0. ],
[ 63. , 154. , 150. , 407. , 4. ]])>
Secara umum, jika sebuah objek dapat dikonversi menjadi tensor dengan tf.convert_to_tensor , objek tersebut dapat diteruskan ke mana pun Anda dapat melewati tf.Tensor .
Dengan Model.fit
DataFrame, yang ditafsirkan sebagai tensor tunggal, dapat digunakan secara langsung sebagai argumen untuk metode Model.fit .
Di bawah ini adalah contoh pelatihan model pada fitur numerik dari dataset.
Langkah pertama adalah menormalkan rentang input. Gunakan lapisan tf.keras.layers.Normalization untuk itu.
Untuk mengatur mean layer dan deviasi standar sebelum menjalankannya, pastikan untuk memanggil metode Normalization.adapt :
normalizer = tf.keras.layers.Normalization(axis=-1)
normalizer.adapt(numeric_features)
Panggil layer pada tiga baris pertama DataFrame untuk memvisualisasikan contoh output dari layer ini:
normalizer(numeric_features.iloc[:3])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 5), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[ 0.93383914, 0.03480718, 0.74578077, -0.26008663, 1.0680453 ],
[ 1.3782105 , -1.7806165 , 1.5923285 , 0.7573877 , 0.38022864],
[ 1.3782105 , -0.87290466, -0.6651321 , -0.33687714, 1.3259765 ]],
dtype=float32)>
Gunakan lapisan normalisasi sebagai lapisan pertama dari model sederhana:
def get_basic_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
normalizer,
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
Saat Anda meneruskan DataFrame sebagai argumen x ke Model.fit , Keras memperlakukan DataFrame seperti halnya array NumPy:
model = get_basic_model()
model.fit(numeric_features, target, epochs=15, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
Epoch 1/15 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 2ms/step - loss: 0.6839 - accuracy: 0.7690 Epoch 2/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5789 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 3/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5195 - accuracy: 0.7723 Epoch 4/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4814 - accuracy: 0.7855 Epoch 5/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4566 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 6/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4427 - accuracy: 0.7888 Epoch 7/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4342 - accuracy: 0.7921 Epoch 8/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4290 - accuracy: 0.7855 Epoch 9/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4240 - accuracy: 0.7987 Epoch 10/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4232 - accuracy: 0.7987 Epoch 11/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4208 - accuracy: 0.7987 Epoch 12/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4186 - accuracy: 0.7954 Epoch 13/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4172 - accuracy: 0.8020 Epoch 14/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4156 - accuracy: 0.8020 Epoch 15/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4138 - accuracy: 0.8020 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1ddc27b110>
Dengan tf.data
Jika Anda ingin menerapkan transformasi tf.data ke DataFrame dengan tipe d yang seragam, Dataset.from_tensor_slices dtype membuat kumpulan data yang berulang pada baris DataFrame. Setiap baris awalnya merupakan vektor nilai. Untuk melatih model, Anda memerlukan pasangan (inputs, labels) , jadi pass (features, labels) dan Dataset.from_tensor_slices akan mengembalikan pasangan irisan yang diperlukan:
numeric_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((numeric_features, target))
for row in numeric_dataset.take(3):
print(row)
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(5,), dtype=float64, numpy=array([ 63. , 150. , 145. , 233. , 2.3])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=0>) (<tf.Tensor: shape=(5,), dtype=float64, numpy=array([ 67. , 108. , 160. , 286. , 1.5])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=1>) (<tf.Tensor: shape=(5,), dtype=float64, numpy=array([ 67. , 129. , 120. , 229. , 2.6])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=0>)
numeric_batches = numeric_dataset.shuffle(1000).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
model = get_basic_model()
model.fit(numeric_batches, epochs=15)
Epoch 1/15 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7677 - accuracy: 0.6865 Epoch 2/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.6319 - accuracy: 0.7591 Epoch 3/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5717 - accuracy: 0.7459 Epoch 4/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5228 - accuracy: 0.7558 Epoch 5/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4820 - accuracy: 0.7624 Epoch 6/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4584 - accuracy: 0.7657 Epoch 7/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4454 - accuracy: 0.7657 Epoch 8/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4379 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 9/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4324 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 10/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4282 - accuracy: 0.7756 Epoch 11/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4273 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 12/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4268 - accuracy: 0.7756 Epoch 13/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4248 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 14/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4235 - accuracy: 0.7855 Epoch 15/15 152/152 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4223 - accuracy: 0.7888 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1ddc406510>
DataFrame sebagai kamus
Saat Anda mulai berurusan dengan data heterogen, tidak mungkin lagi memperlakukan DataFrame seolah-olah itu adalah larik tunggal. Tensor TensorFlow mengharuskan semua elemen memiliki dtype yang sama.
Jadi, dalam hal ini, Anda harus mulai memperlakukannya sebagai kamus kolom, di mana setiap kolom memiliki tipe d yang seragam. DataFrame sangat mirip dengan kamus array, jadi biasanya yang perlu Anda lakukan hanyalah melemparkan DataFrame ke dict Python. Banyak API TensorFlow penting yang mendukung kamus array (bersarang) sebagai input.
pipa input tf.data menangani ini dengan cukup baik. Semua operasi tf.data menangani kamus dan tupel secara otomatis. Jadi, untuk membuat kumpulan data contoh kamus dari DataFrame, cukup masukkan ke dict sebelum memotongnya dengan Dataset.from_tensor_slices :
numeric_dict_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((dict(numeric_features), target))
Berikut adalah tiga contoh pertama dari kumpulan data tersebut:
for row in numeric_dict_ds.take(3):
print(row)
({'age': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=63>, 'thalach': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=150>, 'trestbps': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=145>, 'chol': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=233>, 'oldpeak': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=2.3>}, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=0>)
({'age': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=67>, 'thalach': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=108>, 'trestbps': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=160>, 'chol': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=286>, 'oldpeak': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=1.5>}, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=1>)
({'age': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=67>, 'thalach': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=129>, 'trestbps': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=120>, 'chol': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=229>, 'oldpeak': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=2.6>}, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=0>)
Kamus dengan Keras
Biasanya, model dan lapisan Keras mengharapkan tensor input tunggal, tetapi kelas ini dapat menerima dan mengembalikan struktur kamus, tupel, dan tensor bersarang. Struktur ini dikenal sebagai "sarang" (lihat modul tf.nest untuk detailnya).
Ada dua cara yang setara Anda dapat menulis model keras yang menerima kamus sebagai input.
1. Gaya Model-subclass
Anda menulis subkelas tf.keras.Model (atau tf.keras.Layer ). Anda langsung menangani input, dan membuat output:
def stack_dict(inputs, fun=tf.stack):
values = []
for key in sorted(inputs.keys()):
values.append(tf.cast(inputs[key], tf.float32))
return fun(values, axis=-1)
class MyModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
# Create all the internal layers in init.
super().__init__(self)
self.normalizer = tf.keras.layers.Normalization(axis=-1)
self.seq = tf.keras.Sequential([
self.normalizer,
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
def adapt(self, inputs):
# Stach the inputs and `adapt` the normalization layer.
inputs = stack_dict(inputs)
self.normalizer.adapt(inputs)
def call(self, inputs):
# Stack the inputs
inputs = stack_dict(inputs)
# Run them through all the layers.
result = self.seq(inputs)
return result
model = MyModel()
model.adapt(dict(numeric_features))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'],
run_eagerly=True)
Model ini dapat menerima kamus kolom atau kumpulan data elemen kamus untuk pelatihan:
model.fit(dict(numeric_features), target, epochs=5, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 3s 17ms/step - loss: 0.6736 - accuracy: 0.7063 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 3s 17ms/step - loss: 0.5577 - accuracy: 0.7294 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4869 - accuracy: 0.7591 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4525 - accuracy: 0.7690 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4403 - accuracy: 0.7624 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1de4fa9390>
numeric_dict_batches = numeric_dict_ds.shuffle(SHUFFLE_BUFFER).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
model.fit(numeric_dict_batches, epochs=5)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4328 - accuracy: 0.7756 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 14ms/step - loss: 0.4297 - accuracy: 0.7888 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4270 - accuracy: 0.7888 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4245 - accuracy: 0.8020 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4240 - accuracy: 0.7921 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1ddc0dba90>
Berikut adalah prediksi untuk tiga contoh pertama:
model.predict(dict(numeric_features.iloc[:3]))
array([[[0.00565109]],
[[0.60601974]],
[[0.03647463]]], dtype=float32)
2. Gaya fungsional Keras
inputs = {}
for name, column in numeric_features.items():
inputs[name] = tf.keras.Input(
shape=(1,), name=name, dtype=tf.float32)
inputs
{'age': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'age')>,
'thalach': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'thalach')>,
'trestbps': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'trestbps')>,
'chol': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'chol')>,
'oldpeak': <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'oldpeak')>}
x = stack_dict(inputs, fun=tf.concat)
normalizer = tf.keras.layers.Normalization(axis=-1)
normalizer.adapt(stack_dict(dict(numeric_features)))
x = normalizer(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, x)
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'],
run_eagerly=True)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, rankdir="LR", show_shapes=True)

Anda dapat melatih model fungsional dengan cara yang sama seperti subkelas model:
model.fit(dict(numeric_features), target, epochs=5, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.6529 - accuracy: 0.7492 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5448 - accuracy: 0.7624 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4935 - accuracy: 0.7756 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4650 - accuracy: 0.7789 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4486 - accuracy: 0.7855 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1ddc0d0f90>
numeric_dict_batches = numeric_dict_ds.shuffle(SHUFFLE_BUFFER).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
model.fit(numeric_dict_batches, epochs=5)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4398 - accuracy: 0.7855 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.4330 - accuracy: 0.7855 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4294 - accuracy: 0.7921 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4271 - accuracy: 0.7888 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 2s 16ms/step - loss: 0.4231 - accuracy: 0.7855 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f1d7c5d5d10>
Contoh lengkap
Jika Anda meneruskan DataFrame yang heterogen ke Keras, setiap kolom mungkin memerlukan pemrosesan awal yang unik. Anda dapat melakukan prapemrosesan ini secara langsung di DataFrame, tetapi agar model berfungsi dengan benar, input harus selalu diproses sebelumnya dengan cara yang sama. Jadi, pendekatan terbaik adalah membangun preprocessing ke dalam model. Lapisan pra -pemrosesan keras mencakup banyak tugas umum.
Bangun kepala pra-pemrosesan
Dalam kumpulan data ini beberapa fitur "bilangan bulat" dalam data mentah sebenarnya adalah indeks Kategoris. Indeks ini bukan nilai numerik yang benar-benar berurutan (lihat deskripsi kumpulan data untuk detailnya). Karena ini tidak berurutan, mereka tidak pantas untuk dimasukkan langsung ke model; model akan menafsirkannya sebagai yang dipesan. Untuk menggunakan input ini, Anda harus menyandikannya, baik sebagai vektor one-hot atau vektor embedding. Hal yang sama berlaku untuk fitur kategoris string.
Fitur biner di sisi lain umumnya tidak perlu dikodekan atau dinormalisasi.
Mulailah dengan membuat daftar fitur yang termasuk dalam setiap grup:
binary_feature_names = ['sex', 'fbs', 'exang']
categorical_feature_names = ['cp', 'restecg', 'slope', 'thal', 'ca']
Langkah selanjutnya adalah membangun model preprocessing yang akan menerapkan preprocessing yang sesuai untuk masing-masing input dan menggabungkan hasilnya.
Bagian ini menggunakan Keras Functional API untuk mengimplementasikan preprocessing. Anda mulai dengan membuat satu tf.keras.Input untuk setiap kolom kerangka data:
inputs = {}
for name, column in df.items():
if type(column[0]) == str:
dtype = tf.string
elif (name in categorical_feature_names or
name in binary_feature_names):
dtype = tf.int64
else:
dtype = tf.float32
inputs[name] = tf.keras.Input(shape=(), name=name, dtype=dtype)
inputs
{'age': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'age')>,
'sex': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'sex')>,
'cp': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'cp')>,
'trestbps': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'trestbps')>,
'chol': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'chol')>,
'fbs': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'fbs')>,
'restecg': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'restecg')>,
'thalach': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'thalach')>,
'exang': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'exang')>,
'oldpeak': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'oldpeak')>,
'slope': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'slope')>,
'ca': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'ca')>,
'thal': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=string (created by layer 'thal')>}
Untuk setiap input, Anda akan menerapkan beberapa transformasi menggunakan lapisan Keras dan operasi TensorFlow. Setiap fitur dimulai sebagai sekumpulan skalar ( shape=(batch,) ). Output untuk masing-masing harus berupa kumpulan vektor tf.float32 ( shape=(batch, n) ). Langkah terakhir akan menggabungkan semua vektor itu bersama-sama.
Input biner
Karena input biner tidak memerlukan prapemrosesan, cukup tambahkan sumbu vektor, masukkan ke float32 dan tambahkan ke daftar input praproses:
preprocessed = []
for name in binary_feature_names:
inp = inputs[name]
inp = inp[:, tf.newaxis]
float_value = tf.cast(inp, tf.float32)
preprocessed.append(float_value)
preprocessed
[<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_5')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_6')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_7')>]
Masukan numerik
Seperti di bagian sebelumnya, Anda harus menjalankan input numerik ini melalui lapisan tf.keras.layers.Normalization sebelum menggunakannya. Bedanya, kali ini inputnya berupa dict. Kode di bawah ini mengumpulkan fitur numerik dari DataFrame, menumpuknya bersama-sama dan meneruskannya ke metode Normalization.adapt .
normalizer = tf.keras.layers.Normalization(axis=-1)
normalizer.adapt(stack_dict(dict(numeric_features)))
Kode di bawah ini menumpuk fitur numerik dan menjalankannya melalui lapisan normalisasi.
numeric_inputs = {}
for name in numeric_feature_names:
numeric_inputs[name]=inputs[name]
numeric_inputs = stack_dict(numeric_inputs)
numeric_normalized = normalizer(numeric_inputs)
preprocessed.append(numeric_normalized)
preprocessed
[<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_5')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_6')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_7')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 5) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'normalization_3')>]
Fitur kategoris
Untuk menggunakan fitur kategoris, Anda harus terlebih dahulu mengkodekannya ke dalam vektor biner atau embeddings. Karena fitur ini hanya berisi sejumlah kecil kategori, konversikan input langsung ke vektor one-hot menggunakan opsi output_mode='one_hot' , yang didukung oleh lapisan tf.keras.layers.StringLookup dan tf.keras.layers.IntegerLookup .
Berikut adalah contoh bagaimana lapisan ini bekerja:
vocab = ['a','b','c']
lookup = tf.keras.layers.StringLookup(vocabulary=vocab, output_mode='one_hot')
lookup(['c','a','a','b','zzz'])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 4), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0., 0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
vocab = [1,4,7,99]
lookup = tf.keras.layers.IntegerLookup(vocabulary=vocab, output_mode='one_hot')
lookup([-1,4,1])
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3, 5), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
Untuk menentukan kosakata untuk setiap input, buat layer untuk mengonversi kosakata tersebut menjadi vektor one-hot:
for name in categorical_feature_names:
vocab = sorted(set(df[name]))
print(f'name: {name}')
print(f'vocab: {vocab}\n')
if type(vocab[0]) is str:
lookup = tf.keras.layers.StringLookup(vocabulary=vocab, output_mode='one_hot')
else:
lookup = tf.keras.layers.IntegerLookup(vocabulary=vocab, output_mode='one_hot')
x = inputs[name][:, tf.newaxis]
x = lookup(x)
preprocessed.append(x)
name: cp vocab: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] name: restecg vocab: [0, 1, 2] name: slope vocab: [1, 2, 3] name: thal vocab: ['1', '2', 'fixed', 'normal', 'reversible'] name: ca vocab: [0, 1, 2, 3]
Pasang kepala preprocessing
Pada titik ini preprocessed hanyalah daftar Python dari semua hasil preprocessing, setiap hasil memiliki bentuk (batch_size, depth) :
preprocessed
[<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_5')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_6')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.cast_7')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 5) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'normalization_3')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 6) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'integer_lookup_1')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 4) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'integer_lookup_2')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 4) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'integer_lookup_3')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 6) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'string_lookup_1')>, <KerasTensor: shape=(None, 5) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'integer_lookup_4')>]
Gabungkan semua fitur yang telah diproses sebelumnya di sepanjang sumbu depth , sehingga setiap contoh kamus diubah menjadi satu vektor. Vektor berisi fitur kategoris, fitur numerik, dan fitur one-hot kategoris:
preprocesssed_result = tf.concat(preprocessed, axis=-1)
preprocesssed_result
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 33) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'tf.concat_1')>
Sekarang buat model dari perhitungan itu sehingga dapat digunakan kembali:
preprocessor = tf.keras.Model(inputs, preprocesssed_result)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(preprocessor, rankdir="LR", show_shapes=True)
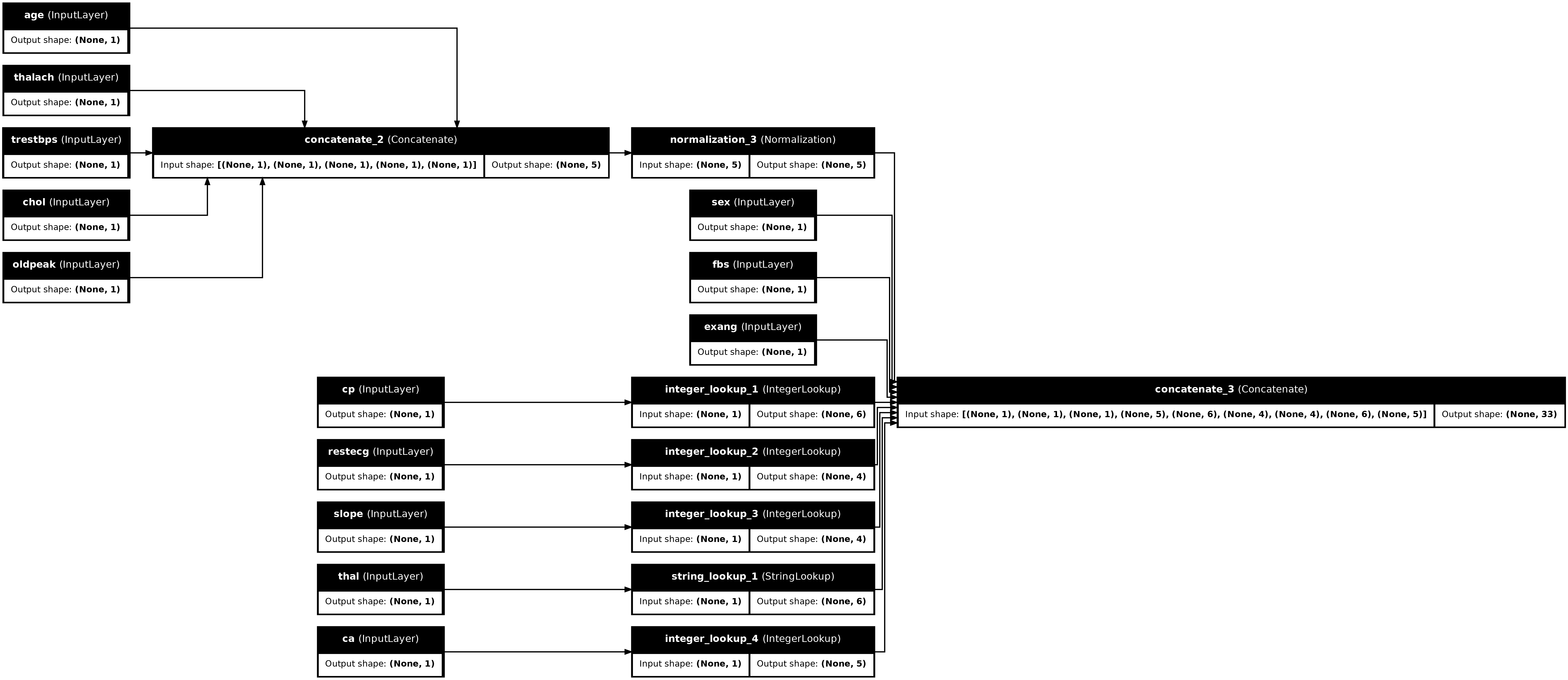
Untuk menguji praprosesor, gunakan pengakses DataFrame.iloc untuk mengiris contoh pertama dari DataFrame. Kemudian konversikan ke kamus dan berikan kamus ke praprosesor. Hasilnya adalah vektor tunggal yang berisi fitur biner, fitur numerik yang dinormalisasi, dan fitur kategoris satu-panas, dalam urutan itu:
preprocessor(dict(df.iloc[:1]))
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 33), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[ 1. , 1. , 0. , 0.93383914, -0.26008663,
1.0680453 , 0.03480718, 0.74578077, 0. , 0. ,
1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0. ,
0. , 1. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. ,
0. , 0. , 0. ]], dtype=float32)>
Buat dan latih model
Sekarang bangun tubuh utama model. Gunakan konfigurasi yang sama seperti pada contoh sebelumnya: Sepasang lapisan linier-lurus yang diratakan dan lapisan keluaran Dense Dense(1) untuk klasifikasi.
body = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
Sekarang satukan kedua bagian tersebut menggunakan API fungsional Keras.
inputs
{'age': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'age')>,
'sex': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'sex')>,
'cp': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'cp')>,
'trestbps': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'trestbps')>,
'chol': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'chol')>,
'fbs': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'fbs')>,
'restecg': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'restecg')>,
'thalach': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'thalach')>,
'exang': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'exang')>,
'oldpeak': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'oldpeak')>,
'slope': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'slope')>,
'ca': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=int64 (created by layer 'ca')>,
'thal': <KerasTensor: shape=(None,) dtype=string (created by layer 'thal')>}
x = preprocessor(inputs)
x
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 33) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'model_1')>
result = body(x)
result
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 1) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'sequential_3')>
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, result)
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
Model ini mengharapkan kamus input. Cara paling sederhana untuk meneruskan datanya adalah dengan mengonversi DataFrame menjadi dict dan meneruskan dict itu sebagai argumen x ke Model.fit :
history = model.fit(dict(df), target, epochs=5, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.6911 - accuracy: 0.6997 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.5073 - accuracy: 0.7393 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4129 - accuracy: 0.7888 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3663 - accuracy: 0.7921 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3363 - accuracy: 0.8152
Menggunakan tf.data juga berfungsi:
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((
dict(df),
target
))
ds = ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
import pprint
for x, y in ds.take(1):
pprint.pprint(x)
print()
print(y)
{'age': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([63, 67])>,
'ca': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([0, 3])>,
'chol': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([233, 286])>,
'cp': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([1, 4])>,
'exang': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([0, 1])>,
'fbs': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([1, 0])>,
'oldpeak': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float64, numpy=array([2.3, 1.5])>,
'restecg': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([2, 2])>,
'sex': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([1, 1])>,
'slope': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([3, 2])>,
'thal': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=string, numpy=array([b'fixed', b'normal'], dtype=object)>,
'thalach': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([150, 108])>,
'trestbps': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([145, 160])>}
tf.Tensor([0 1], shape=(2,), dtype=int64)
history = model.fit(ds, epochs=5)
Epoch 1/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 0.3150 - accuracy: 0.8284 Epoch 2/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2989 - accuracy: 0.8449 Epoch 3/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2870 - accuracy: 0.8449 Epoch 4/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2782 - accuracy: 0.8482 Epoch 5/5 152/152 [==============================] - 1s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2712 - accuracy: 0.8482
